This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(September 2017) |
A stieda process refers to an elongated lateral posterior tubercle of the talus. [1] [2]
This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(September 2017) |
A stieda process refers to an elongated lateral posterior tubercle of the talus. [1] [2]
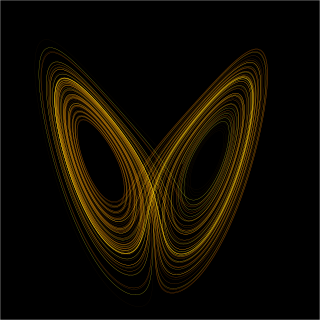
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals, and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state. A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Texas can cause a tornado in Brazil.

Creation science or scientific creationism is a pseudoscientific form of Young Earth creationism which claims to offer scientific arguments for certain literalist and inerrantist interpretations of the Bible. It is often presented without overt faith-based language, but instead relies on reinterpreting scientific results to argue that various myths in the Book of Genesis and other select biblical passages are scientifically valid. The most commonly advanced ideas of creation science include special creation based on the Genesis creation narrative and flood geology based on the Genesis flood narrative. Creationists also claim they can disprove or reexplain a variety of scientific facts, theories and paradigms of geology, cosmology, biological evolution, archaeology, history, and linguistics using creation science. Creation science was foundational to intelligent design.

In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Science is a rigorous, systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the world. Modern science is typically divided into three major branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world; the social sciences, which study individuals and societies; and the formal sciences, which study formal systems, governed by axioms and rules. There is disagreement whether the formal sciences are science disciplines, because they do not rely on empirical evidence. Applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as in engineering and medicine.

Linus Carl Pauling was an American chemist, biochemist, chemical engineer, peace activist, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. New Scientist called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time. For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962. He is one of five people to have won more than one Nobel Prize. Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes, and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being Marie Curie.

Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns.

Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology.

The mad scientist is a stock character of a scientist who is perceived as "mad, bad and dangerous to know" or "insane" owing to a combination of unusual or unsettling personality traits and the unabashedly ambitious, taboo or hubristic nature of their experiments. As a motif in fiction, the mad scientist may be villainous or antagonistic, benign, or neutral; may be insane, eccentric, or clumsy; and often works with fictional technology or fails to recognise or value common human objections to attempting to play God. Some may have benevolent intentions, even if their actions are dangerous or questionable, which can make them accidental antagonists.

Glen David Brin is an American science fiction author. He has won the Hugo, Locus, Campbell and Nebula Awards. His novel The Postman was adapted into a 1997 feature film starring Kevin Costner.

Horticulture is the art and science of growing plants. This definition is seen in the etymology of "horticulture", which is derived from the latin words hortus, which means "garden" and cultura which means "to cultivate". Horticulture is very broad and encompasses many domains. It is normally small-scale, as compared to the larger-scale cultivation of crops that is seen in agriculture.

Sebastião Ribeiro Salgado Júnior is a Brazilian social documentary photographer and photojournalist.

Florian Witold Znaniecki was a Polish and American philosopher and sociologist who taught and wrote in Poland and in the United States. Over the course of his work he shifted his focus from philosophy to sociology. He remains a major figure in the history of Polish and American sociology; the founder of Polish academic sociology, and of an entire school of thought in sociology. He won international renown as co-author, with William I. Thomas, of the study, The Polish Peasant in Europe and America (1918–1920), which is considered the foundation of modern empirical sociology. He also made major contributions to sociological theory, introducing terms such as humanistic coefficient and culturalism.

In science fiction and fantasy literature, the term insectoid ("insect-like") denotes any fantastical fictional creature sharing physical or other traits with ordinary insects. Most frequently, insect-like or spider-like extraterrestrial life forms is meant; in such cases convergent evolution may presumably be responsible for the existence of such creatures. Occasionally, an earth-bound setting — such as in the film The Fly (1958), in which a scientist is accidentally transformed into a grotesque human–fly hybrid, or Kafka's famous novella The Metamorphosis (1915), which does not bother to explain how a man becomes an enormous insect — is the venue.

Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments.

Newtonianism is a philosophical and scientific doctrine inspired by the beliefs and methods of natural philosopher Isaac Newton. While Newton's influential contributions were primarily in physics and mathematics, his broad conception of the universe as being governed by rational and understandable laws laid the foundation for many strands of Enlightenment thought. Newtonianism became an influential intellectual program that applied Newton's principles in many avenues of inquiry, laying the groundwork for modern science, in addition to influencing philosophy, political thought and theology.
Algebra is the branch of mathematics that studies algebraic systems and the manipulation of equations within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that includes variables besides regular numbers and algebraic operations other than the standard arithmetic operations like addition and multiplication.

Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres: the biosphere, hydrosphere/cryosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science but with a much older history.

Cybernetics is a field of systems science that studies circular causal systems whose outputs are also inputs, such as feedback systems. It is concerned with the general principles of circular causal processes, including in ecological, technological, biological, cognitive and social systems and also in the context of practical activities such as designing, learning, and managing.

Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular (single-celled), multicellular, or acellular. Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology, and parasitology.

Dariusz Jemielniak is a professor of management at Kozminski University, faculty associate at the Berkman Klein Center for Internet & Society at Harvard University, and vice-president of Polish Academy of Sciences.