
Defecation is the final act of digestion, by which organisms eliminate solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material from the digestive tract via the anus.

A butt plug is a sex toy that is designed to be inserted into the rectum for sexual pleasure. In some ways, they are similar to a dildo, but they tend to be shorter, and have a flanged end to prevent the device from being lost inside the rectum.

Anal beads are a sex toy consisting of multiple spheres or balls attached together in series which are continuously inserted through the anus into the rectum and then removed with varying speeds depending on the desired effect. Anal bead users enjoy the pleasurable feeling of the ball passing through the narrow sphincter of the anus.
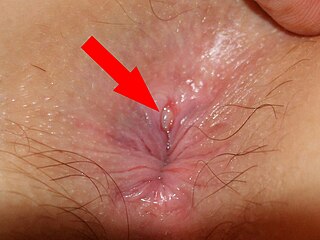
An anal fissure is a break or tear in the skin of the anal canal. Anal fissures may be noticed by bright red anal bleeding on toilet paper and undergarments, or sometimes in the toilet. If acute they are painful after defecation, but with chronic fissures, pain intensity is often less. Anal fissures usually extend from the anal opening and are usually located posteriorly in the midline, probably because of the relatively unsupported nature and poor perfusion of the anal wall in that location. Fissure depth may be superficial or sometimes down to the underlying sphincter muscle. Untreated fissures develop a hood like skin tag which cover the fissure and cause discomfort and pain.

The anal canal is the terminal part of the large intestine. It is situated between the rectum and anus, below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. In humans it is approximately 2.5 to 4 cm (0.98-1.58 in) long. It lies in the anal triangle of perineum in between the right and left ischioanal fossa.
Anal sphincter muscles may refer to:

The external anal sphincter is a flat plane of muscular fibers, elliptical in shape and intimately adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus.

The internal anal sphincter, IAS, is a muscular ring that surrounds about 2.5–4.0 cm of the anal canal; its inferior border is in contact with, but quite separate from, the external anal sphincter.

Anal fistula is a chronic abnormal communication between the epithelialised surface of the anal canal and usually the perianal skin. An anal fistula can be described as a narrow tunnel with its internal opening in the anal canal and its external opening in the skin near the anus. Anal fistulae commonly occur in people with a history of anal abscesses. They can form when anal abscesses do not heal properly.

The muscular layer is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin, tunica muscularis, may also be used.
Anal sphincterotomy is a surgical procedure that involves treating mucosal fissures from the anal canal/sphincter. The word is formed from sphincter + otomy.
Lateral internal sphincterotomy is an operation performed on the internal anal sphincter muscle for the treatment of chronic anal fissure. The internal anal sphincter is one of two muscles that comprise the anal sphincter which controls the passage of feces. The procedure helps by lowering the resting pressure of the internal anal sphincter, which improves blood supply to the fissure and allows faster healing. The procedure has been shown to be very effective, with 96% of fissures healing at a median of 3 weeks in one trial.
The bulbocavernosus reflex (BCR), bulbospongiosus reflex (BSR) or "Osinski reflex" is a polysynaptic reflex that is useful in testing for spinal shock and gaining information about the state of spinal cord injuries (SCI). Bulbocavernosus is an older term for bulbospongiosus, thus this reflex may also be referred to as the bulbospongiosus reflex.
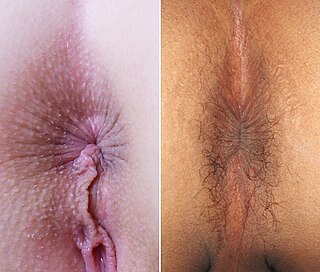
The human anus is the external opening of the rectum. Two sphincters control the exit of feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. It is located behind the perineum which is located behind the vagina in females and behind the scrotum in males.
Anismus is the failure of the normal relaxation of pelvic floor muscles during attempted defecation. It can occur in both children and adults, and in both men and women. It can be caused by physical defects or it can occur for other reasons or unknown reasons. Anismus that has a behavioral cause could be viewed as having similarities with parcopresis, or psychogenic fecal retention.
Dyssynergia is any disturbance of muscular coordination, resulting in uncoordinated and abrupt movements. This is also an aspect of ataxia. It is typical for dyssynergic patients to split a movement into several smaller movements. Types of dyssynergia include Ramsay Hunt syndrome type 1, bladder sphincter dyssynergia, and anal sphincter dyssynergia.
In fecal incontinence (FI), surgery may be carried out if conservative measures alone are not sufficient to control symptoms. There are many surgical options described for FI, and they can be considered in 4 general groups.










