
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.

Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this later date being the most commonly held. In the 12th century it developed into the Gothic style, marked by pointed arches. Examples of Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. The Romanesque style in England is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture.

An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today.

An ogive is the roundly tapered end of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional object. Ogive curves and surfaces are used in engineering, architecture and woodworking.

The flying buttress is a specific form of buttress composed of an arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a pier of great mass, in order to convey to the ground the lateral forces that push a wall outwards, which are forces that arise from vaulted ceilings of stone and from wind-loading on roofs.

A lunette is a half-moon shaped architectural space, variously filled with sculpture, painted, glazed, filled with recessed masonry, or void. A lunette is formed when a horizontal cornice transects a round-headed arch at the level of the imposts, where the arch springs. If a door is set within a round-headed arch, the space within the arch above the door, masonry or glass, is a lunette. If the door is a major access, and the lunette above is massive and deeply set, it may be called a tympanum.

The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monasteries, abbeys, churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style.
The Master of Architecture (M.Arch.) is a professional degree in architecture, qualifying the graduate to move through the various stages of professional accreditation that result in receiving a license.
Springer or springers may refer to:

Tracery is an architectural device by which windows are divided into sections of various proportions by stone bars or ribs of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support the glass in a window. The term probably derives from the tracing floors on which the complex patterns of windows were laid out in late Gothic architecture. Tracery could also be found on the interior of buildings and the exterior.
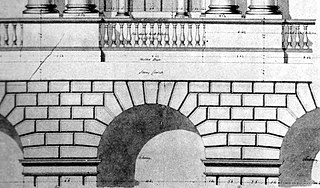
A voussoir is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault.
This page is a glossary of architecture.
The Bachelor of Architecture (B.Arch.) is a bachelor's degree designed to satisfy the academic requirement of practising architecture.

In Gothic architecture, a lierne is a tertiary rib connecting one rib to another, as opposed to connecting to a springer, or to the central boss. The resulting construction is called a lierne vault or stellar vault. The term lierne comes from the French lier.

In architecture, a vault is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. The simplest kind of vault is the barrel vault, which is generally semicircular in shape. The barrel vault is a continuous arch, the length being greater than its diameter. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed. With a barrel vault, the centering can then be shifted on to support the next rings.

A four-centered arch is a low, wide type of arch with a pointed apex. Its structure is achieved by drafting two arcs which rise steeply from each springing point on a small radius, and then turning into two arches with a wide radius and much lower springing point. It is a pointed sub-type of the general flattened depressed arch. Two of the most notable types are known as the Persian arch, which is moderately "depressed", and the Tudor arch, which is much flatter.

English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed arches, rib vaults, buttresses, and extensive use of stained glass. Combined, these features allowed the creation of buildings of unprecedented height and grandeur, filled with light from large stained glass windows. Important examples include Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral. The Gothic style endured in England much longer than in Continental Europe.

In architecture, an impost or impost block is a projecting block resting on top of a column or embedded in a wall, serving as the base for the springer or lowest voussoir of an arch.

A segmental arch is a type of arch with a circular arc of less than 180 degrees. It is sometimes also called a scheme arch.

The pointed arch is an arch with a pointed crown, whose two curving sides meet at a relatively sharp angle at the top of the arch. This architectural element was particularly important in Gothic architecture. It first appeared in Indian architecture and Islamic architecture as a way of making more decorative windows and doorways, but in the 12th century it began to be used in France and England as an important structural element, in combination with other elements, such as the rib vault and later the flying buttress. These allowed the construction of cathedrals, palaces and other buildings with dramatically greater height and larger windows which filled them with light.
















