
CITES is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975.

Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other animals, including cashmere and mohair from goats, qiviut from muskoxen, hide and fur clothing from bison, angora from rabbits, and other types of wool from camelids.

A textile is a flexible material made by creating an interlocking network of yarns or threads, which are produced by spinning raw fibres into long and twisted lengths. Textiles are then formed by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, tatting, felting, bonding or braiding these yarns together.
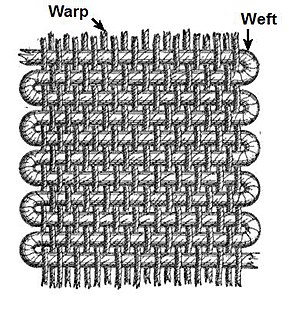
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are inter-woven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band which meets this definition of cloth can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques without looms.

Mohair is a fabric or yarn made from the hair of the Angora goat. Both durable and resilient, mohair is notable for its high luster and sheen, and is often used in fiber blends to add these qualities to a textile. Mohair takes dye exceptionally well. It feels warm in winter as it has excellent insulating properties, while its moisture-wicking properties allow it to remain cool in summer. It is durable, naturally elastic, flame-resistant and crease-resistant. It is considered a luxury fiber, like cashmere, angora, and silk, and can be more expensive than most sheep's wool.

Mineral wool is any fibrous material formed by spinning or drawing molten mineral or rock materials such as slag and ceramics.

New Zealand flax describes the common New Zealand perennial plants Phormium tenax and Phormium colensoi, known by the Māori names harakeke and wharariki respectively. Although given the common name 'flax' they are quite distinct from the Northern Hemisphere plant known as flax

Pashmina refers to a fine variant of spun cashmere, the animal-hair fibre forming the downy undercoat of the Changthangi goat. The word pashm means "wool" in Persian, but in Kashmir, pashm referred to the raw unspun wool of domesticated Changthangi goats. In common parlance today, pashmina may refer either to the material or to the variant of the Kashmir shawl that is made from it. Both generic cashmere and pashmina come from the same goat, but generic cashmere ranges from 12 to 21 microns in diameter, whereas pashmina refers only to those fibres that range from 12 to 16 microns.

The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.

Country of origin (COO) represents the country or countries of manufacture, production, design, or brand origin where an article or product comes from. For multinational brands, COO may include multiple countries within the value-creation process.
The International Wool Textile Organisation (IWTO) is the international body representing the interests of the world's wool-textile trade and industry. Its members include wool growers, traders, primary processors, spinners, weavers, garment makers and retailers of wool and allied fibres, as well as organizations related to wool products.
The African Mine Workers' Strike was a labour dispute involving mine workers of Witwatersrand in South Africa. It started on 12 August, 1946 and lasted approximately a week. The strike was attacked by police and over the week, at least 1,248 workers were wounded and at least 9 killed.
An S number on the label of wool suits or other tailored apparel, wool fabric, or yarn, indicates the fineness of the wool fiber used in the making of the apparel, as measured by its maximum diameter in micrometres. Fiber fineness is one of the factors determining the quality and performance of a wool product. In recent years it has also become an important marketing device used by many mills, garment makers, and retailers. The S number appears as a plural with an s or 's following the number, such as 100s or 100's.
Textile manufacturing is one of the oldest human activities. The oldest known textiles date back to about 5000 B.C. In order to make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving to create cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. Cloth is finished by what are described as wet process to become fabric. The fabric may be dyed, printed or decorated by embroidering with coloured yarns.
The Industrial Organisation and Development Act 1947 enabled the creation of industrial development Boards with powers to raise levies from specific industrial sectors in the United Kingdom for co-ordinated action, particularly in research, marketing and industrial re-organisation. These Boards were to report to the Board of Trade and have equal representation from trades unions and employers alongside independent experts.
The textile industry in India traditionally, after agriculture, is the only industry that has generated huge employment for both skilled and unskilled labour. The textile industry continues to be the second-largest employment generating sector in India. It offers direct employment to over 35 million in the country. According to the Ministry of Textiles, the share of textiles in total exports during April–July 2010 was 11.04%. During 2009–2010, the Indian textile industry was pegged at US$55 billion, 64% of which services domestic demand. In 2010, there were 2,500 textile weaving factories and 4,135 textile finishing factories in all of India. According to AT Kearney’s ‘Retail Apparel Index’, India was ranked as the fourth most promising market for apparel retailers in 2009.

Woolmark is a wool industry certification mark used on pure wool products that meet quality standards set by The Woolmark Company. It is a trade mark owned by The Woolmark Company, which has since 2007 been a subsidiary of Australian Wool Innovation Limited (AWI). The logo was launched in 1964 by the Woolmark Company under its previous name, the International Wool Secretariat.

The International Wool Secretariat (IWS) was formed in 1937 to promote the sale of wool on behalf of woolgrowers and review research carried out by independent bodies such as the Wool Industries' Research Association at Torridon, Headingley Lane, Leeds, England.
The New Zealand Wool Board was established in 1944 under the Wool Industry Act. The McKinsey published a report in 2000 that sparked two years of debate for referendums and reforms to the New Zealand Wool Board. In 2001, McKinsey's recommendations were implemented and Wool Board was dissolved and was completely restructured.
The Australian Wool Board was an Australian Government statutory board that existed in its first phase between May 1936 and January 1945; in its second phase between June 1945 and June 1953; and in its third and final phase, between May 1963 and December 1972. The first Wool Board, in 1936, together with the Wool Boards of New Zealand and South Africa decided to form an organisation to promote wool, to meet the growing challenge from synthetic fibres, which led to the formation in 1937 of the International Wool Secretariat. There have been other reorganisations of the management of the wool sector in Australia since.











