
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The XML Metadata Interchange (XMI) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for exchanging metadata information via Extensible Markup Language (XML).

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. The official reference page may be found at OMG's website.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.

IDEF, initially an abbreviation of ICAM Definition and renamed in 1999 as Integration Definition, is a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis and design, and knowledge acquisition. These definition languages were developed under funding from U.S. Air Force and, although still most commonly used by them and other military and United States Department of Defense (DoD) agencies, are in the public domain.
The common warehouse metamodel (CWM) defines a specification for modeling metadata for relational, non-relational, multi-dimensional, and most other objects found in a data warehousing environment. The specification is released and owned by the Object Management Group, which also claims a trademark in the use of "CWM".
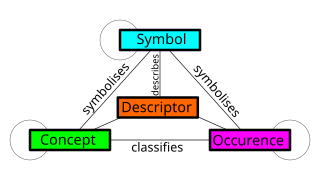
A metamodel or surrogate model is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.

An information model in software engineering is a representation of concepts and the relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. Typically it specifies relations between kinds of things, but may also include relations with individual things. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements or knowledge for the domain context.
The semantic spectrum is a series of increasingly precise or rather semantically expressive definitions for data elements in knowledge representations, especially for machine use.
Metadata publishing is the process of making metadata data elements available to external users, both people and machines using a formal review process and a commitment to change control processes.
Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS) is a W3C recommendation designed for representation of thesauri, classification schemes, taxonomies, subject-heading systems, or any other type of structured controlled vocabulary. SKOS is part of the Semantic Web family of standards built upon RDF and RDFS, and its main objective is to enable easy publication and use of such vocabularies as linked data.
The Business Process Definition Metamodel (BPDM) is a standard definition of concepts used to express business process models, adopted by the OMG. Metamodels define concepts, relationships, and semantics for exchange of user models between different modeling tools. The exchange format is defined by XSD and XMI, a specification for transformation of OMG metamodels to XML. Pursuant to the OMG's policies, the metamodel is the result of an open process involving submissions by member organizations, following a Request for Proposal (RFP) issued in 2003. BPDM was adopted in initial form in July 2007, and finalized in July 2008.
Knowledge Discovery Metamodel (KDM) is a publicly available specification from the Object Management Group (OMG). KDM is a common intermediate representation for existing software systems and their operating environments, that defines common metadata required for deep semantic integration of Application Lifecycle Management tools. KDM was designed as the OMG's foundation for software modernization, IT portfolio management and software assurance. KDM uses OMG's Meta-Object Facility to define an XMI interchange format between tools that work with existing software as well as an abstract interface (API) for the next-generation assurance and modernization tools. KDM standardizes existing approaches to knowledge discovery in software engineering artifacts, also known as software mining.
Architecture-driven modernization in computing and computer science, is the name of the initiative of the Object Management Group related to building and promoting standards that can be applied to modernize legacy systems. The objective of this initiative is to provide standard representations of views of existing systems, in order to enable common modernization activities, such as code analysis and comprehension, and software transformation.
The Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules (SBVR) is an adopted standard of the Object Management Group (OMG) intended to be the basis for formal and detailed natural language declarative description of a complex entity, such as a business. SBVR is intended to formalize complex compliance rules, such as operational rules for an enterprise, security policy, standard compliance, or regulatory compliance rules. Such formal vocabularies and rules can be interpreted and used by computer systems. SBVR is an integral part of the OMG's model-driven architecture (MDA).
The Ontology Definition MetaModel (ODM) is an Object Management Group (OMG) specification to make the concepts of Model-Driven Architecture applicable to the engineering of ontologies. Hence, it links Common Logic (CL), the Web Ontology Language (OWL), and the Resource Description Framework (RDF).
Knowledge extraction is the creation of knowledge from structured and unstructured sources. The resulting knowledge needs to be in a machine-readable and machine-interpretable format and must represent knowledge in a manner that facilitates inferencing. Although it is methodically similar to information extraction (NLP) and ETL, the main criterion is that the extraction result goes beyond the creation of structured information or the transformation into a relational schema. It requires either the reuse of existing formal knowledge or the generation of a schema based on the source data.

The Interaction Flow Modeling Language (IFML) is a standardized modeling language in the field of software engineering. IFML includes a set of graphic notations to create visual models of user interactions and front-end behavior in software systems.





