
Diego Garcia is an atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of 60 small islands comprising the Chagos Archipelago. It was settled by the French in the 1790s and was transferred to British rule after the Napoleonic Wars. It was one of the "Dependencies" of the British Colony of Mauritius until it was detached for inclusion in the newly created British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965.

Ocean City, Maryland, officially the Town of Ocean City, is an Atlantic resort town in Worcester County, Maryland. Ocean City is widely known in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is a frequent destination for vacationers in that area. The population was 7,102 at the 2010 U.S. Census, although during summer weekends the city hosts between 320,000 and 345,000 vacationers, and up to 8 million visitors annually. During the summer, Ocean City becomes the second most populated municipality in Maryland, after Baltimore. It is part of the Salisbury metropolitan area.

The instrumental temperature record provides the temperature of Earth's climate system from the historical network of in situ measurements of surface air temperatures and ocean surface temperatures. Data are collected at thousands of meteorological stations, buoys and ships around the globe. The longest-running temperature record is the Central England temperature data series, which starts in 1659. The longest-running quasi-global record starts in 1850. In recent decades more extensive sampling of ocean temperatures at various depths have begun allowing estimates of ocean heat content but these do not form part of the global surface temperature datasets.

Tidal power or tidal energy is a form of hydropower that converts the energy obtained from tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity.
Texas A&M College of Geosciences is a college of Texas A&M University located in College Station, Texas. The college has six academic departments and programs, including Atmospheric Sciences, Geography, Geology & Geophysics, Oceanography, Environmental Programs in Geosciences, and the Water Management & Hydrological Science (WMHS) Program. In addition, the College hosts three Research Centers and Institutes: https://web.archive.org/web/20080522012111/http://www-gerg.tamu.edu/ Geochemical & Environmental Research Group (GERG), Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP), and Texas Sea Grant College Program.

The K Ingleside is a Muni Metro line in San Francisco, California, mainly serving the West Portal and Ingleside neighborhoods. Opened on February 3, 1918, it was the first line to use the Twin Peaks Tunnel.
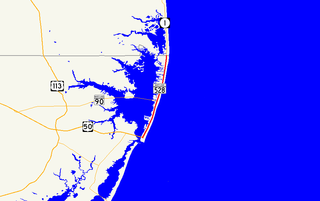
Maryland Route 528 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as Coastal Highway, the state highway runs 9.04 miles (14.55 km) from the southern terminus of its companion route, unsigned Maryland Route 378, in downtown Ocean City north to the Delaware state line at the northern edge of the resort town, where the highway continues as Delaware Route 1. MD 528 and MD 378 are the primary north–south streets of Ocean City, where they provide access to countless hotels, condos, restaurants, shops, and other businesses catering to tourists. These highways experience heavy seasonal traffic and provide access to hurricane evacuation routes, which include U.S. Route 50, MD 90, and DE 54. Both Baltimore Avenue and Philadelphia Avenue date back to the founding of Ocean City in the late 19th century. MD 378 was assigned to Baltimore Avenue in 1927 and MD 528 was assigned to Philadelphia Avenue in 1933. MD 528 was extended north of 15th Street to the Delaware state line in 1939. Both highways were rebuilt and widened in the 1950s. MD 528 was expanded to a six-lane divided highway north of the one-way pair in the late 1980s.

The Marconi National Historic Site and the Marconi Wireless Station National Historic Site are two National Historic Sites of Canada located on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. Both sites commemorate the efforts of Guglielmo Marconi to transmit transatlantic radio signals between North America and Europe in the first decade of the 20th century. The two sites are located within approximately 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) of one another, and are connected by the Marconi Trail.
Hopkins Marine Station is the marine laboratory of Stanford University. It is located ninety miles south of the university's main campus, in Pacific Grove, California on the Monterey Peninsula, adjacent to the Monterey Bay Aquarium. It is home to nine research laboratories and a fluctuating population of graduate and undergraduate students. It has also been used for archaeological exploration including that of the Chinese-American fishing village that existed on the site before being burnt down.

The Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station is a permanent Antarctic research station named after the Brazilian Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz, who visited Antarctica many times with the British exploration team and managed to convince his government to create a self-guided Brazilian Antarctic Program.

Gilgo State Park is a 1,223-acre (4.95 km2) undeveloped state park in Gilgo Beach, Suffolk County, New York. The park is located on Jones Beach Island, a barrier island off the southern shore of Long Island.

GOES 14, known as GOES-O prior to reaching its operational orbit, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) system. The spacecraft was built by Boeing and is based on the BSS-601 bus. It is the second of three GOES satellites to use the BSS-601 bus, after GOES 13, which was launched in May 2006.

The Central Air Defense Force (CADF) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command being stationed at Richards-Gebaur Air Force Base, Missouri. It was inactivated on July 1, 1960.

The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole.

The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean or the Austral Ocean, and the "Southern Icy Ocean".</ref> comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the fourth-largest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. This ocean zone is where cold, northward flowing waters from the Antarctic mix with warmer subantarctic waters.
Progress M-3 was a Soviet unmanned cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1990 to resupply the Mir space station. The twentieth of sixty four Progress flights to visit Mir, it was a Progress-M 11F615A55 spacecraft, and had the serial number 203. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-6 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres.
Progress M-4 was a Soviet unmanned cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1990 to resupply the Mir space station. The twenty-second of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 204. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-7 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres.
Progress M-5 was a Soviet unmanned cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1990 to resupply the Mir space station. The twenty-third of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 206. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-7 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. It was the first of ten Progress flights to carry a VBK-Raduga capsule, which was recovered after the flight.

INS Baaz is an Indian naval air station under the joint-services Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) of the Indian Armed Forces. It is located near Campbell Bay, on Great Nicobar island in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands. It is the southernmost air station of the Indian Armed Forces. It overlooks the Strait of Malacca as well as the Six Degree channel between Great Nicobar and the Indonesian island of Sumatra.
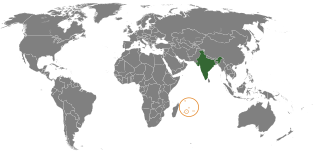
India–Mauritius refers to the historical, political, economic, military, social and cultural connections between the Republic of India and the Republic of Mauritius. Connections between India and Mauritius date back to 1730, diplomatic relations were established in 1948, before Mauritius became independent state. The cultural affinities and long historical ties between the two nations have contributed to strong and cordial relations between the two nations. More than 68% of the Mauritian population are of Indian origin, most commonly known as Indo-Mauritians. India and Mauritius co-operate in combating piracy, which has emerged as a major threat in the Indian Ocean region and Mauritius supports India’s stance against terrorism.


















