
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.

Thomas Savery was an English inventor and engineer, born at Shilstone, a manor house near Modbury, Devon, England. He invented the first commercially used steam-powered device, a steam pump which is often referred to as an "engine", although it is not technically an engine. Savery's steam pump was a revolutionary method of pumping water, which solved the problem of mine drainage and made widespread public water supply practicable.

A fire engine is a road vehicle that functions as a firefighting apparatus. The primary purposes of a fire engine include transporting firefighters and water to an incident as well as carrying equipment for firefighting operations. Some fire engines have specialized functions, such as wildfire suppression and aircraft rescue and firefighting, and may also carry equipment for technical rescue.

The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating a partial vacuum which allowed the atmospheric pressure to push the piston into the cylinder. It was the first practical device to harness steam to produce mechanical work. Newcomen engines were used throughout Britain and Europe, principally to pump water out of mines. Hundreds were constructed throughout the 18th century.

On a ship, the engine room (ER) is the compartment where the machinery for marine propulsion is located. To increase a vessel's safety and chances of surviving damage, the machinery necessary for the ship's operation may be segregated into various spaces. The engine room is generally the largest physical compartment of the machinery space. It houses the vessel's prime mover, usually some variations of a heat engine. On some ships, there may be more than one engine room, such as forward and aft, or port or starboard engine rooms, or may be simply numbered.

Crofton Pumping Station, near the village of Great Bedwyn in Wiltshire, England, supplies the summit pound of the Kennet and Avon Canal with water.
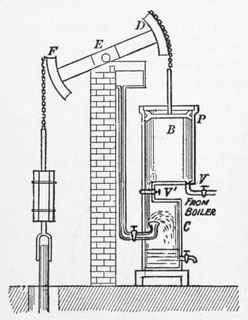
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.

The history of organized firefighting began in ancient Rome while under the rule of Augustus. Prior to that, Ctesibius, a Greek citizen of Alexandria, developed the first fire pump in the third century BC, which was later improved upon in a design by Hero of Alexandria in the first century BC.

A portable engine is an engine, either a steam engine or an internal combustion engine, that sits in one place while operating, but is portable and thus can be easily moved from one work site to another. Mounted on wheels or skids, it is either towed to the work site or moves there via self-propulsion.

Merryweather & Sons of Clapham, later Greenwich, London, were builders of steam fire engines and steam tram engines.
An engine house is a building or other structure that holds one or more engines. It is often practical to bring engines together for common maintenance, as when train locomotives are brought together.

Pyronaut is a specialised form of fireboat known as a fire-float. It was built in 1934 by Charles Hill & Sons Ltd., Albion Dock Bristol, Yard No. 208. Registered number 333833. She is owned by Bristol Museums and based at M Shed in Bristol's Floating Harbour.

The Cambridge Museum of Technology is an industrial heritage museum situated in Cambridge, England. The original building, a Scheduled Ancient Monument, housed a combined sewage pumping and waste destructor station built in 1894. The Museum helps people to explore, enjoy, and learn about their industrial heritage by celebrating the achievements of local industries and the people who worked in them. The large site on the River Cam has green spaces for picnics and a fun, relaxed atmosphere for families. There are audio-visual displays, hands-on exhibits, and children’s activities, as well as traditional museum displays and historic buildings. The Victorian Pumping Station with its original machinery showcases 19th-century engineering and technology. Displays on the forgotten industries of Cambridge reveal an alternative side of the city’s history to the famous colleges. And the story is brought into the 20th Century with exhibitions on innovative local companies in our new Pye building. Featuring Pye and Cambridge Scientific Instrument Company.

The British Engineerium is an engineering and steam power museum in Hove, East Sussex. It is housed in the Goldstone Pumping Station, a set of High Victorian Gothic buildings started in 1866. The Goldstone Pumping Station supplied water to the local area for more than a century before it was converted to its present use. The site has been closed to the public since 2006, and in March 2018, the entire complex was put up for sale.

The Waterous Engine Works was a famous Canadian farm and road engine builder. It made farm, road rollers and steam pumper fire equipment. It also made factory steam engines and marine engines. Many of their engines survive to this day in museums.

The Maryborough Fire Brigade Board of Maryborough, Queensland was the first fire brigade in Queensland, Australia, outside of the capital city of Brisbane.

A firefighting apparatus describes any vehicle that has been customized for use during firefighting operations. These vehicles are highly customized depending on their needs and the duty they will be performing. These duties can include firefighting and emergency medical services.

Paul Rapsey Hodge was an English-American inventor and mechanical engineer. He invented technological improvements used by railroad companies. He also invented a device that ground wheat and other grains into flour that could then be used by bakers, as well as a machine that turned vegetable pulp into paper that could be used by printers. His innovations were useful to many industries. He was a writer of technical manuals in both the United States and England.

The electric fire engine is a fire engine with a water pump, used to distribute water to put out a fire, operated by an electric motor. Electric fire engines were first proposed in the 19th century to replace the steam pumpers used for firefighting. The electric motor was claimed to be simpler, cleaner, and faster in operation, would save money, and require less maintenance than the steam fire engine. Contemporary battery-operated models also exist.

Alexander Bonner Latta was an American manufacturer and inventor. He specialized in engines that used steam for power. He designed railroad steam locomotives and directed the construction of the first such locomotive built west of the Alleghany Mountains. An unusual train locomotive design he innovated was one that had an additional set of cylinders that utilized steam exhaust for more power. He designed and constructed the first efficiently working steam fire engine to be routinely used as a part of a city's fire-fighting equipment. The fire engine was first adopted by Cincinnati, Boston, and New York City. He invented a self-propelled steam-engine fire engine.




















