Related Research Articles

Geophysics is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists, who usually study geophysics, physics, or one of the Earth sciences at the graduate level, complete investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term geophysics classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields ; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.
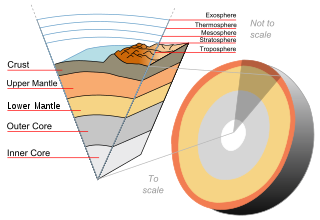
Earth's outer core is a fluid layer about 2,260 km (1,400 mi) thick, composed of mostly iron and nickel that lies above Earth's solid inner core and below its mantle. The outer core begins approximately 2,889 km (1,795 mi) beneath Earth's surface at the core-mantle boundary and ends 5,150 km (3,200 mi) beneath Earth's surface at the inner core boundary.

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo.

In physics, the dynamo theory proposes a mechanism by which a celestial body such as Earth or a star generates a magnetic field. The dynamo theory describes the process through which a rotating, convecting, and electrically conducting fluid can maintain a magnetic field over astronomical time scales. A dynamo is thought to be the source of the Earth's magnetic field and the magnetic fields of Mercury and the Jovian planets.

The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, atmospheric, ocean, hydrologic, space, and planetary scientists and enthusiasts that according to their website includes 130,000 people. AGU's activities are focused on the organization and dissemination of scientific information in the interdisciplinary and international fields within the Earth and space sciences. The geophysical sciences involve four fundamental areas: atmospheric and ocean sciences; solid-Earth sciences; hydrologic sciences; and space sciences. The organization's headquarters is located on Florida Avenue in Washington, D.C.
Allan Verne Cox was an American geophysicist. His work on dating geomagnetic reversals, with Richard Doell and Brent Dalrymple, made a major contribution to the theory of plate tectonics. Allan Cox won numerous awards, including the prestigious Vetlesen Prize, and was the president of the American Geophysical Union. He was the author of over a hundred scientific papers, and the author or editor of two books on plate tectonics. On January 27, 1987, Cox died in an apparent suicide.

Walter Maurice Elsasser was a German-born American physicist, a developer of the presently accepted dynamo theory as an explanation of the Earth's magnetism. He proposed that this magnetic field resulted from electric currents induced in the fluid outer core of the Earth. He revealed the history of the Earth's magnetic field by the study of the magnetic orientation of minerals in rocks. He was also the first to suggest that the wave-like nature of matter might be investigated by electron scattering experiments using crystalline solids.
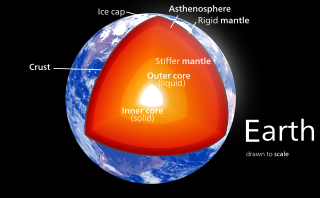
Earth's inner core is the innermost geologic layer of the planet Earth. It is primarily a solid ball with a radius of about 1,220 km (760 mi), which is about 20% of Earth radius or 70% of the Moon's radius.

The Journal of Geophysical Research is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the understanding of the Earth, Sun, and Solar System. It has seven sections: A, B, C (Oceans), D (Atmospheres), E (Planets), F, and G (Biogeosciences). All current and back issues are available online for subscribers.
The historical development of geophysics has been motivated by two factors. One of these is the research curiosity of humankind related to planet Earth and its several components, its events and its problems. The second is economical usage of Earth's resources and Earth-related hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, tides, and floods.

John Stewart Turner, FAA, FRS was an Australian geophysicist.
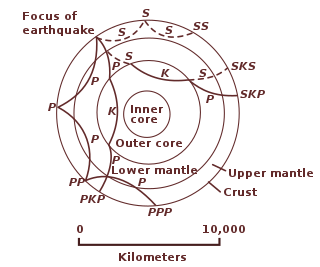
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geophysics:

Kathryn Anne "Kathy" Whaler OBE FRSE FAGU is a professor of geophysics at the University of Edinburgh School of GeoSciences, in the Research Institute of Earth and Planetary Science and is a member of the Solid Earth Geophysics and Natural Hazards Research Group.

In geology, numerical modeling is a widely applied technique to tackle complex geological problems by computational simulation of geological scenarios.
David Gubbins is a British former geophysicist concerned with the mechanism of the Earth's magnetic field and theoretical geophysics. He is Emeritus Professor of Earth Sciences at Leeds University.

Inner core super-rotation is the eastward rotation of the inner core of Earth relative to its mantle, for a net rotation rate that is usually faster than Earth as a whole. A 1995 model of Earth's dynamo predicted super-rotations of up to 3 degrees per year; the following year, this prediction was supported by observed discrepancies in the time that p-waves take to travel through the inner and outer core.
Frank Donald Stacey is an English-born Australian geophysicist, known for his research on rock magnetism and application of thermodynamics to understanding the Earth's core and mantle.
Subir Kumar Banerjee is an Indian-American geophysicist, known for research on rock magnetism, palaeomagnetism, and environmental magnetism.
Paul Harry Roberts FRS was a British physicist who specialized in theoretical physics, particularly in the area of astrophysics and magnetohydrodynamics.
References
- ↑ "People A-B". Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics. University of California Los Angeles. Retrieved 13 March 2013.
- ↑ Roberts, Paul (2007). "How MHD Transformed the Theory of Geomagnetism". In Molokov, Sergei S.; Moreau, R.; Moffatt, H.K. (eds.). Magnetohydrodynamics historical evolution and trends (Online-Ausg. ed.). Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 3–26. ISBN 9781402048333.
- ↑ Roberts, Paul H.; Braginsky, Stanislav I. (1993). "Braginsky receives Fleming Medal". Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union. 74 (27): 300. doi:10.1029/93EO00447.
- ↑ "1992 John Adam Fleming Medal Winner: Stanislav I. Braginsky". American Geophysical Union. Retrieved 13 March 2013.