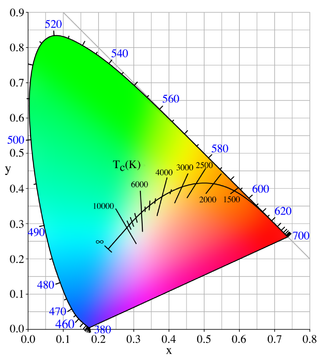
Color temperature is a parameter describing the color of a visible light source by comparing it to the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body. The temperature of the ideal emitter that matches the color most closely is defined as the color temperature of the original visible light source. Color temperature is usually measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale describes only the color of light emitted by a light source, which may actually be at a different temperature.

The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation CMYK refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black).

Cinematography is the art of motion picture photography.

Black-and-white images combine black and white to produce a range of achromatic brightnesses of gray.

A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color. Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale or black-and-white. In physics, monochromatic light refers to electromagnetic radiation that contains a narrow band of wavelengths, which is a distinct concept.

In photography, reversal film or slide film is a type of photographic film that produces a positive image on a transparent base. Instead of negatives and prints, reversal film is processed to produce transparencies or diapositives. Reversal film is produced in various sizes, from 35 mm to roll film to 8×10 inch sheet film.
In Apple's Macintosh operating systems, labels are a type of seven distinct colored and named parameters of metadata that can be attributed to items in the filesystem. Labels were introduced in Macintosh System 7, released in 1991, and they were an improvement of the ability to colorize items in earlier versions of the Finder. Labels remained a feature of the Macintosh operating system through the end of Mac OS 9 in late 2001, but they were omitted from Mac OS X versions 10.0 to 10.2, before being reintroduced in version 10.3 in 2003, though not without criticism. During the short time period when Mac OS X lacked labels, third-party software replicated the feature.

Film colorization is any process that adds color to black-and-white, sepia, or other monochrome moving-picture images. It may be done as a special effect, to "modernize" black-and-white films, or to restore color segregation. The first examples date from the early 20th century, but colorization has become common with the advent of digital image processing.
C-41 is a chromogenic color print film developing process introduced by Kodak in 1972, superseding the C-22 process. C-41, also known as CN-16 by Fuji, CNK-4 by Konica, and AP-70 by AGFA, is the most popular film process in use, with most, if not all photofinishing labs devoting at least one machine to this development process.
Color printing or colour printing is the reproduction of an image or text in color.

In photography, toning is a method of altering the color of black-and-white photographs. In analog photography, it is a chemical process carried out on metal salt-based prints, such as silver prints, iron-based prints, or platinum or palladium prints. This darkroom process cannot be performed with a color photograph. The effects of this process can be emulated with software in digital photography. Sepia is considered a form of black-and-white or monochrome photography.

Color motion picture film refers both to unexposed color photographic film in a format suitable for use in a motion picture camera, and to finished motion picture film, ready for use in a projector, which bears images in color.

The United States Marine Corps (USMC) prescribes several types of military uniform to distinguish its service members from other armed services, depending on the situation.

Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.

Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast, and resolution of the film. Film is typically segmented in frames, that give rise to separate photographs.

Technicolor is a series of color motion picture processes, the first version dating back to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.
Beauty and the Beast is a 1934 Warner Bros. Merrie Melodies animated short film, directed by Friz Freleng. The short was released on April 14, 1934.
In India, there are some regulations and restrictions with regard to establishing industries in certain categories. This is done by making it mandatory to obtain licenses before setting up such an industry.

Traditional clothing is one of the factors that has differentiated this nation from neighboring countries, dating back as far as the Illyrian era.

Reversing type is a method of typographic printing with black or colored inks, in which the entire surface is printed, except for text elements. Reversing is one of the special cases of printing on a color solid, when the color of the solid is black or colored, and the color of the letters is white. This means that the colors of letter background and letters change places. As such, reversing is a meaningfulful way to add emphasis and contrast to the page as well as to develop a visible typographic hierarchy.














