Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and set "due west". This occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September.
Summer solstice is the astronomical phenomenon that occurs on the longest day of the year.
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countries, the seasons of the year are determined by the solstices and the equinoxes.
Winter solstice is an astronomical phenomenon which marks the shortest day and the longest night of the year.

Spring, also known as springtime, is one of the four temperate seasons, succeeding winter and preceding summer. There are various technical definitions of spring, but local usage of the term varies according to local climate, cultures and customs. When it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere, it is autumn in the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa. At the spring equinox, days and nights are approximately twelve hours long, with daytime length increasing and nighttime length decreasing as the season progresses until the Summer Solstice in June and December.
Seasonal lag is the phenomenon whereby the date of maximum average air temperature at a geographical location on a planet is delayed until some time after the date of maximum insolation. This also applies to the minimum temperature being delayed until some time after the date of minimum insolation. Cultural seasons are often aligned with annual temperature cycles, especially in the agrarian context. Peak agricultural growth often depends on both insolation levels and soil/air temperature. Rainfall patterns are also tied to temperature cycles, with warmer air able to hold more water vapor than cold air.
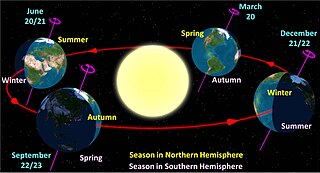
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes 365.256 days, during which time Earth has traveled 940 million km. Ignoring the influence of other Solar System bodies, Earth's orbit is an ellipse with the Earth-Sun barycenter as one focus and a current eccentricity of 0.0167. Since this value is close to zero, the center of the orbit is relatively close to the center of the Sun.

Birkat Hachama refers to a rare Jewish blessing that is recited to the Creator, thanking God for creating the sun. The blessing is recited when the sun completes its cycle every 28 years on a Tuesday at sundown. Jewish tradition says that when the Sun completes this cycle, it has returned to its position when the world was created. Because the blessing needs to be said when the sun is visible, the blessing is postponed to the following day, on Wednesday morning.

The September equinox is the moment when the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator, heading southward. Because of differences between the calendar year and the tropical year, the September equinox may occur anytime from September 21 to 24.

The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the vernal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere and as the autumnal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere.

In many cases astronomical phenomena viewed from the planet Mars are the same or similar to those seen from Earth but sometimes they can be quite different. For example, because the atmosphere of Mars does not contain an ozone layer, it is also possible to make UV observations from the surface of Mars.
Equinox commonly refers to:

The summer solstice, also called the estival solstice or aestival solstice in British English or midsummer, occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere. For that hemisphere, the summer solstice is the day with the longest period of daylight and shortest night of the year, when the Sun is at its highest position in the sky. At either pole there is continuous daylight at the time of its summer solstice. The opposite event is the winter solstice.

Sun path, sometimes also called day arc, refers to the daily and seasonal arc-like path that the Sun appears to follow across the sky as the Earth rotates and orbits the Sun. The Sun's path affects the length of daytime experienced and amount of daylight received along a certain latitude during a given season.

The June solstice is the solstice on Earth that occurs annually between 20 and 22 June according to the Gregorian calendar. In the Northern Hemisphere, the June solstice is the summer solstice, while in the Southern Hemisphere it is the winter solstice. It is also known as the northern solstice.

The December solstice, also known as the southern solstice, is the solstice that occurs each December – typically on 21 December, but may vary by one day in either direction according to the Gregorian calendar. In the Northern Hemisphere, the December solstice is the winter solstice, whilst in the Southern Hemisphere it is the summer solstice.
Vernal is a city in Uintah County, Utah, United States.

A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons varies.
Autumnal equinox or variations, may refer to:
Persian astronomy or Iranian astronomy refers to the astronomy in ancient Persian history.