This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(May 2022) |
Stationary target indication (STI) is a mode of operation for radar that enables the operator to discriminate between a target and clutter. [1]
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(May 2022) |
Stationary target indication (STI) is a mode of operation for radar that enables the operator to discriminate between a target and clutter. [1]
In contrast to another mode, moving target indication (MTI), it cannot take an advantage of the fact that the target moves with respect to clutter. Therefore, the radar must exploit some intrinsic characteristics of the target which are different from those of clutter. The simplest method is available when the apparent size of the target is relatively small with respect to clutter source. In this case the reduced pulse and beam width, which matches the expected target size, may produce good signal-to-noise ratio (target to clutter ratio). Additional discrimination capabilities rely on target imaging or scattering properties of the target. [1]

Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (ranging), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the object(s). Radio waves from the transmitter reflect off the object and return to the receiver, giving information about the object's location and speed.

Millimeter-wave cloud radars, also denominated cloud radars, are radar systems designed to monitor clouds with operating frequencies between 24 and 110 GHz. Accordingly, their wavelengths range from 1 mm to 1.11 cm, about ten times shorter than those used in conventional S band radars such as NEXRAD.
Radar cross-section (RCS), also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected.
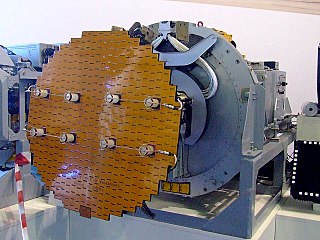
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics.

The AN/APG-66 radar is a solid state medium range pulse-Doppler planar array radar originally designed by the Westinghouse Electric Corporation for use in the F-16 Fighting Falcon. This radar was employed in all domestic and export versions of the F-16 A/B models throughout the production. Subsequent upgrades have been installed in many varying aircraft types, including the U.S. Customs and Border Protection's C-550 Cessna Citation, US Navy P-3 Orion, and Piper PA-42 Cheyenne II's, as well as the Small Aerostat Surveillance System (SASS). Primary air-combat mode is look-down. In that mode, the AN/APG-66 can detect a fighter-size plane at a range of 34.5 Nautical miles. Four modes are available in air-to-air combat. In dogfight mode, the radar scans a 20 degrees x 20 degrees field. In high-g maneuvers, it scans a 40 degrees x10 degrees pattern. The radar system consists of the following line-replaceable units:

The AN/AWG-9 and AN/APG-71 radars are all-weather, multi-mode X band pulse-Doppler radar systems used in the F-14 Tomcat, and also tested on TA-3B. It is a very long-range air-to-air system with the capability of guiding several AIM-54 Phoenix or AIM-120 AMRAAM missiles at the same time using its track while scan mode. The primary difference between the AWG-9 and APG-71 is the replacement of the former's analog computer with all-digital computer. Both the AWG-9 and APG-71 were designed and manufactured by Hughes Aircraft; contractor support is now being provided by Raytheon. The AWG-9 was originally developed for the failed naval F-111B program.
A radar system has look-down/shoot-down capability if it can detect, track and guide a weapon to an air target that is silhouetted against the ground.

Space-time adaptive processing (STAP) is a signal processing technique most commonly used in radar systems. It involves adaptive array processing algorithms to aid in target detection. Radar signal processing benefits from STAP in areas where interference is a problem. Through careful application of STAP, it is possible to achieve order-of-magnitude sensitivity improvements in target detection.
Constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection refers to a common form of adaptive algorithm used in radar systems to detect target returns against a background of noise, clutter and interference.
A radar system uses a radio-frequency electromagnetic signal reflected from a target to determine information about that target. In any radar system, the signal transmitted and received will exhibit many of the characteristics described below.
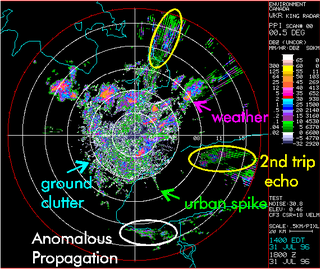
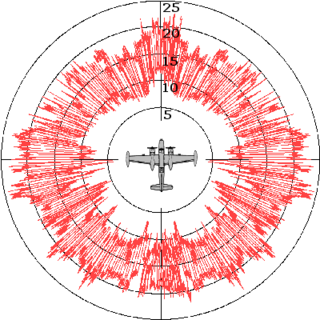
Clutter is a term used for unwanted echoes in electronic systems, particularly in reference to radars. Such echoes are typically returned from ground, sea, rain, animals/insects, chaff and atmospheric turbulences, and can cause serious performance issues with radar systems.

The AN/SPS-67 is a short-range, two-dimensional, surface-search/navigation radar system that provides highly accurate surface and limited low-flyer detection and tracking capabilities.
Radar engineering details are technical details pertaining to the components of a radar and their ability to detect the return energy from moving scatterers — determining an object's position or obstruction in the environment. This includes field of view in terms of solid angle and maximum unambiguous range and velocity, as well as angular, range and velocity resolution. Radar sensors are classified by application, architecture, radar mode, platform, and propagation window.
In radar systems, the blip-to-scan ratio, or blip/scan, is the ratio of the number of times a target appears on a radar display to the number of times it theoretically could be displayed. Alternately it can be defined as the ratio of the number of scans in which an accurate return is received to the total number of scans.
Radar MASINT is a subdiscipline of measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities that bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of signals intelligence (SIGINT), imagery intelligence (IMINT), or human intelligence (HUMINT).
Moving target indication (MTI) is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against the clutter. It describes a variety of techniques used to find moving objects, like an aircraft, and filter out unmoving ones, like hills or trees. It contrasts with the modern stationary target indication (STI) technique, which uses details of the signal to directly determine the mechanical properties of the reflecting objects and thereby find targets whether they are moving or not.
The AN/APG-67 is a multi-mode all-digital X band coherent pulse doppler radar originally developed by General Electric for the Northrop F-20 Tigershark program of the early 1980s. It offers a variety of air-to-air, air-to-ground, sea-search and mapping modes, and compatibility with most weapons used by the US Air Force in the 1980s.
The AN/APY-10 is an American multifunction radar developed for the U.S. Navy's Boeing P-8 Poseidon maritime patrol and surveillance aircraft. AN/APY-10 is the latest descendant of a radar family originally developed by Texas Instruments, and now Raytheon after it acquired the radar business of TI, for Lockheed P-3 Orion, the predecessor of P-8.
Radar envelope is a critical Measure of Performance (MOP) identified in the Test and Evaluation Master Plan (TEMP). This is the volume of space where a radar system is required to reliably detect an object with a specific size and speed. This is one of the requirements that must be evaluated as part of the acceptance testing process.

The radar horizon is a critical area of performance for aircraft detection systems that is defined by the distance at which the radar beam rises enough above the Earth's surface to make detection of a target at low level impossible. It is associated with the low elevation region of performance, and its geometry depends on terrain, radar height, and signal processing. This is associated with the notions of radar shadow, the clutter zone, and the clear zone.