Related Research Articles
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used in Internet telephony, in private IP telephone systems, as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE).
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.
Telnet is a client/server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. Telnet consists of two components: (1) the protocol itself which specifies how two parties are to communicate and (2) the software application that provides the service. User data is interspersed in-band with Telnet control information in an 8-bit byte oriented data connection over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Telnet was developed in 1969 beginning with RFC 15, extended in RFC 855, and standardized as Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Standard STD 8, one of the first Internet standards. Telnet transmits all information including usernames and passwords in plaintext so it is not recommended for security-sensitive applications such as remote management of routers. Telnet's use for this purpose has waned significantly in favor of SSH. Some extensions to Telnet which would provide encryption have been proposed.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behaviour. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more.
In computing, Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a secure network protocol suite that authenticates and encrypts packets of data to provide secure encrypted communication between two computers over an Internet Protocol network. It is used in virtual private networks (VPNs).

An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent (MUA) or mail user agent is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a plain-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
A virtual private network (VPN) is a mechanism for creating a secure connection between a computing device and a computer network, or between two networks, using an insecure communication medium such as the public Internet.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network. The protocol is widely used in applications such as email, instant messaging, and voice over IP, but its use in securing HTTPS remains the most publicly visible.

Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop-sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It transmits the keyboard and mouse input from one computer to another, relaying the graphical-screen updates, over a network.
In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any reliable data stream. It was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0 to provide secure file transfer capabilities, and is seen as a replacement of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) due to superior security. The IETF Internet Draft states that, even though this protocol is described in the context of the SSH-2 protocol, it could be used in a number of different applications, such as secure file transfer over Transport Layer Security (TLS) and transfer of management information in VPN applications.
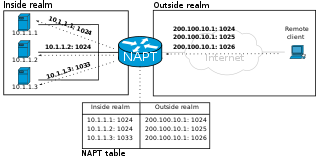
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
OpenVPN is a virtual private network (VPN) system that implements techniques to create secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities. It implements both client and server applications.
In computer networks, a tunneling protocol is a communication protocol which allows for the movement of data from one network to another. It involves allowing private network communications to be sent across a public network through a process called encapsulation.
NX technology, commonly known as NX or NoMachine, is a remote access and remote control computer software, allowing remote desktop access and maintenance of computers. It is developed by the Luxembourg-based company NoMachine S.à r.l.. NoMachine is proprietary software and is free-of-charge for non-commercial use.
The National Information Standards Organization is a United States non-profit standards organization that develops, maintains and publishes technical standards related to publishing, bibliographic and library applications. It was founded in 1939 as the Z39 Committee, incorporated as a not-for-profit education association in 1983, and assumed its current name in 1984.
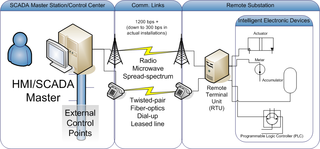
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
NISO Circulation Interchange Protocol (NCIP) is a protocol that is limited to the exchange of messages between and among computer-based applications to enable them to perform functions necessary to lend and borrow items, to provide controlled access to electronic resources, and to facilitate cooperative management of these functions.

The Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP) is an extensible communication protocol that defines message formats for the manipulation of cryptographic keys on a key management server. This facilitates data encryption by simplifying encryption key management. Keys may be created on a server and then retrieved, possibly wrapped by other keys. Both symmetric and asymmetric keys are supported, including the ability to sign certificates. KMIP also allows for clients to ask a server to encrypt or decrypt data, without needing direct access to the key.

OpenSSH is a suite of secure networking utilities based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, which provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client–server architecture.
References
- ↑ Tedd, L. A. (2007). "Library management systems". In Bowman, J. H. (ed.). British librarianship and information work 2001-2005. Ashgate Publishing Group. pp. 431–453. hdl:2160/679. ISBN 978-0-7546-4778-2.
- ↑ "NISO Circulation Interchange Protocol Implementation Group". What is NCIP?. NCIP Implementation Group. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ↑ "3M will Lead Open Development on next release of Standard Interchange Protocol". Press release. 3M. Archived from the original on 15 October 2010. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- ↑ "3M Standard Interchange Protocol". 3M. April 11, 2006. p. 15. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- ↑ Vinod, Chachra (August 2003). "Experiences in Implementing the VTLS RFID Solution in a Multi-vendor Environment" (PDF). World Library and Information Congress: 69th IFLA General Conference.
- ↑ "3M Standard Interchange Protocol". 3M. April 11, 2006. pp. 3–13. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- ↑ "Encrypting SIP2 Traffic with Koha". jsn4lib. 2012-02-06. Retrieved 2018-10-30.
- ↑ Scott, Dan (2010-04-16). "Setting up secure self-check connections using SIP tunneled through SSH". Coffee|Code: Dan Scott's blog. Retrieved 2018-10-30.