History
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| Type | Private |
|---|---|
| Industry | Engineering |
| Founded | March 2001 |
| Headquarters | , USA |
Key people | Dr. Mark Holtzapple, President Dr. Kyle Ross, chemical engineer Andrew Rabroker, mechanical engineer Tom Beck, mechanical engineer |
| Products | Compressors Expanders Engines (under development) Air Conditioners (under development) Integrated Motors/Generators (under development) |
| Website | www.starrotor.com |
StarRotor Corporation is a startup company founded to commercialize technology from Texas A&M University. It was incorporated in March 2001 by Dr. Mark Holtzapple and Andrew Rabroker. The company gets its name and logo design from the gerotor the company designed to compress and expand gasses.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2011) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2011) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2011) |
The StarRotor engine is being designed to use the Brayton cycle instead of the Otto cycle found in almost all gasoline automobiles. It is predicted to be efficient (45%-60% efficiency compared to 15% to 20% efficiency of other engines) and to produce fewer pollutants than traditional engines. Like turbine engines, the StarRotor engine will be capable of running on many types of fuel, including but not limited to gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel, alcohol, methane, hydrogen, and vegetable oil.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2011) |

An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.

The Tesla turbine is a bladeless centripetal flow turbine patented by Nikola Tesla on October 21,1913. It was his 100th patent.
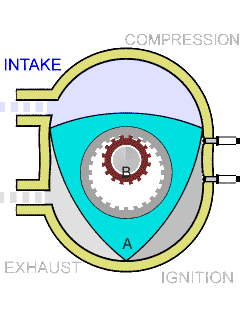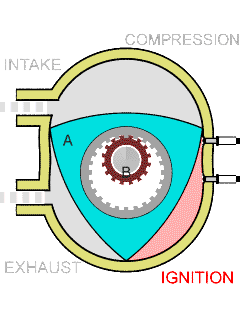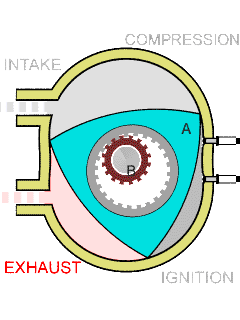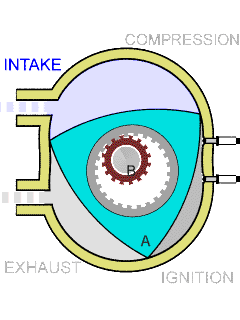
The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was invented and proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, and the commercially feasible engine designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor spins inside a figure-eight-like epitrochoidal housing, around a fixed toothed gearing. The midpoint of the rotor moves in a circle around the output shaft, spinning the shaft via a cam.
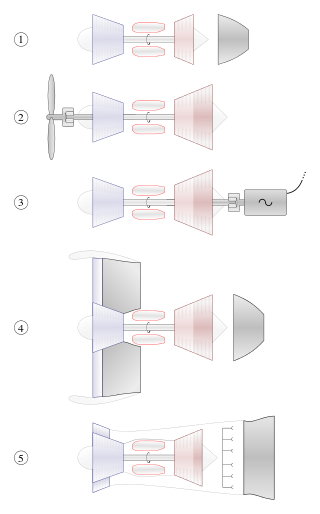
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:

A pulsejet engine is a type of jet engine in which combustion occurs in pulses. A pulsejet engine can be made with few or no moving parts, and is capable of running statically. The best known example may be the Argus As 109-014 used to propel Nazi Germany's V-1 flying bomb.

The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a combination of the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet, and a reference to the additional fan stage added. It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to force air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust.

An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.

A petrol engine is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends.

A four-strokeengine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed:

The Roots-type blower is a positive displacement lobe pump which operates by pumping a fluid with a pair of meshing lobes resembling a set of stretched gears. Fluid is trapped in pockets surrounding the lobes and carried from the intake side to the exhaust. The most common application of the Roots-type blower has been the induction device on two-stroke diesel engines, such as those produced by Detroit Diesel and Electro-Motive Diesel. Roots-type blowers are also used to supercharge four-stroke Otto cycle engines, with the blower being driven from the engine's crankshaft via a toothed or V-belt, a roller chain or a gear train.

The Mazda Wankel engines are a family of Wankel rotary combustion car engines produced by Mazda.

E85 is an abbreviation typically referring to an ethanol fuel blend of 85% ethanol fuel and 15% gasoline or other hydrocarbon by volume.
Gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE) or gasoline-equivalent gallon (GEG) is the amount of an alternative fuel it takes to equal the energy content of one liquid gallon of gasoline. GGE allows consumers to compare the energy content of competing fuels against a commonly known fuel, namely gasoline.

The fuel economy of an automobile relates to the distance traveled by a vehicle and the amount of fuel consumed. Consumption can be expressed in terms of the volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance traveled per unit volume of fuel consumed. Since fuel consumption of vehicles is a significant factor in air pollution, and since the importation of motor fuel can be a large part of a nation's foreign trade, many countries impose requirements for fuel economy. Different methods are used to approximate the actual performance of the vehicle. The energy in fuel is required to overcome various losses encountered while propelling the vehicle, and in providing power to vehicle systems such as ignition or air conditioning. Various strategies can be employed to reduce losses at each of the conversions between the chemical energy in the fuel and the kinetic energy of the vehicle. Driver behavior can affect fuel economy; maneuvers such as sudden acceleration and heavy braking waste energy.
Engine efficiency of thermal engines is the relationship between the total energy contained in the fuel, and the amount of energy used to perform useful work. There are two classifications of thermal engines-

LiquidPiston is the developer and manufacturer of a pistonless rotary engine called the X-engine, located in Bloomfield, Connecticut.
Mark Holtzapple is a chemical engineering professor at Texas A&M University. His research focuses on technologies that improve sustainability.
Brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is a measure of the fuel efficiency of any prime mover that burns fuel and produces rotational, or shaft power. It is typically used for comparing the efficiency of internal combustion engines with a shaft output.
The MidWest AE series are lightweight, liquid-cooled, single- and twin-rotor Wankel engines, with dual ignition, designed for light aircraft. They were produced by Mid-West Engines Ltd. at Staverton Airport, Gloucestershire, UK.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.