
Hashish, also known as hash, "dry herb, hay" is a drug made by compressing and processing parts of the cannabis plant, typically focusing on flowering buds containing the most trichomes. It is consumed by smoking, typically in a pipe, bong, vaporizer or joint, or via oral ingestion. Hash has a long history of usage in countries such as Morocco, Afghanistan, India, Iran, Israel, and Lebanon. Hash consumption is also popular in Europe. In the United States, dried flowers or concentrates are more popular, though hash has seen a rise in popularity following changes in law. Like many recreational drugs, multiple synonyms and alternative names for hash exist, and vary greatly depending on the country and native language.

A bong is a filtration device generally used for smoking cannabis, tobacco, or other herbal substances. In the bong shown in the photo, the gas flows from the lower port on the left to the upper port on the right.
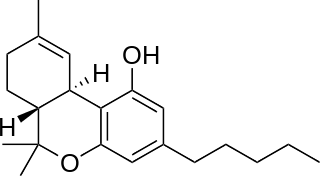
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, THC is a lipid found in cannabis, assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress.

A cannabis edible, also known as a cannabis-infused food or simply an edible, is a food product that contains decarboxylated cannabinoids from cannabis extract as an active ingredient. Although edible may refer to either a food or a drink, a cannabis-infused drink may be referred to more specifically as a liquid edible or drinkable. Edibles are a way to consume cannabis. Unlike smoking, in which cannabinoids are inhaled into the lungs and pass rapidly into the bloodstream, peaking in about ten minutes and wearing off in a couple of hours, cannabis edibles may take hours to digest, and their effects may peak two to three hours after consumption and persist for around six hours. The food or drink used may affect both the timing and potency of the dose ingested.

Tincture of cannabis, sometimes known as green dragon, is an alcoholic cannabis concentrate. The solubility of THC in ethanol is greater than 1 g/mL.

Medical cannabis, or medical marijuana (MMJ), is cannabis and cannabinoids that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has not been rigorously tested due to production and governmental restrictions, resulting in limited clinical research to define the safety and efficacy of using cannabis to treat diseases.

A vaporizer or vaporiser, colloquially known as a vape, is a device used to vaporize substances for inhalation. Plant substances can be used, commonly cannabis, tobacco, or other herbs or blends of essential oil. However, they can also be filled with a combination propylene glycol, glycerin, and drugs such as nicotine or tetrahydrocannabinol as a liquid solution.

Cannabivarin (CBV), also known as cannabivarol, is considered a non-psychoactive cannabinoid — it does not produce the euphoric side effects found in THC. Minor amounts of CBV are found in the hemp plant Cannabis sativa. It is an analog of cannabinol (CBN) with the side chain shortened by two methylene bridges (-CH2-). CBV is an oxidation product of tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV, THV).

Kief, sometimes transliterated as keef, also known as ‘’Dust’’ and "Chief" a.k.a cannabis crystals among other names, refers to the pure and clean collection of loose cannabis trichomes, which are accumulated by being sifted from cannabis flowers or buds with a mesh screen or sieve. Like some other cannabis concentrates, it contains a much higher concentration of THC and other psychoactive cannabinoids than that of the cannabis flower from which it is derived. Since it contains a higher level of THC, many consumers choose to add collected kief to their cannabis for a more intense "high"; by the same token, this preparation may induce unwelcome levels of intoxication.

Cannabis smoking is the inhalation of smoke or vapor released by heating the flowers, leaves, or extracts of cannabis and releasing the main psychoactive chemical, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is absorbed into the bloodstream via the lungs. Archaeological evidence indicates cannabis with high levels of THC was being smoked at least 2,500 years ago.

Spots refers to a method of smoking cannabis. In this method, small pieces of cannabis are rolled to form the "spot". The practice originated in the 1970s when drops or dabs of hashish oil were smoked. Generally, the tips of two knife blades are heated, the spot is compressed between the two blades, and the subsequent smoke is inhaled through the nose or mouth. Another means that is gaining popularity is specially made glass presses heated with a propane or butane torch. In order to facilitate this process, a "spottle" or "hitter" is often, but not always, used to funnel the smoke and maximize the amount inhaled. A spottle is generally made from a funnel or cone-shaped container, such as the top of a plastic or glass bottle or a gallon of milk/water.

Cannabis consumption refers to the variety of ways cannabis is consumed, among which inhalation and ingestion are most common. All consumption methods involve heating the plant's THCA to decarboxylate it into THC, either at the time of consumption or during preparation. Salves and absorption through the skin (transdermal) are increasingly common in medical uses, both of CBD, THC, and other cannabinoids. Each method leads to subtly different psychoactive effects due to the THC and other chemicals being activated, and then consumed through different administration routes. It is generally considered that smoking, which includes combustion toxins, comes on quickly but lasts for a short period of time, while eating delays the onset of effect but the duration of effect is typically longer. In a 2007 ScienceDaily report of research conducted at the University of California–San Francisco, researchers reported that vaporizer users experience the same biological effect, but without the toxins associated with smoking. Δ9-THC is the primary component when inhaled, but when eaten the liver converts this to the more psychoactive 11-hydroxy-THC form.

Hash oil, also known as honey oil or cannabis oil, is an oleoresin obtained by the extraction of cannabis or hashish. It is a cannabis concentrate containing many of its resins and terpenes – in particular, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and other cannabinoids. There are various extraction methods, most involving a solvent, such as butane or ethanol. Hash oil is usually consumed by smoking, vaporizing or eating. Hash oil may be sold in cartridges used with pen vaporizers. Preparations of hash oil may be solid or colloidal depending on both production method and temperature and are usually identified by their appearance or characteristics. Color most commonly ranges from transparent golden or light brown, to tan or black. Cannabis retailers in California have reported about 40% of their sales are from cannabis oils. Hash oil is an extracted cannabis product that may use any part of the plant, with minimal or no residual solvent. It is generally thought to be indistinct from traditional hashish, according to the 1961 UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, as it is "the separated resin, whether crude or purified, obtained from the cannabis plant".

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active component of cannabis.
The entourage effect is a proposed mechanism by which cannabis compounds other than tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) act synergistically with it to modulate the overall psychoactive effects of the plant.

Cannabis concentrate is a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) concentrated mass. Cannabis concentrates contain high THC levels that range from 40% to over 90%, stronger in THC content than high-grade marijuana, which normally measures around 20% THC levels.

Two main questions arise in the law surrounding driving after having ingested cannabis: (1) whether cannabis actually impairs driving ability, and (2) whether the common practice of testing for THC is a reliable means to measure impairment. On the first question, studies are mixed. Several recent, extensive studies–including one conducted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and one conducted by the American Automobile Association (AAA)–show that drivers with detectable THC in their blood are no more likely to cause car crashes than drivers with no amount of THC in their blood. Others show that cannabis can impair certain abilities important to safe driving –but no studies have been able to show that this increases the actual risk of crashing, or that drivers with THC in their blood cause a disproportionate number of crashes. On the second question, the studies that have been conducted so far have consistently found that THC blood levels and degree of impairment are not closely related. No known relationship between blood levels of THC and increased relative crash risk, or THC blood levels and level of driving impairment, has been shown by single-crash or classic-control studies. Thus, even though it is possible that cannabis impairs driving ability to some extent, there are currently no reliable means to test or measure whether a driver was actually impaired.
A CBD cigarette is a cigarette made with hemp instead of purely tobacco, containing cannabidiol (CBD) but a negligible amount of psychoactive tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The effects typically last between 2–3 hours and can take anywhere from seconds to several minutes to set in, making it one of the fastest methods to feel the effects of cannabidiol.

(-)-Trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol (Δ9-THCP, (C7)-Δ9-THC, and THC-Heptyl), is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from Cannabis sativa. It is structurally similar to Δ9-THC, the main active component of cannabis, but with the pentyl side chain extended to heptyl. Since it has a longer side chain, its cannabinoid effects are "far higher than Δ9-THC itself." It is said to have at least 30 times higher affinity to cannabinoid receptors than THC. The binding activity of Delta-9-THCP against human CB1 receptor in vitro is Ki = 1.2 nM. and the binding activity of Delta-8-THCP against human CB1 receptor in vitro is Ki = 22 nM.

Delta-6-cannabidiol (∆6-CBD) is a positional isomer of cannabidiol, found in only trace amounts in natural cannabis plants but readily synthesised from cannabidiol by base-catalysed migration of the double bond.












