
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of the Earth, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds. Jet streams may start, stop, split into two or more parts, combine into one stream, or flow in various directions including opposite to the direction of the remainder of the jet.
The quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) is a quasiperiodic oscillation of the equatorial zonal wind between easterlies and westerlies in the tropical stratosphere with a mean period of 28 to 29 months. The alternating wind regimes develop at the top of the lower stratosphere and propagate downwards at about 1 km (0.6 mi) per month until they are dissipated at the tropical tropopause. Downward motion of the easterlies is usually more irregular than that of the westerlies. The amplitude of the easterly phase is about twice as strong as that of the westerly phase. At the top of the vertical QBO domain, easterlies dominate, while at the bottom, westerlies are more likely to be found. At the 30mb level, with regards to monthly mean zonal winds, the strongest recorded easterly was 29.55 m/s in November 2005, while the strongest recorded westerly was only 15.62 m/s in June 1995.

A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.

The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled colonial expansion into the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
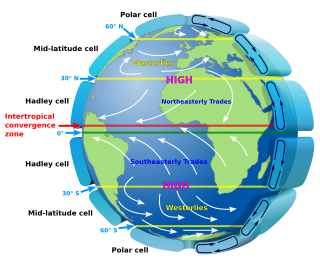
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze/land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind; in areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow.

The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere.
In the study of Earth's atmosphere, polar easterlies are the dry, cold prevailing winds that blow around the high-pressure areas of the polar highs at the North and South Poles. Cold air subsides at the poles creating high pressure zones, forcing an equatorward outflow of air; that outflow is then deflected westward by the Coriolis effect. Unlike the westerlies in the middle latitudes and trade winds in tropics, the polar easterlies are often weak and irregular. Note, winds are named based on where they came from. The polar easterlies are one of the five primary wind zones, known as wind belts, that make up our atmosphere's circulatory system. This particular belt of wind begins at approximately 60 degrees north and south latitude and reaches to the poles.

A tropical wave, in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves from east to west across the tropics, causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. Tropical waves form in the easterly flow along the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge or belt of high air pressure which lies north and south of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Tropical waves are generally carried westward by the prevailing easterly winds along the tropics and subtropics near the equator. They can lead to the formation of tropical cyclones in the north Atlantic and northeastern Pacific basins. A tropical wave study is aided by Hovmöller diagrams, a graph of meteorological data.
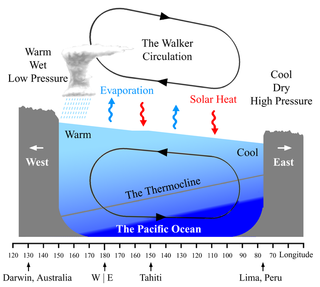
The Walker circulation, also known as the Walker cell, is a conceptual model of the air flow in the tropics in the lower atmosphere (troposphere). According to this model, parcels of air follow a closed circulation in the zonal and vertical directions. This circulation, which is roughly consistent with observations, is caused by differences in heat distribution between ocean and land. It was discovered by Gilbert Walker. In addition to motions in the zonal and vertical direction the tropical atmosphere also has considerable motion in the meridional direction as part of, for example, the Hadley Circulation.

The Fremantle Doctor, the Freo Doctor, or simply The Doctor, is the Western Australian vernacular term for the cooling afternoon sea breeze that occurs during summer months in south west coastal areas of Western Australia. The sea breeze occurs because of the major temperature difference between the land and sea.
"Cape Doctor" is the local name for the strong, often persistent and dry south-easterly wind that blows on the South African coast from spring to late summer. It is known as the Cape Doctor because of a local belief that it clears Cape Town of pollution and 'pestilence'.
The 1780 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and fall in 1780. The 1780 season was extraordinarily destructive, and was the deadliest Atlantic hurricane season in recorded history, with over 28,000 deaths. Four different hurricanes, one in June and three in October, caused at least 1,000 deaths each; this event has never been repeated, and only in the 1893 and 2005 seasons were there two such hurricanes. The season also had the deadliest Atlantic hurricane of all time, the Great Hurricane of 1780. Only one of the known storms was not a hurricane.
The African easterly jet is a region of the lower troposphere over West Africa where the seasonal mean wind speed is at a maximum and the wind is easterly. The temperature contrast between the Sahara Desert and the Gulf of Guinea causes the jet to form to the north of the monsoon trough. The jet's maximum wind speeds are at a height of 3 kilometres (1.9 mi). The jet moves northward from its south-most location in January, reaching its most northerly latitude in August. Its strongest winds are in September while it begins shifting back towards the equator. Within the easterly jet, tropical waves form. Convective complexes associated with these waves can form tropical cyclones. If the jet is south of its normal location during August and September, tropical cyclogenesis is suppressed. If desertification continues across Sub-Saharan Africa, the strength of the jet could increase, although tropical wave generation probably would decrease, which would decrease the number of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin.

A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane, typhoon, tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms".

Traditionally, areas of tropical cyclone formation are divided into seven basins. These include the north Atlantic Ocean, the eastern and western parts of the northern Pacific Ocean, the southwestern Pacific, the southwestern and southeastern Indian Oceans, and the northern Indian Ocean. The western Pacific is the most active and the north Indian the least active. An average of 86 tropical cyclones of tropical storm intensity form annually worldwide, with 47 reaching hurricane/typhoon strength, and 20 becoming intense tropical cyclones, super typhoons, or major hurricanes.

In meteorology, haar or sea fret is a cold sea fog. It occurs most often on the east coast of Great Britain between April and September, when warm air passes over the cold North Sea. The term is also known as harr, hare, harl, har and hoar.

Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet. Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail.
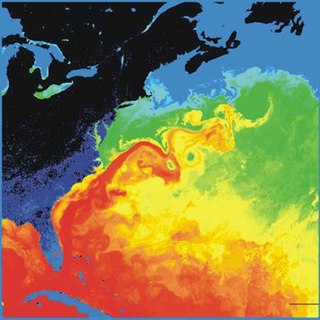
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.

The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving.













