Related Research Articles

The Armstrong Whitworth F.K.3 was a British two-seat general-purpose biplane built by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft during the First World War. By the end of the war it was considered obsolete for combat.

The Nord Aviation 3202 was a 1950s French military trainer aircraft designed and built by Nord Aviation to meet a French Army requirement for a two-seat basic trainer, as a replacement for the biplane Stampe SV.4. Altogether, 101 examples were built, with the first flying on 17 April 1957.

The BAT F.K.24 Baboon was a British two-seat training biplane produced by British Aerial Transport Company Limited of London during World War I.
The Blériot-SPAD S.81 was a French fighter aircraft developed in 1923 to a requirement by the French Air Force. It was flown competitively against the Dewoitine D.1 and was selected over that aircraft due to the Dewoitine's more radical design, leading to an order for 80 aircraft. The S.81 was a single-bay biplane of conventional configuration with I-shaped interplane struts and lacking Herbemont's usual swept upper wing. It featured a wooden fuselage of monocoque construction and metal wings skinned in fabric. Production versions differed from the prototypes in having a lengthened fuselage and larger tail fin.

The CAMS 46 was a flying boat trainer aircraft built in France in the mid-1920s, essentially an updated version of the CAMS 30 that had flown in 1922. While retaining that aircraft's basic form, CAMS offered the French Navy two new versions with aerodynamic refinements over the earlier aircraft: the CAMS 46 E primary trainer, and the CAMS 46 ET intermediate trainer. Only the latter was selected for production and was built in quantity to supply one escadrille at the Naval training station at Hourtin.

The Breguet 730 was a French flying boat of the 1930s. Built to meet the requirements of the French Navy, it was ordered into production but no aircraft were delivered before France surrendered to Germany in June 1940. Four remaining incomplete airframes were completed after the end of World War II, serving with the French Navy until 1954.
The Nieuport-Delage NiD 640 was a French four-passenger transport monoplane built by Nieuport-Delage.

The Potez 32 and its military version the Potez 33 was a single-engine French monoplane transport built by Potez and based on the Potez 29 biplane.

The Nord 1221 Norélan was a 1940s three-seat training monoplane designed and built in France by Nord Aviation.

The Morane-Saulnier MS.138 was a military trainer aircraft produced in France in the late 1920s,

The Jurca MJ-2 Tempete (French:Tempest) is a single-seat sport aircraft designed in France by Marcel Jurca in the mid-1950s and marketed for amateur construction from plans.
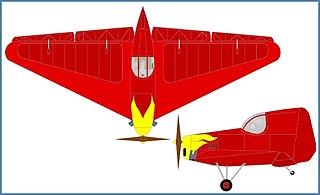
The BICh-20 Pionyer was a tail-less research aircraft designed and built in the USSR from 1937.

The Starck AS-70 Jac is a French-built single-seat light aircraft of the mid-1940s.
The FVA-18 Primitivkrähe was a 1960s German lightweight training aircraft designed and built at Flugwissenschaftliche Vereinigung Aachen.

The Eastman E-2 Sea Rover, also called the Beasley-Eastman E-2 Sea Rover, was a light seaplane built in the late 1920s for business and shuttle use.

The Elias EC-1 Aircoupe was an American two-seat parasol wing monoplane designed and built by Elias of Buffalo, New York.
The Ganagobie is a single place, parasol wing homebuilt aircraft that was built by Willam and James Lobet, first flying in 1953.

The Caudron C.161 was a lightweight French two-seat biplane designed by Caudron for sport or flight training use. A conventional biplane with a square fuselage powered by a 65 hp (48 kW) Salmson radial engine. It had two cockpits in tandem with dual controls in both, when not used as a trainer the controls could be removed from the rear cockpit. A variant, the C.168, with a more powerful 70 hp (52 kW) Anzani radial engine was also available.

The Starck AS-80 Holiday is a conventional two-seat, single-engine high-wing monoplane designed and built in France around 1950. It was sold in kit form but only a few were completed.

The Buscaylet-de Monge 5/2 was a 1920s French single-seat, parasol-wing fighter prototype designed by Louis de Monge for the Buscaylet et Cie company.
References
- 1 2 Gaillard, Pierre (1990). Les avions français de 1944 à 1964 (in French). E.P.A. ISBN 2851203509.
- ↑ Taylor, John W.R., ed. (1982). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1982–83. London: Jane's Publishing Company. p. 510. ISBN 978-0-7106-0748-5.
- ↑ Parmentier, Bruno (2017-12-08). "Starck AS.90 'New Look'". Aviafrance (in French). Retrieved 9 March 2019.