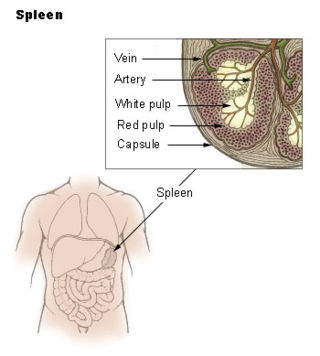
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes from Ancient Greek σπλήν (splḗn).
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of the spleen runs the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, a medical emergency and rapidly fatal disease caused by the inability of the body's immune system to properly fight infection following splenectomy or asplenia.

Hemangiosarcoma is a rapidly growing, highly invasive variety of cancer that occurs almost exclusively in dogs, and only rarely in cats, horses, mice, or humans. It is a sarcoma arising from the lining of blood vessels; that is, blood-filled channels and spaces are commonly observed microscopically. A frequent cause of death is the rupturing of this tumor, causing the patient to rapidly bleed to death.

Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder, wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype leads to a spherical shaping of erythrocytic cellular morphology. As erythrocytes are sphere-shaped (spherocytosis), rather than the normal biconcave disk-shaped, their morphology interferes with these cells' abilities to be flexible during circulation throughout the entirety of the body - arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, and organs. This difference in shape also makes the red blood cells more prone to rupture under osmotic and/or mechanical stress. Cells with these dysfunctional proteins are degraded in the spleen, which leads to a shortage of erythrocytes resulting in hemolytic anemia.
Asplenia refers to the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is used to describe reduced ('hypo-') splenic functioning, but not as severely affected as with asplenism.
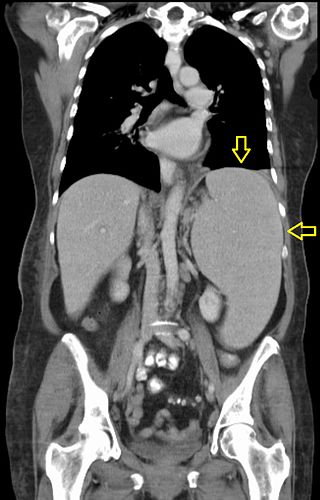
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload, which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension.

Gastric varices are dilated submucosal veins in the lining of the stomach, which can be a life-threatening cause of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. They are most commonly found in patients with portal hypertension, or elevated pressure in the portal vein system, which may be a complication of cirrhosis. Gastric varices may also be found in patients with thrombosis of the splenic vein, into which the short gastric veins that drain the fundus of the stomach flow. The latter may be a complication of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or other abdominal tumours, as well as hepatitis C. Gastric varices and associated bleeding are a potential complication of schistosomiasis resulting from portal hypertension.
An autosplenectomy is a negative outcome of disease and occurs when a disease damages the spleen to such an extent that it becomes shrunken and non-functional. The spleen is an important immunological organ that acts as a filter for red blood cells, triggers phagocytosis of invaders, and mounts an immunological response when necessary. Lack of a spleen, called asplenia, can occur by autosplenectomy or the surgical counterpart, splenectomy. Asplenia can increase susceptibility to infection. Autosplenectomy can occur in cases of sickle-cell disease where the misshapen cells block blood flow to the spleen, causing scarring and eventual atrophy of the organ. Autosplenectomy is a rare condition that is linked to certain diseases but is not a common occurrence. It is also seen in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).

In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery, an older term, is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the spleen.
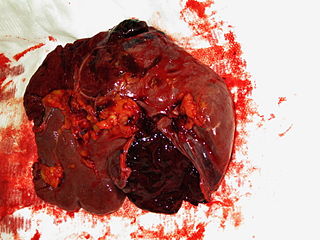
A splenic injury, which includes a ruptured spleen, is any injury to the spleen. The rupture of a normal spleen can be caused by trauma, such as a traffic collision.

Castell's sign is a medical sign assessed to evaluate splenomegaly and typically part of an abdominal examination. It is an alternative physical examination maneuver to percussion over Traube's space.

Splenic infarction is a condition in which blood flow supply to the spleen is compromised, leading to partial or complete infarction in the organ. Splenic infarction occurs when the splenic artery or one of its branches are occluded, for example by a blood clot.
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) is a type of marginal zone lymphoma, a cancer made up of B-cells that replace the normal architecture of the white pulp of the spleen. The neoplastic cells are both small lymphocytes and larger, transformed lymphoblasts, and they invade the mantle zone of splenic follicles and erode the marginal zone, ultimately invading the red pulp of the spleen. Frequently, the bone marrow and splenic hilar lymph nodes are involved along with the peripheral blood. The neoplastic cells circulating in the peripheral blood are termed villous lymphocytes due to their characteristic appearance.
Hemoperitoneum is the presence of blood in the peritoneal cavity. The blood accumulates in the space between the inner lining of the abdominal wall and the internal abdominal organs. Hemoperitoneum is generally classified as a surgical emergency; in most cases, urgent laparotomy is needed to identify and control the source of the bleeding. In selected cases, careful observation may be permissible. The abdominal cavity is highly distensible and may easily hold greater than five liters of blood, or more than the entire circulating blood volume for an average-sized individual. Therefore, large-scale or rapid blood loss into the abdomen will reliably induce hemorrhagic shock and, if untreated, may rapidly lead to death.

A fold of peritoneum, the phrenicocolic ligament is continued from the left colic flexure to the thoracic diaphragm opposite the tenth and eleventh ribs; it passes below and serves to support the spleen, and therefore has received the name of sustentaculum lienis.

An accessory spleen is a small nodule of splenic tissue found apart from the main body of the spleen. Accessory spleens are found in approximately 10 percent of the population and are typically around 1 centimetre in diameter. They may resemble a lymph node or a small spleen. They form either by the result of developmental anomalies or trauma. They are medically significant in that they may result in interpretation errors in diagnostic imaging or continued symptoms after therapeutic splenectomy. Polysplenia is the presence of multiple accessory spleens rather than one normal spleen.

Wandering spleen is a rare medical disease caused by the loss or weakening of the ligaments that help to hold the spleen stationary.

Blunt splenic trauma occurs when a significant impact to the spleen from some outside source damages or ruptures the spleen. Treatment varies depending on severity, but often consists of embolism or splenectomy.

Splenogonadal fusion is a rare congenital malformation that results from an abnormal connection between the primitive spleen and gonad during gestation. A portion of the splenic tissue then descends with the gonad. Splenogonadal fusion has been classified into two types: continuous, where there remains a connection between the main spleen and gonad; and discontinuous, where ectopic splenic tissue is attached to the gonad, but there is no connection to the orthotopic spleen. Patients can also have an accessory spleen. Patients with continuous splenogonadal fusion frequently have additional congenital abnormalities including limb defects, micrognathia, skull anomalies, Spina bifida, cardiac defects, anorectal abnormalities, and most commonly cryptorchidism. Terminal limb defects have been documented in at least 25 cases which makes up a separate diagnosis of splenogonadal fusion limb defect (SGFLD) syndrome.

Spleen pain is a pain felt from the left upper quadrant of the abdomen or epigastrium where the human spleen is located or neighboring.













