
David James Mattacks is an English rock and folk drummer, best known for his work with British folk rock band Fairport Convention.

The Zygnematales, also called the Conjugatales, are an order of green algae, comprising several thousand different species in two families. The larger family Zygnemataceae, with well-known genera such as Zygnema and Spirogyra, includes members that grow as unbranched filaments, which grow longer through normal cell division. This group includes the desmids. Most members of both families live in freshwater, and form an important component of the algal scum that grows on or near plants and rocks.

Emerson, Lake & Palmer were an English progressive rock supergroup formed in London in 1970. The band consisted of Keith Emerson (keyboards) of The Nice, Greg Lake of King Crimson, and Carl Palmer of Atomic Rooster. With nine RIAA-certified gold record albums in the US, and an estimated 48 million records sold worldwide, they are one of the most popular and commercially successful progressive rock groups of the 1970s, with a musical sound including adaptations of classical music with jazz and symphonic rock elements, dominated by Emerson's flamboyant use of the Hammond organ, Moog synthesizer, and piano.

Signy Island is a small subantarctic island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was named by the Norwegian whaler Petter Sørlle (1884–1933) after his wife, Signy Therese.

Spyro Gyra is an American jazz fusion band that was formed in Buffalo, New York, in 1974. The band's music combines jazz, R&B, funk, and pop music. The band's name comes from Spirogyra, a genus of green algae which founder Jay Beckenstein had learned about in college.
Twenty or 20 may refer to:

Gregory Stuart Lake was an English musician, singer, and songwriter. He gained prominence as a founding member of the progressive rock bands King Crimson and Emerson, Lake & Palmer (ELP).

Barbara Gaskin is an English singer formerly associated with the UK Canterbury scene.
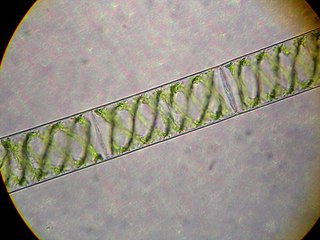
Spirogyra is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. Spirogyra species, of which there are more than 400, are commonly found in freshwater habitats. Spirogyra measures approximately 10 to 100 micrometres in width and may grow to several centimetres in length. It is often observed as green slimy patches on the ground near ponds and other water bodies having stagnant water.

The Zygnemataceae are a family of filamentous or unicellular, uniseriate (unbranched) green algae. The filaments are septated and reproduction is by conjugation; Spirogyra is commonly used in schools to demonstrate this kind of reproduction. The family is notable for its diversely shaped chloroplasts, such as stellate in Zygnema, helical in Spirogyra, and flat in Mougeotia. The Zygnemataceae are cosmopolitan, but though all generally occur in the same types of habitats, Mougeotia, Spirogyra, and Zygnema are by far the most common; in one study across North America, 95% of the Zygnemataceae collected were in these three genera. Classification and identification is primarily by the morphology of the conjugation, which is somewhat rare to find in natural populations of permanent water bodies; when in the vegetative state, the rarer genera resemble the three most common, and are often mistaken for them and catalogued as such. Conjugation can be induced in low-nitrogen culture. While they occupy many habitats, in North America all are found solely in freshwater or subaerial habitats. Species typically exist as floating mats in stagnant water in ditches and ponds, but some also grow in moving water, attaching themselves to a substrate by rhizoid-like projections of the basal cells of the filament. The mat species rise to the surface in early spring, grow rapidly through the summer, disappearing by late summer. Members of the Zygnemataceae, such as Spirogyra, fall prey to parasites, especially chytrids. Most genera previously assigned to Mesotaeniaceae as well as the Desmidiales actually emerged in the Zygnematacae.

Spirogyra were a British folk rock/prog band that released three albums between 1971 and 1973. The group's most well-known members are co-founder, songwriter, and guitarist Martin Cockerham and singer Barbara Gaskin. Their sound has been described as "whimsically English" and their third album, Bells, Boots and Shambles, has come to be regarded as "a lost masterpiece". A later incarnation of the band was formed in the early 2000s, with further studio albums in 2009 and 2011. The band conclusively ceased to exist with Martin Cockerham's 2018 death.

Theodor Wilhelm Engelmann was a German botanist, physiologist, microbiologist, university professor, and musician whose 1882 experiment measured the effects of different colors of light on photosynthetic activity and showed that the conversion of light energy to chemical energy took place in the chloroplast.
Dorothy Ann Collins, was an English folk musician, arranger and composer. She was the older sister of Shirley Collins.

Lake Mohawk is a private reservoir located about 1.5 mi (2.4 km) south of Malvern, Ohio, USA and 2.5 mi (4.0 km) east of Waynesburg, Ohio. It resides in Brown Township and Harrison Township. The lake is relatively small, being a private lake containing 0.7922 sq mi (2.052 km2) of water with a maximum depth of 30 ft (9.1 m). There is only one place to put in boats, however, there are 13 community access docks that can hold boats. The lake is formed by Lake Mohawk Dam across Middle Run, a tributary of Sandy Creek. The lake is fed by a series of springs and rainwater runoff.
Brain was a Hamburg-based record label prominent in the 1970s releasing several important Krautrock records by bands such as Neu!, Cluster and Guru Guru. Many of its more prominent records are currently being reissued on CD by Repertoire Records.
In genetics, a polycentric chromosome is any chromosome featuring multiple centromeres. Polycentric chromosomes are produced by chromosomal aberrations such as deletion, duplication, or translocation. Polycentric chromosomes usually result in the death of the cell because polycentric chromosomes may fail to move to opposite poles of spindle fiber during anaphase. As a result, the chromosome is fragmented, which causes the death of the cell. In some algae, such as Spirogyra, polycentric chromosomes appear normally. They also occur in the sedge, Luzula.











