Applications
Text mining technology is now broadly applied to a wide variety of government, research, and business needs. All these groups may use text mining for records management and searching documents relevant to their daily activities. Legal professionals may use text mining for e-discovery, for example. Governments and military groups use text mining for national security and intelligence purposes. Scientific researchers incorporate text mining approaches into efforts to organize large sets of text data (i.e., addressing the problem of unstructured data), to determine ideas communicated through text (e.g., sentiment analysis in social media [15] [16] [17] ) and to support scientific discovery in fields such as the life sciences and bioinformatics. In business, applications are used to support competitive intelligence and automated ad placement, among numerous other activities.
Security applications
Many text mining software packages are marketed for security applications, especially monitoring and analysis of online plain text sources such as Internet news, blogs, etc. for national security purposes. [18] It is also involved in the study of text encryption/decryption.
Biomedical applications
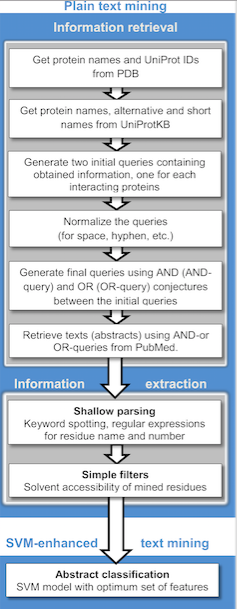
A range of text mining applications in the biomedical literature has been described, [20] including computational approaches to assist with studies in protein docking, [21] protein interactions, [22] [23] and protein-disease associations. [24] In addition, with large patient textual datasets in the clinical field, datasets of demographic information in population studies and adverse event reports, text mining can facilitate clinical studies and precision medicine. Text mining algorithms can facilitate the stratification and indexing of specific clinical events in large patient textual datasets of symptoms, side effects, and comorbidities from electronic health records, event reports, and reports from specific diagnostic tests. [25] One online text mining application in the biomedical literature is PubGene, a publicly accessible search engine that combines biomedical text mining with network visualization. [26] [27] GoPubMed is a knowledge-based search engine for biomedical texts. Text mining techniques also enable us to extract unknown knowledge from unstructured documents in the clinical domain [28]
Software applications
Text mining methods and software is also being researched and developed by major firms, including IBM and Microsoft, to further automate the mining and analysis processes, and by different firms working in the area of search and indexing in general as a way to improve their results. Within the public sector, much effort has been concentrated on creating software for tracking and monitoring terrorist activities. [29] For study purposes, Weka software is one of the most popular options in the scientific world, acting as an excellent entry point for beginners. For Python programmers, there is an excellent toolkit called NLTK for more general purposes. For more advanced programmers, there's also the Gensim library, which focuses on word embedding-based text representations.
Online media applications
Text mining is being used by large media companies, such as the Tribune Company, to clarify information and to provide readers with greater search experiences, which in turn increases site "stickiness" and revenue. Additionally, on the back end, editors are benefiting by being able to share, associate and package news across properties, significantly increasing opportunities to monetize content.
Business and marketing applications
Text analytics is being used in business, particularly, in marketing, such as in customer relationship management. [30] Coussement and Van den Poel (2008) [31] [32] apply it to improve predictive analytics models for customer churn (customer attrition). [31] Text mining is also being applied in stock returns prediction. [33]
Sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis may involve analysis of products such as movies, books, or hotel reviews for estimating how favorable a review is for the product. [34] Such an analysis may need a labeled data set or labeling of the affectivity of words. Resources for affectivity of words and concepts have been made for WordNet [35] and ConceptNet, [36] respectively.
Text has been used to detect emotions in the related area of affective computing. [37] Text based approaches to affective computing have been used on multiple corpora such as students evaluations, children stories and news stories.
Scientific literature mining and academic applications
The issue of text mining is of importance to publishers who hold large databases of information needing indexing for retrieval. This is especially true in scientific disciplines, in which highly specific information is often contained within the written text. Therefore, initiatives have been taken such as Nature's proposal for an Open Text Mining Interface (OTMI) and the National Institutes of Health's common Journal Publishing Document Type Definition (DTD) that would provide semantic cues to machines to answer specific queries contained within the text without removing publisher barriers to public access.
Academic institutions have also become involved in the text mining initiative:
- The National Centre for Text Mining (NaCTeM), is the first publicly funded text mining centre in the world. NaCTeM is operated by the University of Manchester [38] in close collaboration with the Tsujii Lab, [39] University of Tokyo. [40] NaCTeM provides customised tools, research facilities and offers advice to the academic community. They are funded by the Joint Information Systems Committee (JISC) and two of the UK research councils (EPSRC & BBSRC). With an initial focus on text mining in the biological and biomedical sciences, research has since expanded into the areas of social sciences.
- In the United States, the School of Information at University of California, Berkeley is developing a program called BioText to assist biology researchers in text mining and analysis.
- The Text Analysis Portal for Research (TAPoR), currently housed at the University of Alberta, is a scholarly project to catalogue text analysis applications and create a gateway for researchers new to the practice.
Methods for scientific literature mining
Computational methods have been developed to assist with information retrieval from scientific literature. Published approaches include methods for searching, [41] determining novelty, [42] and clarifying homonyms [43] among technical reports.
Digital humanities and computational sociology
The automatic analysis of vast textual corpora has created the possibility for scholars to analyze millions of documents in multiple languages with very limited manual intervention. Key enabling technologies have been parsing, machine translation, topic categorization, and machine learning.

The automatic parsing of textual corpora has enabled the extraction of actors and their relational networks on a vast scale, turning textual data into network data. The resulting networks, which can contain thousands of nodes, are then analyzed by using tools from network theory to identify the key actors, the key communities or parties, and general properties such as robustness or structural stability of the overall network, or centrality of certain nodes. [45] This automates the approach introduced by quantitative narrative analysis, [46] whereby subject-verb-object triplets are identified with pairs of actors linked by an action, or pairs formed by actor-object. [44]
Content analysis has been a traditional part of social sciences and media studies for a long time. The automation of content analysis has allowed a "big data" revolution to take place in that field, with studies in social media and newspaper content that include millions of news items. Gender bias, readability, content similarity, reader preferences, and even mood have been analyzed based on text mining methods over millions of documents. [47] [48] [49] [50] [51] The analysis of readability, gender bias and topic bias was demonstrated in Flaounas et al. [52] showing how different topics have different gender biases and levels of readability; the possibility to detect mood patterns in a vast population by analyzing Twitter content was demonstrated as well. [53] [54]