
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in eastern Mexico, Veracruz is bordered by seven states, which are Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Hidalgo, Puebla, Oaxaca, Chiapas, and Tabasco. Veracruz is divided into 212 municipalities, and its capital city is Xalapa-Enríquez.

The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges that stretch 1,500 km (930 mi) from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Ranges, which run along the Pacific coast from Alaska to Mexico. Elevations range from 150 to 3,300 m.

The Sierra de la Laguna is a mountain range at the southern end of the Baja California peninsula in Mexico, and is the southernmost range of the Peninsular Ranges System.

Los Tuxtlas is a region in the south of the Mexican state of Veracruz.

The Sierra de Los Tuxtlas are a volcanic belt and mountain range along the southeastern Veracruz Gulf coast in Eastern Mexico. The Los Tuxtlas Biosphere Reserve includes the coastal and higher elevations of the Sierra de Los Tuxtlas.

Montepío is a small village on the Gulf Coast of Mexico, within the San Andrés Tuxtla municipality, Veracruz, 1 hour away from the major tourist center of Catemaco.
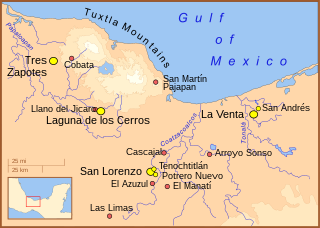
The Olmec heartland is the southern portion of Mexico's Gulf Coast region between the Tuxtla mountains and the Olmec archaeological site of La Venta, extending roughly 80 km inland from the Gulf of Mexico coastline at its deepest. It is today, as it was during the height of the Olmec civilization, a tropical lowland forest environment, crossed by meandering rivers.

La Mojarra is an archaeological site in the Mexican state of Veracruz, located near Gulf Coast, at a bend in the Acula River. It was continually occupied from the late Formative period until perhaps as late as 1000 CE.

Matacapan or Matacapan Piedra is a Classic era archaeological site in present-day Mexican state of Veracruz situated in the Sierra de Los Tuxtlas, near Catemaco.

The San Lucan xeric scrub is a xeric shrubland ecoregion of the southernmost Baja California Peninsula, in Los Cabos Municipality and eastern La Paz Municipality of southern Baja California Sur state, Mexico.
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

Catemaco is a municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz. It is located in the state's Los Tuxtlas region. The municipal seat is the city of Catemaco.
Lerdo de Tejada is a municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz, located 207 kilometres (129 mi) southeast of the state capital Xalapa. It is named after Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada, the 27th President of Mexico.

Hueyapan de Ocampo is a municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz. It is located in south of the state, about 245 km from state capital Xalapa. The municipality has an area of 824.18 km2.
Isla is a municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz. It is located in the south zone of the state, about 370 km from the state capital Xalapa. It has a surface of 714.80 km2. It is located at 18°02′N95°32′W.
Soteapan is a municipality and city located in the south-central zone of the Mexican state of Veracruz, about 260 km from state capital Xalapa. As of 2000, the municipality counted 27,487 inhabitants within 528.07 km², including about 10,000 in the main city area of Soteapan.

The St. Joseph and St. Andrew Cathedral is a Catholic church in the Diocese of San Andrés Tuxtla located in the city of San Andrés Tuxtla, in Veracruz, Mexico. It dominates the center of the town with its two towering sotaventino Colonial-style towers. The beginning of its construction dates to the late nineteenth and mid-twentieth century.

The Tehuantepec-El Manchon mangroves ecoregion covers a series of mangrove woodlands along the Pacific Ocean coast of the state of Chiapas, Mexico. The ecoregion is relatively large and continuous, with trees up to 25 meters in height. The region supports stands of a type of yellow mangrove that normally only grown further south. The coast of Mexico here is wet - over 2,500 mm/year of rain. Four RAMSAR wetlands of international important are found in the zone, and a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Of particular importance are the wide variety of permanent and migratory birds in the area.

The Alvarado mangroves ecoregion covers a series of mangrove forest areas along the Gulf of Mexico coast of the states of Tamaulipas and Veracruz in Mexico. they are the most northerly mangroves in the western Gulf. The largest tracts of mangrove swamps occur at the mouths of rivers, and nearby coastal lagoon.

Barranca de Metztitlán is a biosphere reserve in the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is protected for its dramatic scenery of steep cliffs and deep winding canyons, and its distinctive flora and fauna.















