Related Research Articles
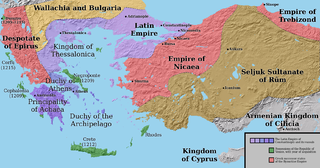
The Principality of Achaea or Principality of Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom of Thessalonica, along with the Duchy of Athens, until Thessalonica was captured by Theodore, the despot of Epirus, in 1224. After this, Achaea became for a while the dominant power in Greece.
The Prince of Achaea was the ruler of the Principality of Achaea, one of the crusader states founded in Greece in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade (1202–1204). Though more or less autonomous, the principality was never a fully independent state, initially being a vassal state subservient of the Latin Empire of Constantinople, which had supplanted the Byzantine Empire, and later of the Angevin Kingdom of Naples. During the Angevin period, the princes were often absent, being represented in the Principality by their baillis, who governed in their name.

The Despotate of the Morea or Despotate of Mystras was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centuries. Its territory varied in size during its existence but eventually grew to include almost all the southern Greek peninsula now known as the Peloponnese, which was known as the Morea during the medieval and early modern periods. The territory was usually ruled by one or more sons of the current Byzantine emperor, who were given the title of despotes. Its capital was the fortified city of Mystras, near ancient Sparta, which became an important centre of the Palaiologan Renaissance.

Centurione II Zaccaria, scion of a powerful Genoese merchant family established in the Morea, was installed as Prince of Achaea by Ladislaus of Naples in 1404 and was the last ruler of the Latin Empire not under Byzantine suzerainty.

Martino Zaccaria was the Lord of Chios from 1314 to 1329, ruler of several other Aegean islands, and baron of Veligosti–Damala and Chalandritsa in the Principality of Achaea. He distinguished himself in the fight against Turkish corsairs in the Aegean Sea, and received the title of "King and Despot of Asia Minor" from the titular Latin Emperor, Philip II. He was deposed from his rule of Chios by a Byzantine expedition in 1329, and imprisoned in Constantinople until 1337. Martino then returned to Italy, where he was named the Genoese ambassador to the Holy See. In 1343 he was named commander of the Papal squadron in the Smyrniote crusade against Umur Bey, ruler of the Emirate of Aydin, and participated in the storming of Smyrna in October 1344. He was killed, along with several other of the crusade's leaders, in a Turkish attack on 17 January 1345.

The Frankokratia, also known as Latinokratia and, for the Venetian domains, Venetokratia or Enetokratia, was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French and Italian states were established by the Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae on the territory of the dissolved Byzantine Empire.

Chlemoutsi, also known as Clermont, is a medieval castle in the northwest of the Elis regional unit in the Peloponnese peninsula of southern Greece, in the Kastro-Kyllini municipality.

Glarentza, also known as or Clarenia, Clarence, or Chiarenza, was a medieval town located near the site of modern Kyllini in Elis, at the westernmost point of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece. Founded in the mid-13th century by William II of Villehardouin, the town served as the main port and mint of the Frankish Principality of Achaea, being located next to the Principality's capital, Andravida. Commerce with Italy brought great prosperity, but the town began to decline in the early 15th century as the Principality itself declined. In 1428, Glarentza was ceded to the Byzantine Despotate of the Morea, and served as its co-capital, being the residence of one of the Palaiologos despots, until the Ottoman conquest in 1460. Under Ottoman rule, Glarentza declined rapidly as the commercial links with Italy were broken, and by the 16th century was abandoned and falling into ruin. Little remains of the town today: traces of the city wall, of a church and a few other buildings, as well as the silted-up harbour.

The Morea revolt of 1453–1454 was a failed peasant rebellion carried out against the rule of the brothers Thomas and Demetrios Palaiologos, rulers of the Byzantine Despotate of the Morea in the Peloponnese peninsula.

The Battle of the Echinades was fought in 1427 among the Echinades islands off western Greece between the fleets of Carlo I Tocco and the Byzantine Empire. The battle was a decisive Byzantine victory, the last in the Empire's naval history, and led to the consolidation of the Peloponnese under the Byzantine Despotate of the Morea.

The Old Navarino castle is a 13th-century Frankish fortress near Pylos, Greece. It is one of two castles guarding the bay on which it sits; the other is the Ottoman-built New Navarino. It is frequently known simply as Palaiokastro or Paliokastro. It occupies the site of the Athenian fort at the 425 BC Battle of Pylos.
Leonardo II Tocco was a scion of the Tocco family and lord of Zakynthos, who played an important role as a military leader for his brother, Carlo I Tocco, in early 15th-century western Greece.

The Barony of Vostitsa was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the northern coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the town of Vostitsa.

The Barony of Patras was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the northwestern coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the town of Patras. It was among the twelve original baronies of the Principality of Achaea, but passed into the hands of the Latin Archbishop of Patras at about the middle of the 13th century. From 1337 on, Patras was an ecclesiastical domain de facto independent of the Principality, although the archbishops still recognized its suzerainty for their secular fiefs. The archbishops maintained close relations with the Republic of Venice, which governed the barony in 1408–1413 and 1418. The barony survived until the Byzantine reconquest in 1429–30.

The Barony of Arcadia was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located on the western coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the town of Arcadia, ancient and modern Kyparissia.

The Barony of Chalandritsa was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the northern Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the town of Chalandritsa south of Patras.

The Barony of Estamira or Stamira was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the fertile plains of the Elis region of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the now vanished fortress of Estamira.
Andronikos Asen Zaccaria de Damala or Asanes was a Genoese lord of the Principality of Achaea in southern Greece.
Paolo Foscari was a Venetian noble and churchman, who rose to become Bishop of Castello in 1367–1375, and Latin Archbishop of Patras from 1375 until his death in 1393/4. In the latter capacity he played a leading role in the affairs of the Principality of Achaea.

The Battle of Saint George took place on 9 September 1320 between the Latin Principality of Achaea and the forces of the Byzantine governor of Mystras, at the fortress of Saint George in Skorta in Arcadia. As a result of the battle, Arcadia, the heartland of the Morea, came firmly under Byzantine control.
References
- ↑ Bon 1969, p. 708.
- ↑ Topping 1975, p. 160.
- ↑ Topping 1975, pp. 160–161.
- ↑ Bon 1969, pp. 280–283.
- ↑ Topping 1975, p. 161.
- ↑ Topping 1975, pp. 161–162.
- ↑ Topping 1975, pp. 162–163.
- ↑ Topping 1975, p. 163.
- ↑ Topping 1975, pp. 163–164.
- ↑ Bon 1969, p. 290.
- ↑ Topping 1975, p. 164.
- ↑ Bon 1969, p. 292.