
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. As an aspect of strategic management, M&A can allow enterprises to grow or downsize, and change the nature of their business or competitive position.
A shareholder rights plan, colloquially known as a "poison pill", is a type of defensive tactic used by a corporation's board of directors against a takeover.
In business, a takeover is the purchase of one company by another. In the UK, the term refers to the acquisition of a public company whose shares are listed on a stock exchange, in contrast to the acquisition of a private company.

A leveraged buyout (LBO) is one company's acquisition of another company using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition. The assets of the company being acquired are often used as collateral for the loans, along with the assets of the acquiring company. The use of debt, which normally has a lower cost of capital than equity, serves to reduce the overall cost of financing the acquisition. This is done at the risk of magnified cash flow losses should the acquisition perform poorly after the buyout.
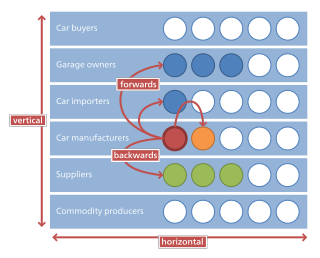
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same level of the value chain, in the same industry. A company may do this via internal expansion, acquisition or merger.

The Financial Times Stock Exchange 100 Index, also called the FTSE 100 Index, FTSE 100, FTSE, or, informally, the "Footsie", is a stock market index of 100 of the most highly capitalised blue chip companies listed on the London Stock Exchange.

SABMiller plc was a South African multinational brewing and beverage company headquartered in Woking, England on the outskirts of London until 10 October 2016 when it was acquired by AB InBev. It was the world's second-largest brewer measured by revenues and was also a major bottler of Coca-Cola. Its brands included Foster's, Miller, and Pilsner Urquell. It operated in 80 countries worldwide and in 2009 sold around 21 billion litres of beverages. Since 10 October 2016, SABMiller is a business division of AB InBev, a Belgian multinational corporation with headquarters in Leuven.
Greenmail or greenmailing is the action of purchasing enough shares in a firm to challenge a firm's leadership with the threat of a hostile takeover to force the target company to buy the purchased shares back at a premium in order to prevent the potential takeover.
In corporate finance, a tender offer is a type of public takeover bid. The tender offer is a public, open offer or invitation by a prospective acquirer to all stockholders of a publicly traded corporation to tender their stock for sale at a specified price during a specified time, subject to the tendering of a minimum and maximum number of shares. In a tender offer, the bidder contacts shareholders directly; the directors of the company may or may not have endorsed the tender offer proposal.
In business, a white knight is a friendly investor that acquires a corporation at a fair consideration with support from the corporation's board of directors and management. This may be during a period while it is facing a hostile acquisition from another potential acquirer or it is facing bankruptcy. White knights are preferred by the board of directors and/or management as in most cases as they do not replace the current board or management with a new board, whereas, in most cases, a black knight will seek to replace the current board of directors and/or management with its new board reflective of its net interest in the corporation's equity.
Risk arbitrage, also known as merger arbitrage, is an investment strategy that speculates on the successful completion of mergers and acquisitions. An investor that employs this strategy is known as an arbitrageur. Risk arbitrage is a type of event-driven investing in that it attempts to exploit pricing inefficiencies caused by a corporate event.
Lock-up provision is a term used in corporate finance which refers to the option granted by a seller to a buyer to purchase a target company’s stock as a prelude to a takeover. The major or controlling shareholder is then effectively "locked-up" and is not free to sell the stock to a party other than the designated party.

Deutsche Börse AG, or the Deutsche Börse Group, is a German multinational that offers a marketplace for organizing the trading of shares and other securities. It is also a transaction services provider, giving companies and investors access to global capital markets. It is a joint stock company and was founded in 1992, with headquarters in Frankfurt. On 1 October 2014, Deutsche Börse AG became the 14th announced member of the United Nations Sustainable Stock Exchanges initiative.

First Union Corporation was a bank holding company that provided commercial and retail banking services in eleven states in the eastern U.S. First Union also provided various other financial services, including mortgage banking, credit card, investment banking, investment advisory, home equity lending, asset-based lending, leasing, insurance, international and securities brokerage services and private equity through First Union Capital Partners, and through other subsidiaries.
A squeeze-out or squeezeout, sometimes synonymous with freeze-out, is the compulsory sale of the shares of minority shareholders of a joint-stock company for which they receive a fair cash compensation.
Mead Johnson & Company, LLC is an American company that is a leading manufacturer of infant formula, both domestically and globally, with its flagship product Enfamil. It operates as an independent subsidiary of Reckitt.

London Stock Exchange Group plc is a United Kingdom-based stock exchange and financial information company headquartered in the City of London, England. It owns the London Stock Exchange, Refinitiv, LSEG Technology, FTSE Russell, and majority stakes in LCH and Tradeweb.
The following is a glossary which defines terms used in mergers, acquisitions, and takeovers of companies, whether private or public.
Allergan plc is an American, Irish-domiciled pharmaceutical company that acquires, develops, manufactures and markets brand name drugs and medical devices in the areas of medical aesthetics, eye care, central nervous system, and gastroenterology. The company is the maker of Botox.







