Related Research Articles

Organ donation is the process when a person allows an organ of their own to be removed and transplanted to another person, legally, either by consent while the donor is alive or dead with the assent of the next of kin.
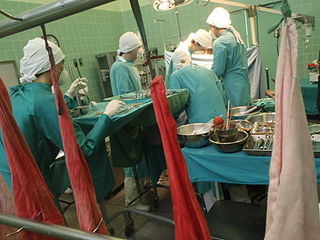
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source.
Brain death is the permanent, irreversible, and complete loss of brain function which may include cessation of involuntary activity necessary to sustain life. It differs from persistent vegetative state, in which the person is alive and some autonomic functions remain. It is also distinct from comas as long as some brain and bodily activity and function remain, and it is also not the same as the condition locked-in syndrome. A differential diagnosis can medically distinguish these differing conditions.

The United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) is a non-profit, scientific and educational organization that administers the only Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) in the United States, established by the U.S. Congress in 1984 by Gene A. Pierce, founder of United Network for Organ Sharing. Located in Richmond, Virginia, the organization's headquarters are situated near the intersection of Interstate 95 and Interstate 64 in the Virginia BioTechnology Research Park.
Organ procurement is a surgical procedure that removes organs or tissues for reuse, typically for organ transplantation.

The National Organ Transplant Act (NOTA) of 1984 is an Act of the United States Congress that created the framework for the organ transplant system in the country. The act provided clarity on the property rights of human organs obtained from deceased individuals and established a public-private partnership known as Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). The OPTN was given the authority to oversee the national distribution of organs.
Kendall Ciesemier is a writer, producer, and reporter, originally from Wheaton, Illinois. She is also the founder of Kids Caring 4 Kids, a non-profit organization she started at age 11.
Organ trade is the trading of human organs, tissues, or other body products, usually for transplantation. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), organ trade is a commercial transplantation where there is a profit, or transplantations that occur outside of national medical systems. There is a global need or demand for healthy body parts for transplantation, which exceeds the numbers available.

The Methuselah Foundation is an American-based global non-profit organization based in Springfield, Virginia, with a declared mission to "make 90 the new 50 by 2030" by supporting tissue engineering and regenerative medicine therapies. The organization was originally incorporated by David Gobel in 2001 as the Performance Prize Society, a name inspired by the British governments Longitude Act, which offered monetary rewards for anyone who could devise a portable, practical solution for determining a ship's longitude.
The Center for Ethical Solutions (CES), founded by Sigrid Fry-Revere, is a 501(c)(3) non-profit bioethics think tank based in Lovettsville, Virginia whose mission is to find practical solutions to controversial problems in the field of medical ethics. CES supports research and public education, seeking to achieve its goals through research and developing products including books and documentary films to educate the public. Lobbying and participation in political campaigns are specifically excluded from its activities.
The Final Rule is a national policy in the United States that dictates the protocol for all cadaveric organ donation. The Final Rule replaced a variety of local and regional protocols with a unified policy for the first time. It also increased the Department of Health and Human Services' control of organ donation.
In the United States, an organ procurement organization (OPO) is a non-profit organization that is responsible for the evaluation and procurement of deceased-donor organs for organ transplantation. There are 57 such organizations in the United States, each responsible for organ procurement in a specific region, and each a member of the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN), a federally-mandated network managed by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) under federal contract. The individual OPOs represent the front line of organ procurement, having direct contact with the donor's hospital and the family of the recently deceased donor. Once the OPO receives authorization for donation from the decedent's family or through first-person authorization, it works with UNOS to identify the best candidates for the available organs, and coordinates with the surgical team for each organ recipient.

MOHAN Foundation is a not-for-profit, registered non-government charity organisation in India that works in the field of deceased organ donation and transplantation. MOHAN is an acronym for Multi Organ Harvesting Aid Network. It has offices in Chennai, Hyderabad, Bengaluru, Delhi, Mumbai, Chandigarh, Nagpur, Jaipur and information centers at Kerala and Imphal.

The HIV Organ Policy Equity Act is a law that modifies rules regarding organ donation between HIV-positive individuals. The law authorizes clinical research and the revision of rules about organ donation and transportation as a result of the research. Organs from HIV donors would only be going to individuals who are already HIV positive, but could lead to 600 additional organ transplants a year. The use of HIV-positive organs was previously a federal crime. This bill passed the United States Senate during the 113th United States Congress, and also passed the United States House of Representatives. It was signed into law as PL 113-51 by President Barack Obama on November 21, 2013.
Transplant coordinator is a healthcare professional – doctor, nurse, or allied health science graduate – who coordinates activities related to organ donation and transplantation. Transplant coordinators can either be Donor Coordinators or Recipient Coordinators.
J. Michael Henderson is an American general and transplant surgeon, with experience in portal hypertension, liver transplantation, and pancreatic disease. Henderson is the Chief Medical Officer at the University of Mississippi Medical Center since 2015. Prior to this role, he was with the Cleveland Clinic from 1992–2014. He was the Chairman of the Department of General Surgery and Director of the Transplant Center for 12 years, and was the Chief Quality Officer for the Cleveland Clinic’s 10-hospital system for eight years.
Deemed status is a hospital accreditation for hospitals in the United States.
Kidney paired donation (KPD), or paired exchange, is an approach to living donor kidney transplantation where patients with incompatible donors swap kidneys to receive a compatible kidney. KPD is used in situations where a potential donor is incompatible. Because better donor HLA and age matching are correlated with lower lifetime mortality and longer lasting kidney transplants, many compatible pairs are also participating in swaps to find better matched kidneys. In the United States, the National Kidney Registry organizes the majority of U.S. KPD transplants, including the largest swaps. The first large swap was a 60 participant chain in 2012 that appeared on the front page of the New York Times and the second, even larger swap, included 70 participants and was completed in 2014. Other KPD programs in the U.S. include the UNOS program, which was launched in 2010 and completed its 100th KPD transplant in 2014, and the Alliance for Paired Donation.

Jenna Arnold is an American activist, entrepreneur and author of Raising Our Hands (2020). She is known as the co-founder of ORGANIZE, for her work at the United Nations and MTV, and was a National Organizer for the 2017 Women's March on Washington. Oprah has called Arnold one of the "100 Awakened Leaders who are using their voice and talent to elevate humanity". She is a frequent contributor on the subjects of American identity, politics and foreign policy on FOX, CNN, and MSNBC.
Organ donation in India is regulated by the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994. The law allows both deceased and living donors to donate their organs. It also identifies brain death as a form of death. The National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) functions as the apex body for activities of relating to procurement, allotment and distribution of organs in the country.
References
- 1 2 "Texas Organ Procurement Organizations | Texas Donor Registry". Donatelifetexas.org. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- 1 2 "STA". Organ.org. 2014-06-20. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- ↑ "Organ Donation Alliance". Organ Donation Alliance. 2014-06-20. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- ↑ Patti Niles. "Southwest Transplant Alliance Celebrates 40th Anniversary of Life-Saving Work". AOPO. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- ↑ Goodman, Matt (2016-02-04). "In 2015, Southwest Transplant Alliance Set A Texas Record For Organs Recovered « D Healthcare Daily". Healthcare.dmagazine.com. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- ↑ Goodman, Matt (2016-07-08). "Southwest Transplant Alliance Execs Receive National Recognition « D Healthcare Daily". Healthcare.dmagazine.com. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- ↑ "Organ Procurement Organization (OPO) List - organdonor.gov". 1 October 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-10-01.
- ↑ "HRSA - Find Organ Procurement Organizations (OPO) or Organ Transplant Programs (OTP) - Search Page". 7 October 2009. Archived from the original on 2009-10-07.
- ↑ "Donate Life Float Rose Parade". Donatelifefloat.org. Retrieved 2017-01-18.