
An optical spectrometer is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength.
Interferometry is a technique in which waves are superimposed to cause the phenomenon of interference, which is used to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.

The W. M. Keck Observatory is a two-telescope astronomical observatory at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes have 10 m (33 ft) aperture primary mirrors, and when completed in 1993 and 1996 were the largest astronomical telescopes in the world. They are currently the 3rd and 4th largest.

A reflecting telescope is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope.

Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments.

A monochromator is an optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. The name is from the Greek roots mono-, "single", and chroma, "colour", and the Latin suffix -ator, denoting an agent.

The Southern African Large Telescope (SALT) is a 10-metre class optical telescope designed mainly for spectroscopy. It consists of 91 hexagonal mirror segments each with a 1-metre inscribed diameter, resulting in a total hexagonal mirror of 11.1 by 9.8 m. It is located close to the town of Sutherland in the semi-desert region of the Karoo, South Africa. It is a facility of the South African Astronomical Observatory, the national optical observatory of South Africa.

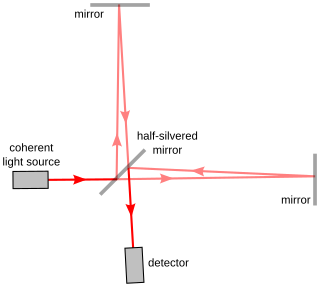
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by Albert Abraham Michelson. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test.
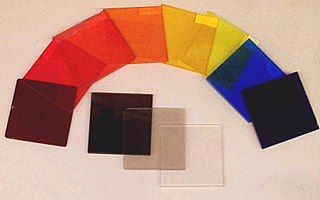
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical properties of filters are completely described by their frequency response, which specifies how the magnitude and phase of each frequency component of an incoming signal is modified by the filter.

The VISTA is a wide-field reflecting telescope with a 4.1 metre mirror, located at the Paranal Observatory in Chile. It is operated by the European Southern Observatory and started science operations in December 2009. VISTA was conceived and developed by a consortium of universities in the United Kingdom led by Queen Mary University of London and became an in-kind contribution to ESO as part of the UK's accession agreement, with the subscription paid by the UK Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC).
The Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) is an instrument on the SOHO spacecraft used to obtain high-resolution images of the solar corona in the ultraviolet range. The EIT instrument is sensitive to light of four different wavelengths: 17.1, 19.5, 28.4, and 30.4 nm, corresponding to light produced by highly ionized iron (XI)/(X), (XII), (XV), and helium (II), respectively. EIT is built as a single telescope with a quadrant structure to the entrance mirrors: each quadrant reflects a different colour of EUV light, and the wavelength to be observed is selected by a shutter that blocks light from all but the desired quadrant of the main telescope.

The NASA Infrared Telescope Facility is a 3-meter (9.8 ft) telescope optimized for use in infrared astronomy and located at the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii. It was first built to support the Voyager missions and is now the US national facility for infrared astronomy, providing continued support to planetary, solar neighborhood, and deep space applications. The IRTF is operated by the University of Hawaii under a cooperative agreement with NASA. According to the IRTF's time allocation rules, at least 50% of the observing time is devoted to planetary science.
A staring array, also known as staring-plane array or focal-plane array (FPA), is an image sensor consisting of an array of light-sensing pixels at the focal plane of a lens. FPAs are used most commonly for imaging purposes, but can also be used for non-imaging purposes such as spectrometry, LIDAR, and wave-front sensing.
X-ray optics is the branch of optics that manipulates X-rays instead of visible light. It deals with focusing and other ways of manipulating the X-ray beams for research techniques such as X-ray crystallography, X-ray fluorescence, small-angle X-ray scattering, X-ray microscopy, X-ray phase-contrast imaging, X-ray astronomy etc.

A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph.

A telescope is an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects, or various devices used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century, by using glass lenses. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy.

Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption or emission of a solid, liquid or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time.
An integral field spectrograph, or a spectrograph equipped with an integral field unit (IFU), is an optical instrument combining spectrographic and imaging capabilities, used to obtain spatially resolved spectra in astronomy and other fields of research such as bio-medical science and earth observation.

An astronomical filter is a telescope accessory consisting of an optical filter used by amateur astronomers to simply improve the details of celestial objects, either for viewing or for photography. Research astronomers, on the other hand, use various band-pass filters for photometry on telescopes, in order to obtain measurements which reveal objects' astrophysical properties, such as stellar classification and placement of a celestial body on its Wien curve.

The Goode Solar Telescope (GST) is a scientific facility for studies of the Sun named after Philip R. Goode. It was the solar telescope with the world's largest aperture in operation for more than a decade. Located in Big Bear Lake; California, the Goode Solar Telescope is the main telescope of the Big Bear Solar Observatory operated by the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT). Initially named New Solar Telescope (NST), first engineering light was obtained in December 2008, and scientific observations of the Sun began in January 2009. On July 17, 2017, the NST was renamed in honor of Goode, a former, and founding director of NJIT's Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research and the principal investigator of the facility. Goode conceived, raised the funds, and assembled the team that built and commissioned the telescope, and it was the highest resolution solar telescope in the world and the first facility class solar telescope built in the U.S. in a generation.

















