
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis.

The esophagus or oesophagus, informally known as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about 25 cm (10 in) long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word oesophagus is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω + ἔφαγον.

The gastropods, commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda.

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

Sea slug is a common name for some marine invertebrates with varying levels of resemblance to terrestrial slugs. Most creatures known as sea slugs are actually gastropods, i.e. they are sea snails that over evolutionary time have either completely lost their shells, or have seemingly lost their shells due to having a greatly reduced or internal shell. The name "sea slug" is most often applied to nudibranchs, as well as to a paraphyletic set of other marine gastropods without obvious shells.
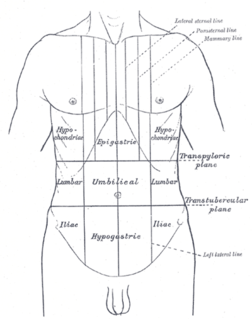
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.

The mantle is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself.
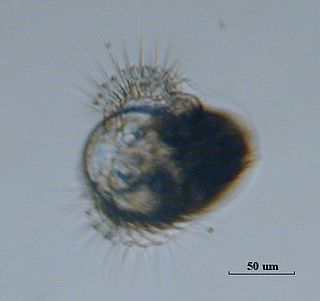
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of sea snails and freshwater snails, as well as most bivalve molluscs (clams) and tusk shells.

Limpets are a group of aquatic snails that exhibit a conical shell shape (patelliform) and a strong, muscular foot. Limpets are members of the class Gastropoda, but are polyphyletic, meaning the various groups called "limpets" descended independently from different ancestral gastropods. This general category of conical shell is known as "patelliform" (dish-shaped). All members of the large and ancient marine clade Patellogastropoda are limpets. Within that clade, the members of the Patellidae family in particular are often referred to as "true limpets".

The Patellogastropoda, common name true limpets and historically called the Docoglossa, are members of a major phylogenetic group of marine gastropods, treated by experts either as a clade or as a taxonomic order.

In differential geometry, the notion of torsion is a manner of characterizing a twist or screw of a moving frame around a curve. The torsion of a curve, as it appears in the Frenet–Serret formulas, for instance, quantifies the twist of a curve about its tangent vector as the curve evolves. In the geometry of surfaces, the geodesic torsion describes how a surface twists about a curve on the surface. The companion notion of curvature measures how moving frames "roll" along a curve "without twisting".

The gastropod shell is part of the body of a gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group.
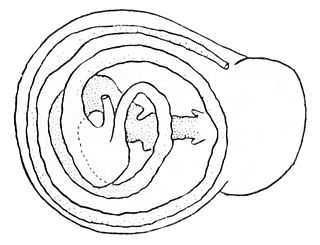
Torsion is a gastropod synapomorphy which occurs in all gastropods during larval development. Torsion is the rotation of the visceral mass, mantle, and shell 180˚ with respect to the head and foot of the gastropod. This rotation brings the mantle cavity and the anus to an anterior position above the head.

Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda. The members are known as molluscs or mollusks. Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied.
The digestive system of gastropods has evolved to suit almost every kind of diet and feeding behavior. Gastropods as the largest taxonomic class of the mollusca are very diverse: the group includes carnivores, herbivores, scavengers, filter feeders, and even parasites.

The nervous system of gastropods consists of a series of paired ganglia connected by major nerve cords, and a number of smaller branching nerves. It is sometimes called ganglionic.

Pseudunela cornuta is a species of minute sea slug, an acochlidian, a shell-less marine and temporarily brackish gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudunelidae. Adults are about 3 mm long and live in the spaces between sand grains.

Euthyneury is a plesiomorphic condition present in some gastropods which is a result of two evolutionary events. The first event, which was experienced by the ancestors of all extant gastropods, is known as torsion. Torsion describes the event in which the intestines, heart, nephridia, gills, and nerve cords "twisted" causing some organs to migrate from the animal's left to its right in order to accommodate the relocation of the mantle cavity close to the animal's head. Torsion created a condition in the cerebrovisceral commissures called streptoneury. Secondarily, some gastropod lineages detorted: they reversed the torsion event and straightened out their internal organs, uncrossing the commissures in the process. It is this second state, one in which the commissures have once again become untwisted, that is called euthyneury.
Bathyacmaea secunda is a species of very small, deep-sea limpet, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Pectinodontidae. This species inhabits the dark, chemosynthesis-based marine communities of ocean vents and cold seeps near Japan.
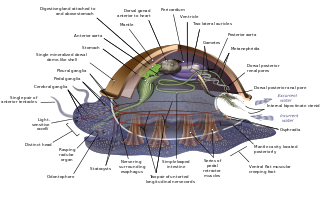
A circumesophageal or circumpharyngeal nerve ring is an arrangement of nerve ganglia around the esophagus/ pharynx of an animal. It is a common feature of nematodes, molluscs, and many other invertebrate animals, though it is absent in all vertebrate animals and is not structurally possible in simpler ones such as water bears.


















