Related Research Articles

A subwoofer is a loudspeaker designed to reproduce low-pitched audio frequencies, known as bass and sub-bass, that are lower in frequency than those which can be (optimally) generated by a woofer. The typical frequency range that is covered by a subwoofer is about 20–200 Hz for consumer products, below 100 Hz for professional live sound, and below 80 Hz in THX-certified systems. Thus, one or more subwoofers are important for high-quality sound reproduction as they are responsible for the lowest two to three octaves of the ten octaves that are audible. This very low-frequency (VLF) range reproduces the natural fundamental tones of the bass drum, electric bass, double bass, grand piano, contrabassoon, tuba, in addition to thunder, gunshots, explosions, etc.

A loudspeaker is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections. The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound.

Binaural recording is a method of recording sound that uses two microphones, arranged with the intent to create a 3D stereo sound sensation for the listener of actually being in the room with the performers or instruments. This effect is often created using a technique known as dummy head recording, wherein a mannequin head is fitted with a microphone in each ear. Binaural recording is intended for replay using headphones and will not translate properly over stereo speakers. This idea of a three-dimensional or "internal" form of sound has also translated into useful advancement of technology in many things such as stethoscopes creating "in-head" acoustics and IMAX movies being able to create a three-dimensional acoustic experience.
An audiophile is a person who is enthusiastic about high-fidelity sound reproduction. An audiophile seeks to reproduce recorded music to achieve high sound quality, typically in a quiet listening space and in a room with good acoustics.
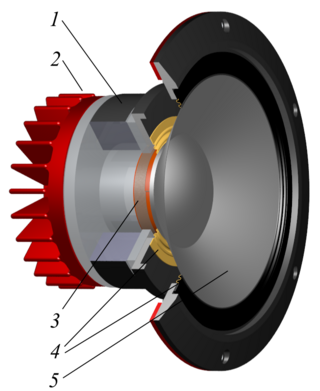
A mid-range speaker is a loudspeaker driver that reproduces sound in the frequency range from 250 to 2000 Hz.
The low-frequency effects (LFE) channel is a band-limited audio track that is used for reproducing deep and intense low-frequency sounds in the 3–120 Hz frequency range.

Audio system measurements are used to quantify audio system performance. These measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements to specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are within limits considered acceptable. Audio system measurements often accommodate psychoacoustic principles to measure the system in a way that relates to human hearing.

Active noise control (ANC), also known as noise cancellation (NC), or active noise reduction (ANR), is a method for reducing unwanted sound by the addition of a second sound specifically designed to cancel the first. The concept was first developed in the late 1930s; later developmental work that began in the 1950s eventually resulted in commercial airline headsets with the technology becoming available in the late 1980s. The technology is also used in road vehicles, mobile telephones, earbuds, and headphones.

A sound reinforcement system is the combination of microphones, signal processors, amplifiers, and loudspeakers in enclosures all controlled by a mixing console that makes live or pre-recorded sounds louder and may also distribute those sounds to a larger or more distant audience. In many situations, a sound reinforcement system is also used to enhance or alter the sound of the sources on the stage, typically by using electronic effects, such as reverb, as opposed to simply amplifying the sources unaltered.
Klipsch Audio Technologies is an American loudspeaker company based in Indianapolis, Indiana. Founded in Hope, Arkansas, in 1946 as 'Klipsch and Associates' by Paul W. Klipsch, the company produces loudspeaker drivers and enclosures, as well as complete loudspeakers for high-end, high-fidelity sound systems, public address applications, and personal computers.
In the field of acoustics, a diaphragm is a transducer intended to inter-convert mechanical vibrations to sounds, or vice versa. It is commonly constructed of a thin membrane or sheet of various materials, suspended at its edges. The varying air pressure of sound waves imparts mechanical vibrations to the diaphragm which can then be converted to some other type of signal; examples of this type of diaphragm are found in microphones and the human eardrum. Conversely a diaphragm vibrated by a source of energy beats against the air, creating sound waves. Examples of this type of diaphragm are loudspeaker cones and earphone diaphragms and are found in air horns.
High-end audio is a class of consumer home audio equipment marketed to audiophiles on the basis of high price or quality, and esoteric or novel sound reproduction technologies. The term can refer simply to the price, to the build quality of the components, or to the subjective or objective quality of sound reproduction.
Virtual surround is an audio system that attempts to create the perception that there are many more sources of sound than are actually present. In order to achieve this, it is necessary to devise some means of tricking the human auditory system into thinking that a sound is coming from somewhere that it is not. Most recent examples of such systems are designed to simulate the true (physical) surround sound experience using one, two or three loudspeakers. Such systems are popular among consumers who want to enjoy the experience of surround sound without the large number of speakers that are traditionally required to do so.

Loudspeaker measurement is the practice of determining the behaviour of loudspeakers by measuring various aspects of performance. This measurement is especially important because loudspeakers, being transducers, have a higher level of distortion than other audio system components used in playback or sound reinforcement.
Latency refers to a short period of delay between when an audio signal enters a system, and when it emerges. Potential contributors to latency in an audio system include analog-to-digital conversion, buffering, digital signal processing, transmission time, digital-to-analog conversion, and the speed of sound in the transmission medium.
A speaker grille is usually found in front of many consumer and industrial loudspeakers, and consists of either a hard or soft screen/grille mounted directly over the face of the speaker driver. Its main purpose is to protect the driver element and speaker internals from foreign objects while still allowing the sound to clearly pass. However, because it sits in the direct path of the driver, the grille interacts with the sound produced. A suitable compromise between protection and sound quality must be made based on the speaker's application.
The Franssen effect is an auditory illusion where the listener incorrectly localizes a sound. It was found in 1960 by Nico Valentinus Franssen (1926–1979), a Dutch physicist and inventor. There are two classical experiments, which are related to the Franssen effect, called Franssen effect F1 and Franssen effect F2.

A stage monitor system is a set of performer-facing loudspeakers called monitor speakers, stage monitors, floor monitors, wedges, or foldbacks on stage during live music performances in which a sound reinforcement system is used to amplify a performance for the audience. The monitor system allows musicians to hear themselves and fellow band members clearly.

The Linn Isobarik, nicknamed "Bariks" or "Briks", is a loudspeaker designed and manufactured by Linn Products. The Isobarik is known for both its reproduction of low bass frequencies and being very demanding on amplifiers.

Fred Roy Cizek was an American inventor, hi-fi designer, and manufacturer.
References
- ↑ Atacama Audio, one of the first companies to recognise the importance of sound dampening, was founded in 1986