
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Commandaria wine, and the aromatised wine vermouth.

Galicia is an autonomous community of Spain and historic nationality under Spanish law. Located in the northwest Iberian Peninsula, it includes the provinces of A Coruña, Lugo, Ourense, and Pontevedra.
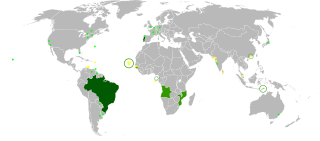
Portuguese is a western Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as "Lusophone". As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology in its lexicon.

Pontevedra is a Spanish city in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. It is the capital of both the Comarca (County) and Province of Pontevedra, and of the Rías Baixas in Galicia. It is also the capital of its own municipality which is often considered an extension of the actual city.
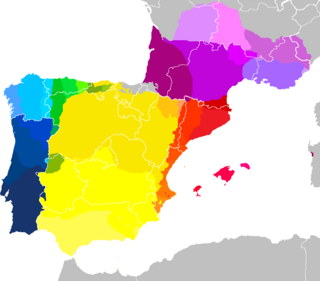
The Iberian Romance, Ibero-Romance or sometimes Iberian languages are a group of Romance languages that developed on the Iberian Peninsula, an area consisting primarily of Spain, Portugal, Gibraltar, Andorra and southern France. They are today more commonly separated into West Iberian and Occitano-Romance language groups.

Vigo is a city and municipality in the province of Pontevedra, within the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain. Located in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, it sits on the southern shore of an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, the Ria de Vigo, the southernmost of the Rías Baixas.

A Coruña is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. A Coruña is the most populated city in Galicia and the second most populated municipality in the autonomous community and seventeenth overall in the country. The city is the provincial capital of the province of the same name, having also served as political capital of the Kingdom of Galicia from the 16th to the 19th centuries, and as a regional administrative centre between 1833 and 1982, before being replaced by Santiago de Compostela.

Galician-Portuguese, also known as Old Galician, Old Portuguese, Medieval Portuguese or as Medieval Galician when referring to the history of each modern language, was a West Iberian Romance language spoken in the Middle Ages, in the northwest area of the Iberian Peninsula. Alternatively, it can be considered a historical period of the Galician and Portuguese languages.

Saudade is an emotional state of melancholic or profoundly nostalgic longing for a beloved yet absent something or someone. It is often associated with a repressed understanding that one might never encounter the recipient of longing ever again. It is a recollection of feelings, experiences, places, or events— often illusive — that cause a sense of separation from the exciting, pleasant, or joyous sensations they once caused. It derives from the Latin word for solitude.

Aguardente (Portuguese), or aguardiente (Spanish), is a generic term for alcoholic beverages that contain between 29% and 60% alcohol by volume (ABV). It originates in the Iberian Peninsula and in Iberian America.
A comarca is a traditional region or local administrative division found in Portugal, Spain and some of their former colonies, like Brazil, Nicaragua, and Panama. The term is derived from the term marca, meaning a "march, mark", plus the prefix co-, meaning "together, jointly".
European Portuguese, also known as Portuguese of Portugal, Iberian Portuguese, and Peninsular Portuguese, refers to the dialects of the Portuguese language spoken in Portugal. The word "European" was chosen to avoid the clash of "Portuguese Portuguese" as opposed to Brazilian Portuguese.
Reintegrationism is the linguistic and cultural movement in Galicia which advocates for the unity of Galician and Portuguese as a single language. In other words, the movement postulates that Galician and Portuguese languages did not only share a common origin and literary tradition, but that they are in fact variants of the same language even today. According to this, Galicia should re-integrate into the Community of Portuguese Language Countries.

Galicians are a Romance ethnic group from Spain that is closely related to the Portuguese people and has its historic homeland is Galicia, in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Two Romance languages are widely spoken and official in Galicia: the native Galician and Spanish.

Ángel Fabián Di María is an Argentine professional footballer who plays for Serie A club Juventus and the Argentina national team. He can play as either a winger or attacking midfielder. Known for his rapid pace, dribbling, and agility, Di María is considered to be one of the greatest players of his generation and one of the greatest Argentine players of all time.

Real Club Celta de Vigo, commonly known as Celta de Vigo or simply Celta, is a Spanish professional football club based in Vigo, Galicia, that competes in La Liga, the top tier of Spanish football. Nicknamed Os Celestes, the club was founded in August 1923 as Club Celta, following the merger of two Vigo-based teams. The club's home stadium is Balaídos, which seats 29,000 spectators.

Galician, also known as Galego and Gallego, is a Western Ibero-Romance language. Around 2.4 million people have at least some degree of competence in the language, mainly in Galicia, an autonomous community located in northwestern Spain, where it has official status along Spanish. The language is also spoken in some border zones of the neighbouring Spanish regions of Asturias and Castile and León, as well as by Galician migrant communities in the rest of Spain, in Latin America including Puerto Rico, the United States, Switzerland and elsewhere in Europe.
Bernal(do) de Bonaval(le), also known as Bernardo (de) Bonaval, was a 13th-century troubadour in the Kingdom of Galicia who wrote in the Galician-Portuguese language.

María Pérez, called La Balteira, was a Galician trobairitz and soldadeira.

Pilar García Negro is a Galician/Spanish politician, writer, sociolinguist, teacher, and campaigner in support of Galego, the Galician language, which is spoken in the northwest of Spain and the extreme north of Portugal.
















