Related Research Articles

An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation.
Tissue expansion is a technique used by plastic, maxillofacial and reconstructive surgeons to cause the body to grow additional skin, bone, or other tissues. Other biological phenomena such as tissue inflammation can also be considered expansion.
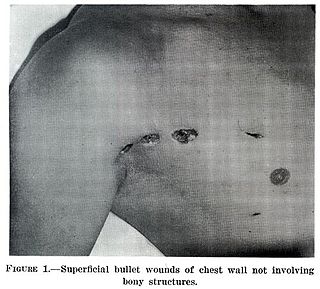
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin, or a contusion from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a wound is an acute injury that damages the epidermis of the skin. To heal a wound, the body undertakes a series of actions collectively known as the wound healing process.
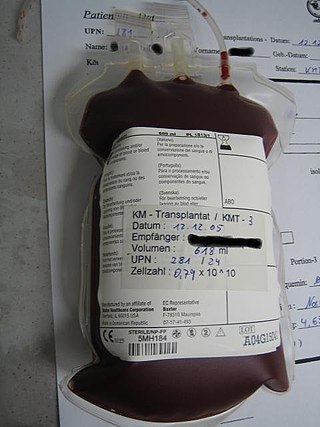
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous, allogeneic or syngeneic.

Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft.
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis.

The corneal endothelium is a single layer of endothelial cells on the inner surface of the cornea. It faces the chamber formed between the cornea and the iris.
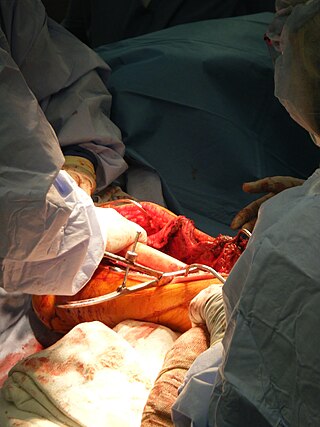
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured without bone grafting, but the risk is greater for large fractures like compound fractures.
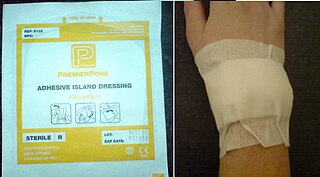
A dressing is a sterile pad or compress applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place. Many modern dressings are self-adhesive.

Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that removes hair follicles from one part of the body, called the 'donor site', to a bald or balding part of the body known as the 'recipient site'. The technique is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness. In this minimally invasive procedure, grafts containing hair follicles that are genetically resistant to balding are transplanted to the bald scalp.

Venous ulcer is defined by the American Venous Forum as "a full-thickness defect of skin, most frequently in the ankle region, that fails to heal spontaneously and is sustained by chronic venous disease, based on venous duplex ultrasound testing." Venous ulcers are wounds that are thought to occur due to improper functioning of venous valves, usually of the legs. They are an important cause of chronic wounds, affecting 1% of the population. Venous ulcers develop mostly along the medial distal leg, and can be painful with negative effects on quality of life.
A chronic wound is a wound that does not heal in an orderly set of stages and in a predictable amount of time the way most wounds do; wounds that do not heal within three months are often considered chronic. Chronic wounds seem to be detained in one or more of the phases of wound healing. For example, chronic wounds often remain in the inflammatory stage for too long. To overcome that stage and jump-start the healing process, a number of factors need to be addressed such as bacterial burden, necrotic tissue, and moisture balance of the whole wound. In acute wounds, there is a precise balance between production and degradation of molecules such as collagen; in chronic wounds this balance is lost and degradation plays too large a role.
The history of wound care spans from prehistory to modern medicine. Wounds naturally heal by themselves, but hunter-gatherers would have noticed several factors and certain herbal remedies would speed up or assist the process, especially if it was grievous. In ancient history, this was followed by the realisation of the necessity of hygiene and the halting of bleeding, where wound dressing techniques and surgery developed. Eventually the germ theory of disease also assisted in improving wound care.

Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a vacuum assisted closure (VAC), is a therapeutic technique using a suction pump, tubing, and a dressing to remove excess exudate and promote healing in acute or chronic wounds and second- and third-degree burns. The therapy involves the controlled application of sub-atmospheric pressure to the local wound environment using a sealed wound dressing connected to a vacuum pump. The use of this technique in wound management started in the 1990s and this technique is often recommended for treatment of a range of wounds including dehisced surgical wounds, closed surgical wounds, open abdominal wounds, open fractures, pressure injuries or pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, venous insufficiency ulcers, some types of skin grafts, burns, sternal wounds. It may also be considered after a clean surgery in a person who is obese.
A hydrocolloid dressing is an opaque or transparent dressing for wounds. A hydrocolloid dressing is biodegradable, breathable, and adheres to the skin, so no separate taping is needed.
Transplantable organs and tissues may refer to both organs and tissues that are relatively often transplanted, as well as organs and tissues which are relatively seldom transplanted. In addition to this it may also refer to possible-transplants which are still in the experimental stage.
Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is an autoimmune disorder stemming from an underlying tumor. It is hypothesized that antigens associated with the tumor trigger an immune response resulting in blistering of the skin and mucous membranes.
A coma blister, or coma bullae, is a skin lesion or blister that typically arises due to pressure in an individual with impaired consciousness. They vary in size, ranging from 4 to 5 centimeters in diameter, and may appear hemorrhagic or blood filled. Coma blisters are usually found in the extremities and trunk. These types of blisters have been associated with the overdose of central nervous system (CNS) depressants especially barbiturates, but also tricyclic antidepressants, hypnotics, benzodiazepines, opiates, antipsychotics, and alcohol. However, studies have found that coma blisters are not caused by the toxicity of these drugs, but due to hypoxia and external pressure on the comatose individual's skin from being immobilized. Coma blisters have been frequently found on individuals who have overdosed on drugs, but have also been found on individuals with chronic kidney failure, hypercalcemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and a variety of neurologic conditions. Coma blisters are more frequent in adults and less common among children as demonstrated by the few cases published in literature.

Diabetic foot ulcer is a major complication of diabetes mellitus, and probably the major component of the diabetic foot.
Fat transfer, also known as fat graft, lipomodelling, or fat injections, is a surgical process in which a person's own fat is transferred from one area of the body to another area. The major aim of this procedure is to improve or augment the area that has irregularities and grooves. Carried out under either general anesthesia or local anesthesia, the technique involves 3 main stages: fat harvesting, fat processing, fat injection.
References
- ↑ Costanzo, U; Streit, M; Braathen, LR (2007). "Autologous suction blister grafting for chronic leg ulcers". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 22 (1): 7–10. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02148.x. PMID 18181967.