The Stockade Building System was designed by Richard Buckminster Fuller and his father-in-law, James Monroe Hewlett, and was patented in 1927. [1] [2] Both of them had previously formed a company, in 1922, [3] which made bricks out of compressed wood shavings with vertical holes cast in them.
The blocks were made up of a fibrous material with large interstices between the fibers. (One suggested fiber was excelsior, which is also known as wood wool.) Despite having large interstices, Fuller and Hewlett designed the blocks so they would not be absorbent. To make the blocks, the fibers were coated with plaster and molded in a form. [2] This is called the Stockade Pneumatic Forming Process. [4]
These blocks were cast with large holes in them so that a weight-bearing structure, such as concrete, could be poured inside them. The block's fibers were designed to be easily sawed so workers could cut holes in them to rest floor joists on the weight-bearing structure. The blocks came in various shapes and sizes. Some had two vertical holes for filling with concrete. Other blocks were much larger, with openings in the side for inserting large beams. [2]
The system was evaluated at a residence in Tarpon Springs, Florida, in 1926. [5]
On October 8, 1926, Fuller and Hewlett filed for a patent for their brick design. After several months, on June 28, 1927, they received US patent #1,633,702 entitled Building System. It was an extension of Fuller's previous patent (US patent #1,604,097) from October 19, 1926. [2]

Richard Buckminster Fuller was an American architect, systems theorist, author, designer, inventor, and futurist. He styled his name as R. Buckminster Fuller in his writings, publishing more than 30 books and coining or popularizing such terms as "Spaceship Earth", "Dymaxion", "ephemeralization", "synergetics", and "tensegrity".

A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term brick denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using mortar, adhesives or by interlocking them. Bricks are produced in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region and time period, and are produced in bulk quantities.

Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term masonry can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are brick, building stone such as marble, granite, and limestone, cast stone, concrete block, glass block, and adobe. Masonry is generally a highly durable form of construction. However, the materials used, the quality of the mortar and workmanship, and the pattern in which the units are assembled can substantially affect the durability of the overall masonry construction. A person who constructs masonry is called a mason or bricklayer. These are both classified as construction trades.

A geodesic dome is a hemispherical thin-shell structure (lattice-shell) based on a geodesic polyhedron. The triangular elements of the dome are structurally rigid and distribute the structural stress throughout the structure, making geodesic domes able to withstand very heavy loads for their size.
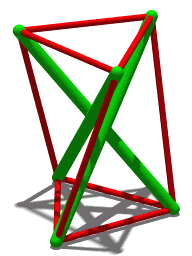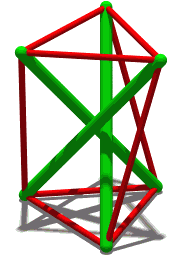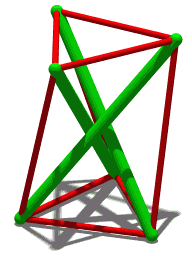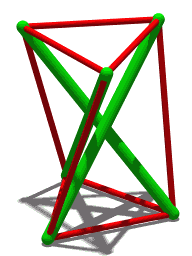
Tensegrity, tensional integrity or floating compression is a structural principle based on a system of isolated components under compression inside a network of continuous tension, and arranged in such a way that the compressed members do not touch each other while the prestressed tensioned members delineate the system spatially.

The Dymaxion House was developed by inventor and architect Buckminster Fuller to address several perceived shortcomings with existing homebuilding techniques. Fuller designed several versions of the house at different times — all of them factory manufactured kits, assembled on site, intended to be suitable for any site or environment and to use resources efficiently. A key design consideration was ease of shipment and assembly.

Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rocks, sand and wood, even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-made products are in use, some more and some less synthetic. The manufacturing of building materials is an established industry in many countries and the use of these materials is typically segmented into specific specialty trades, such as carpentry, insulation, plumbing, and roofing work. They provide the make-up of habitats and structures including homes.

Seismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with our recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries and late 1970s for many other parts of the world, many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world – such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.
A load-bearing wall or bearing wall is a wall that is an active structural element of a building, which holds the weight of the elements above it, by conducting its weight to a foundation structure below it.

A concrete masonry unit (CMU) is a standard-size rectangular block used in building construction. CMUs are some of the most versatile building products available because of the wide variety of appearances that can be achieved using them.
This page is a list of construction topics.

Insulating concrete form or insulated concrete form (ICF) is a system of formwork for reinforced concrete usually made with a rigid thermal insulation that stays in place as a permanent interior and exterior substrate for walls, floors, and roofs. The forms are interlocking modular units that are dry-stacked and filled with concrete. The units lock together somewhat like Lego bricks and create a form for the structural walls or floors of a building. ICF construction has become commonplace for both low rise commercial and high performance residential construction as more stringent energy efficiency and natural disaster resistant building codes are adopted.

Papercrete is a building material that consists of re-pulped paper fiber with Portland cement or clay and/or other soil added. First patented in 1928, it was revived during the 1980s. Although perceived as an environmentally friendly material due to the significant recycled content, this is offset by the presence of cement. The material lacks standardisation, and proper use therefore requires care and experience. Eric Patterson and Mike McCain, who have been credited with independently "inventing" papercrete, have both contributed considerably to research into machinery to make it and ways of using it for building.

A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can slowly draw rainwater or even humidity into the wall. One function of the cavity is to drain water through weep holes at the base of the wall system or above windows. The weep holes allow wind to create an air stream through the cavity that exports evaporated water from the cavity to the outside. Usually, weep holes are created by separating several vertical joints approximately two meters apart at the base of each story. Weep holes are also placed above windows to prevent dry rot of wooden window frames. A cavity wall with masonry as both inner and outer skins is more commonly referred to as a double wythe masonry wall.

Anna Wagner Keichline was an American architect, inventor, suffragist, and World War I Special Agent from Pennsylvania. She was the first woman to be registered as an architect in Pennsylvania and she was "one of the first women to actually practice architecture professionally". She was awarded seven patents, including one for a notched brick in 1927.

The R. Buckminster Fuller and Anne Hewlett Dome Home, located at 407 S. Forest Ave. in Carbondale, Illinois, is a geodesic dome house which was the residence of Buckminster Fuller from 1960 to 1971. The house, inhabited by Fuller while he taught at Southern Illinois University, was the only geodesic dome Fuller lived in, as well as the only property he ever owned. Fuller, a prolific architect and engineer, popularized the geodesic dome as a building design, and his house was one of the first geodesic dome residences to be constructed. The home was built and designed by Al Miller of the Pease Woodworking Company. While living in the home, Fuller was awarded nine patents, published eleven books, and designed the Montreal Biosphère, one of his most famous works.

Translucent concrete is a concrete based building material with light-transmissive properties due to embedded light optical elements — usually optical fibers. Light is conducted through the stone from one end to the other. Therefore, the fibers have to go through the whole object. This results in a certain light pattern on the other surface, depending on the fiber structure. Shadows cast onto one side appear as silhouettes through the material.

Structural clay tile describes a category of burned-clay building materials used to construct roofing, walls, and flooring for structural and non-structural purposes, especially in fireproofing applications. Also called building tile, structural terra cotta, hollow tile, and clay block, the material is an extruded clay shape with substantial depth that allows it to be laid in the same manner as other clay or concrete masonry. In North America it was chiefly used during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, reaching peak popularity at the turn of the century and declining around the 1950s. Structural clay tile grew in popularity in the end of the nineteenth-century because it could be constructed faster, was lighter, and required simpler flat falsework than earlier brick vaulting construction. Each unit is generally made of clay or terra-cotta with hollow cavities, or cells, inside it. The material is commonly used in floor arches, fireproofing, partition walls, and furring. It continues to be used in Europe to build fire-resistant walls and partitions. In North America the material has largely been replaced by concrete masonry units.
This glossary of structural engineering terms pertains specifically to structural engineering and its sub-disciplines. Please see glossary of engineering for a broad overview of the major concepts of engineering.

Mount Elliott Company Metallurgical Plant and Mill is a heritage-listed smelting works via Sheaffe Street, Cloncurry, Shire of Cloncurry, Queensland, Australia. It was built from 1926 to April 1927. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 17 June 2003.