Related Research Articles

A sackbut is an early form of the trombone used during the Renaissance and Baroque eras. A sackbut has the characteristic telescopic slide of a trombone, used to vary the length of the tube to change pitch, but is distinct from later trombones by its smaller, more cylindrically-proportioned bore, and its less-flared bell. Unlike the earlier slide trumpet from which it evolved, the sackbut possesses a U-shaped slide with two parallel sliding tubes, rather than just one.
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "placement of rhythmic stresses or accents where they wouldn't normally occur". It is the correlation of at least two sets of time intervals.

Giovanni Gabrieli was an Italian composer and organist. He was one of the most influential musicians of his time, and represents the culmination of the style of the Venetian School, at the time of the shift from Renaissance to Baroque idioms.

The Piano Sonata No. 12 in F major, K. 332 (300k) by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was published in 1784 along with the Piano Sonata No. 10 in C major, K. 330, and Piano Sonata No. 11, K. 331. Mozart wrote these sonatas either while visiting Munich in 1781, or during his first two years in Vienna. Some believe, however that Mozart wrote this and the other sonatas during a summer 1783 visit to Salzburg made for the purpose of introducing his wife, Constanze to his father, Leopold. All three sonatas were published in Vienna in 1784 as Mozart's Op. 6.
Andrea Gabrieli was an Italian composer and organist of the late Renaissance. The uncle of the somewhat more famous Giovanni Gabrieli, he was the first internationally renowned member of the Venetian School of composers, and was extremely influential in spreading the Venetian style in Italy as well as in Germany.

The Requiem in D minor, K. 626, is a Requiem Mass by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756–1791). Mozart composed part of the Requiem in Vienna in late 1791, but it was unfinished at his death on 5 December the same year. A completed version dated 1792 by Franz Xaver Süssmayr was delivered to Count Franz von Walsegg, who had commissioned the piece for a requiem service on 14 February 1792 to commemorate the first anniversary of the death of his wife Anna at the age of 20 on 14 February 1791.
Concertato is a term in early Baroque music referring to either a genre or a style of music in which groups of instruments or voices share a melody, usually in alternation, and almost always over a basso continuo. The term derives from Italian concerto which means "playing together"—hence concertato means "in the style of a concerto." In contemporary usage, the term is almost always used as an adjective, for example "three pieces from the set are in concertato style."

The Venetian polychoral style was a type of music of the late Renaissance and early Baroque eras which involved spatially separate choirs singing in alternation. It represented a major stylistic shift from the prevailing polyphonic writing of the middle Renaissance, and was one of the major stylistic developments which led directly to the formation of what is now known as the Baroque style. A commonly encountered term for the separated choirs is cori spezzati—literally, "broken choruses" as they were called, added the element of spatial contrast to Venetian music. These included the echo device, so important in the entire baroque tradition; the alternation of two contrasting bodies of sound, such as chorus against chorus, single line versus a full choir, solo voice opposing full choir, instruments pitted against voices and contrasting instrumental groups; the alternation of high and low voices; soft level of sound alternated with a loud one; the fragmentary versus the continuous; and blocked chords contrasting with flowing counterpoint.

In music history, the Venetian School was the body and work of composers working in Venice from about 1550 to around 1610, many working in the Venetian polychoral style. The Venetian polychoral compositions of the late sixteenth century were among the most famous musical works in Europe, and their influence on musical practice in other countries was enormous. The innovations introduced by the Venetian school, along with the contemporary development of monody and opera in Florence, together define the end of the musical Renaissance and the beginning of the musical Baroque.
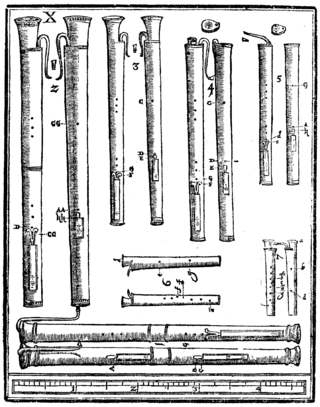
The dulcian is a Renaissance woodwind instrument, with a double reed and a folded conical bore. Equivalent terms include English: curtal, German: Dulzian, French: douçaine, Dutch: dulciaan, Italian: dulciana, Spanish: bajón, and Portuguese: baixão.
Girolamo Dalla Casa, also known as Hieronymo de Udene, was an Italian composer, instrumentalist, and writer of the late Renaissance. He was a member of the Venetian School, and more influential as a performer than as a composer.
Dario Castello was an Italian composer and violinist from the early Baroque period who worked and published in Venice. As a composer, he was a late member of the Venetian School and had a role in the transformation of the instrumental canzona into the sonata.
Giovanni Croce was an Italian composer of the late Renaissance, of the Venetian School. He was particularly prominent as a madrigalist, one of the few among the Venetians other than Monteverdi and Andrea Gabrieli.
Vincenzo Bellavere was an Italian composer of the Venetian School. While a fairly minor figure in the Venetian School, he was a competent composer of madrigals and wrote a few works in the grand Venetian polychoral style.

Ludwig van Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 5 in C minor, Op. 10, No. 1 was composed some time during 1796–98.

Ludwig van Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 1 in F minor, Op. 2 No. 1, was written in 1795 and dedicated to Joseph Haydn. It was published simultaneously with his second and third piano sonatas in 1796.
In Ecclesiis is one of Giovanni Gabrieli's most famous single works. An example of polychoral techniques, it also epitomizes Baroque and Renaissance styles, with its use of hexachord-based harmonies, chromatic mediants, movement by fifths, pedal points and extended plagal cadences.

Johannes Brahms's Violin Sonata No. 3 in D minor, Op. 108 is the last of his violin sonatas, composed between 1886 and 1888. Unlike the two previous violin sonatas, it is in four movements. The sonata is dedicated to Brahms' friend and colleague Hans von Bülow and was premiered in Budapest in 1888, with Jenő Hubay on violin and the composer at the piano.

The Symphony No. 21 in A major, Hoboken I/21, was composed by Joseph Haydn around the year 1764. The symphony’s movements have unusual structures that make their form hard to identify. The parts that pertain to sonata form are often hard to recognize immediately and are often identified “only in retrospect.”
His Majestys Sagbutts & Cornetts (HMSC) is a British early music group founded in 1982. The ensemble presently consists of three cornetts and four sackbuts, with chamber organ or harpsichord. The group frequently collaborates with other instrumentalists and singers, and has an extensive discography on Hyperion Records and other labels.
References
- ↑ Arnold, Denis (1979). Giovanni Gabrieli and the Music of the Venetian High Renaissance. London: Oxford University Press. p. [ page needed ]. ISBN 0-19-315247-9.
- ↑ Fenlon, Iain (November 1990). "Gabrieli and St Mark's Venetian Brass Music". Gramophone (review of Nimbus Records NI5236). Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ↑ Giovanni Gabrieli Opera Omnia, Richard Charteris (ed.), vol. X, p. XIII (American Institute of Musicology, 1998)
- ↑ Bartholomew, Leland Earl (December 1965). Alessandro Rauerij's Collection of Canzoni per Sonare (Venice, 1608) Volume I – Historical and Analytical Study. Fort Hays Studies—New Series no. 1. Fort Hays State University. p. 215. doi:10.58809/HVMG1779.