Related Research Articles

Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mother-to-child spread during birth or after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as lamivudine/zidovudine and abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine. It can be used by mouth or by slow injection into a vein.
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs in an attempt to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multiple drugs that act on different viral targets is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART decreases the patient's total burden of HIV, maintains function of the immune system, and prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death. HAART also prevents the transmission of HIV between serodiscordant same sex and opposite sex partners so long as the HIV-positive partner maintains an undetectable viral load.

Stavudine (d4T), sold under the brand name Zerit among others, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for prevention after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. However, it is not a first-line treatment. It is given by mouth.

Lamivudine, commonly called 3TC, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B when other options are not possible. It is effective against both HIV-1 and HIV-2. It is typically used in combination with other antiretrovirals such as zidovudine and abacavir. Lamivudine may be included as part of post-exposure prevention in those who have been potentially exposed to HIV. Lamivudine is taken by mouth as a liquid or tablet.

Nevirapine (NVP), sold under the brand name Viramune among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS, specifically HIV-1. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretroviral medications. It may be used to prevent mother to child spread during birth but is not recommended following other exposures. It is taken by mouth.
DREAM is an AIDS therapy program promoted by the Christian Community of Sant'Egidio. The Community of Sant'Egidio, based in Rome, was formerly involved in the peace talks in Mozambique, facilitating the eleven rounds of negotiations in Rome that helped to end the Mozambican Civil War. The Community has worked closely with both the Mozambican Ministry of Health and the United States' PEPFAR in order to implement the DREAM program. The DREAM program is designed to give access to free ARV treatment with generic HAART drugs to the poor in Africa on a large scale: So far, 5,000 people are receiving ARV treatment, especially in Mozambique, but the program is being built up also in other countries, including Angola, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of Congo, Guinea, Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, Swaziland and Tanzania. Despite being free, the program aims at excellence in treatment, providing the best existent range of drugs (HAART) and regular blood testing according to European standards. It is linked with a nutrition program as well as guidance and sanitary education by volunteers, which encourages new patients to comply and come to the appointments. The compliance rate is very high. The annual cost per person and year of the program is $800.
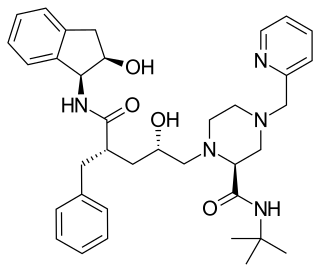
Indinavir is a protease inhibitor used as a component of highly active antiretroviral therapy to treat HIV/AIDS. It is soluble white powder administered orally in combination with other antiviral drugs. The drug prevents protease from functioning normally. Consequently, HIV viruses cannot reproduce, causing a decrease in the viral load. Commercially sold indinavir is indinavir anhydrous, which is indinavir with an additional amine in the hydroxyethylene backbone. This enhances its solubility and oral bioavailability, making it easier for users to intake. It was synthetically produced for the purpose of inhibiting the protease in the HIV virus.

Rifabutin (Rfb) is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and prevent and treat Mycobacterium avium complex. It is typically only used in those who cannot tolerate rifampin such as people with HIV/AIDS on antiretrovirals. For active tuberculosis it is used with other antimycobacterial medications. For latent tuberculosis it may be used by itself when the exposure was with drug-resistant TB.

Lamivudine/zidovudine, sold under the brand name Combivir among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. It contains two antiretroviral medications, lamivudine and zidovudine. It is used together with other antiretrovirals. It is taken by mouth twice a day.
The Division of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (DAIDS) is a division of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases which is part of the National Institutes of Health. It was formed in 1986 as a part of the initiative to address the national research needs created by the advent and spread of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. Specifically, the Division’s mission is to increase basic knowledge of the pathogenesis, natural history, and transmission of HIV disease and to support research that promotes progress in its detection, treatment, and prevention. DAIDS accomplishes this through planning, implementing, managing, and evaluating programs in (1) fundamental basic research, (2) discovery and development of therapies for HIV infection and its complications, and (3) discovery and development of vaccines and other prevention strategies.

Raltegravir (RAL), sold under the brand name Isentress, is an antiretroviral medication used, together with other medication, to treat HIV/AIDS. It may also be used, as part of post exposure prophylaxis, to prevent HIV infection following potential exposure. It is taken by mouth.
Leronlimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeted against the CCR5 receptor found on T lymphocytes of the human immune system. It is being investigated as a potential therapy in the treatment of COVID-19, triple negative breast cancer, and HIV infection. The United States Food and Drug Administration has designated PRO 140 for fast-track approval. In February 2008, the drug entered Phase 2 clinical trials and a phase 3 trial was begun in 2015. In February 2018, Cytodyn Inc reported that the primary endpoint had been achieved in the PRO 140 pivotal combination therapy trial in HIV infection. In 2020 CytoDyn submitted a fast-track biologics license application for treatment of CCR5-tropic HIV-1 Infection. In August, 2020 CytoDyn submitted an emergency use authorization for treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19.
HIV drug resistance occurs when microevolution causes virions to become tolerant to antiretroviral treatments (ART). ART can be used to successfully manage HIV infection, but a number of factors can contribute to the virus mutating and becoming resistant. Drug resistance occurs as bacterial or viral populations evolve to no longer respond to medications that previously worked. In the case of HIV, there have been recognized cases of treatment resistant strains since 1989, with drug resistance being a major contributor to treatment failure. While global incidence varies greatly from region to region, there has been a general increase in overall HIV drug resistance. The two main types of resistance, primary and induced, differ mostly in causation, with the biggest cause of resistance being a lack of adherence to the specific details of treatment. These newly created resistant strains of HIV pose a public health issue as they infect a growing number of people because they are harder to treat, and can be spread to other individuals. For this reason, the reaction to the growing number of cases of resistant HIV strains has mostly been to try to increase access to treatment and implement other measures to make sure people stay in care, as well as to look into the development of a HIV vaccine or cure.

The affected community is composed of people who are living with HIV and AIDS, plus individuals whose lives are directly influenced by HIV infection. This originally was defined as young to middle aged adults who associate with being gay or bisexual men, and or injection drug users. HIV-affected community is a community that is affected directly or indirectly affected by HIV. These communities are usually influenced by HIV and undertake risky behaviours that lead to a higher chance of HIV infection. To date HIV infection is still one of the leading cause of deaths around the world with an estimate of 36.8 million people diagnosed with HIV by the end of 2017, but there can particular communities that are more vulnerable to HIV infection, these communities include certain races, gender, minorities, and disadvantaged communities. One of the most common communities at risk is the gay community as it is commonly transmitted through unsafe sex. The main factor that contributes to HIV infection within the gay/bisexual community is that gay men do not use protection when performing anal sex or other sexual activities which can lead to a higher risk of HIV infections. Another community will be people diagnosed with mental health issues, such as depression is one of the most common related mental illnesses associated with HIV infection. HIV testing is an essential role in reducing HIV infection within communities as it can lead to prevention and treatment of HIV infections but also helps with early diagnosis of HIV. Educating young people in a community with the knowledge of HIV prevention will be able to help decrease the prevalence within the community. As education is an important source for development in many areas. Research has shown that people more at risk for HIV are part of disenfranchised and inner city populations as drug use and sexually transmitted diseases(STDs) are more prevalent. People with mental illnesses that inhibit making decisions or overlook sexual tendencies are especially at risk for contracting HIV.
The cost of HIV treatment is a complicated issue with an extremely wide range of costs due to varying factors such as the type of antiretroviral therapy and the country in which the treatment is administered. The first line therapy of HIV, or the initial antiretroviral drug regimen for an HIV-infected patient, is generally cheaper than subsequent second-line or third-line therapies. There is also a great variability of drug prices among low, middle, and high income countries. In general, low-income countries have the lowest cost of antiretroviral therapy, while middle- and high-income tend to have considerably higher costs. Certain prices of HIV drugs may be high and difficult to afford due to patent barriers on antiretroviral drugs and slow regulatory approval for drugs, which may lead to indirect consequences such as greater HIV drug resistance and an increased number of opportunistic infections. Government and activist movements have taken efforts to limit the price of HIV drugs.
Jacques Leibowitch was a French medical doctor and clinical researcher known for his contributions to the knowledge and treatment of HIV and AIDS, starting with his initial designation of a human retrovirus as the cause of AIDS, and his ground-breaking use of triple combination therapy for the effective control of HIV in the patient. A practicing physician in the infectiology department of the Raymond Poincaré University Hospital of Garches, University lecturer Emeritus, he led the treatment program ICCARRE that proposes a dramatic reduction of weekly anti-HIV drug intake, down to 2-3 anti-viral pills a day taken 2 to 3 or 4 days a week, as opposed to the presently recommended seven days a week, as still universally prescribed. These reduced medical dosages are adequate, necessary and sufficient according to the results of his exploratory clinical research carried out since 2003. He is the author of the books "Un virus étrange venu d'ailleurs", and "Pour en finir avec le sida".
Julio S. G. Montaner, is an Argentine-Canadian physician, professor and researcher. He is the director of the British Columbia Centre for Excellence in HIV/AIDS, the chair in AIDS Research and head of the Division of AIDS in the Faculty of Medicine at the University of British Columbia and the past-president of the International AIDS Society. He is also the director of the John Ruedy Immunodeficiency Clinic, and the Physician Program Director for HIV/AIDS PHC. He is known for his work on HAART, a role in the discovery of triple therapy as an effective treatment for HIV in the late 1990s, and a role in advocating the "Treatment as Prevention" Strategy in the mid-2000s, led by Myron Cohen of the HPTN 052 trial.
Deborah Persaud is an South America-born American virologist who primarily works on HIV/AIDS at Johns Hopkins Children's Center.
Treatment as prevention (TasP) is a concept in public health that promotes treatment as a way to prevent and reduce the likelihood of HIV illness, death and transmission from an infected individual to others. Expanding access to earlier HIV diagnosis and treatment as a means to address the global epidemic by preventing illness, death and transmission was first proposed in 2000 by Garnett et al. The term is often used to talk about treating people that are currently living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) to prevent illness, death and transmission. Although some experts narrow this to only include only preventing infections, treatment prevents illnesses such as tuberculosis and has been shown to prevent death. The dual impact on well being and its 100% effectiveness in reducing transmission makes TasP the most important element in the HIV prevention toolkit. In relation to HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is a three or more drug combination therapy that is used to decrease the viral load, or the measured amount of virus, in an infected individual. Such medications are used as a preventative for infected individuals to not only spread the HIV virus to their negative partners but also improve their current health to increase their lifespans. Other names for ART include highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), combination antiretroviral therapy (cART), triple therapy and triple drug cocktail. When taken correctly, ARVs are able to diminish the presence of the HIV virus in the bodily fluids of an infected person to a level of undetectability. Undetectability ensures that infection does not necessarily have an effect on a person's general health, and that there is no longer a risk of passing along HIV to others. Consistent adherence to an ARV regimen, monitoring, and testing are essential for continued confirmed viral suppression. Treatment as prevention rose to great prominence in 2011, as part of the HPTN 052 study, which shed light on the benefits of early treatment for HIV positive individuals.

Diane Havlir is a Professor of Medicine and Chief of the HIV/AIDS Division at the University of California, San Francisco. Her research considers novel therapeutic strategies to improve the lives of people with HIV and to support public health initiatives in East Africa. She was elected to the National Academy of Medicine in 2019.
References
- Medscape Today (2002)