Professional certification, trade certification, or professional designation, often called simply certification or qualification, is a designation earned by a person to assure qualification to perform a job or task. Not all certifications that use post-nominal letters are an acknowledgement of educational achievement, or an agency appointed to safeguard the public interest.
An accountant is a practitioner of accounting or accountancy. Accountants who have demonstrated competency through their professional associations' certification exams are certified to use titles such as Chartered Accountant, Chartered Certified Accountant or Certified Public Accountant, or Registered Public Accountant. Such professionals are granted certain responsibilities by statute, such as the ability to certify an organization's financial statements, and may be held liable for professional misconduct. Non-qualified accountants may be employed by a qualified accountant, or may work independently without statutory privileges and obligations.

Certified Management Accountant (CMA) is a professional certification credential in the management accounting and financial management fields. The certification signifies that the person possesses knowledge in the areas of financial planning, analysis, control, decision support, and professional ethics. There are many professional bodies globally that have management accounting professional qualifications. The main bodies that offer the CMA certification are:
- Institute of Cost Accountants of India;
- Institute of Management Accountants USA;
- Institute of Certified Management Accountants (Australia);
- Certified Management Accountants of Canada.
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process through which an engineer becomes licensed to practice engineering and to provide professional services and products to the public.

An engineering technologist is a professional trained in certain aspects of development and implementation of a respective area of technology. An education in engineering technology concentrates more on application and less on theory than does an engineering education. Engineering technologists often assist engineers; but after years of experience, they can also become engineers. Like engineers, areas where engineering technologists can work include product design, fabrication, and testing. Engineering technologists sometimes rise to senior management positions in industry or become entrepreneurs.

The British Computer Society (BCS), branded BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, since 2009, is a professional body and a learned society that represents those working in information technology (IT), computing, software engineering, computer engineering and computer science, both in the United Kingdom and internationally. Founded in 1957, BCS has played an important role in educating and nurturing IT professionals, computer scientists, software engineers, computer engineers, upholding the profession, accrediting Chartered IT Professional (CITP) and Chartered Engineer (CEng) status, and creating a global community active in promoting and furthering the field and practice of computing.
The Sydney Accord is an international mutual recognition agreement for qualifications in the fields of engineering technology.
A national qualifications framework (NQF) is a formal system describing qualifications. 47 countries participating in the Bologna Process are committed to producing a national qualifications framework. Other countries not part of this process also have national qualifications frameworks.
Engineers Canada is the national organization of the 12 provincial and territorial associations that regulate the practice of engineering in Canada. Engineers Canada serves these associations, which are its sole members, by delivering national programs for standards of engineering education, professional qualifications and professional practice.

Certification is part of testing, inspection and certification and the provision by an independent body of written assurance that the product, service or system in question meets specific requirements. It is the formal attestation or confirmation of certain characteristics of an object, person, or organization. This confirmation is often, but not always, provided by some form of external review, education, assessment, or audit. Accreditation is a specific organization's process of certification. According to the U.S. National Council on Measurement in Education, a certification test is a credentialing test used to determine whether individuals are knowledgeable enough in a given occupational area to be labeled "competent to practice" in that area.

The National Institute of Business Management also known as NIBM, is a public business school based in Colombo, Sri Lanka.
The International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) is a software testing certification board that operates internationally. Founded in Edinburgh in November 2002, the ISTQB is a non-profit association legally registered in Belgium.
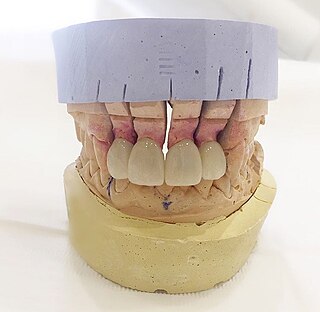
Dental laboratories manufacture or customize a variety of products to assist in the provision of oral health care by a licensed dentist. These products include crowns, bridges, dentures and other dental products. Dental lab technicians follow a prescription from a licensed dentist when manufacturing these items, which include prosthetic devices and therapeutic devices. The FDA regulates these products as medical devices and they are therefore subject to FDA's good manufacturing practice ("GMP") and quality system ("QS") requirements. In most cases, however, they are exempt from manufacturer registration requirements. Some of the most common restorations manufactured include crowns, bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental implants is one of the most advanced dental technologies in the field of dentistry.
Regulation of acupuncture is done by governmental bodies to ensure safe practice.
A software quality assurance (QA) analyst, also referred to as a software quality analyst or simply a quality assurance (QA) analyst, is an individual who is responsible for applying the principles and practices of software quality assurance throughout the software development life cycle.
Rex Black is a software engineer, entrepreneur and an author in the field of software testing. Black graduated from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) in 1990 with a bachelors of science in computer science and engineering. In 1983, Black started work in the software engineering field and has spent more than 20 years in software testing.
Professional requirements for architects vary from place to place, but usually consist of three elements: a university degree or advanced education, a period of internship or training in an office, and examination for registration with a jurisdiction.
The Construction Management Association of America (CMAA) is a non-profit and non-governmental, professional association serving the construction management industry. The Association was formed in 1982. Current membership is more than 14,000, including individual CM/PM practitioners, corporate members, and construction owners in both public and private sectors, along with academic and associate members. CMAA has 29 regional chapters.

Better Software magazine was a quarterly digital magazine published by TechWell Corporation. It covered topics of interest to software testers, developers, project managers, and business analysts. Better Software was originally published in 1996 as Software QA magazine, focusing primarily on software QA and testing. Software QA was renamed Better Software magazine in 2004.
A software testing certification board is an organization that provides professional certification for software testing and software quality assurance.







