
The Mali Empire was an empire in West Africa from c. 1226 to 1670. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa. At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of its language, laws, and customs.

The Bambara are a Mandé ethnic group native to much of West Africa, primarily southern Mali, Ghana, Guinea, Burkina Faso and Senegal. They have been associated with the historic Bambara Empire. Today, they make up the largest Mandé ethnic group in Mali, with 80% of the population speaking the Bambara language, regardless of ethnicity.

The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a lingua franca in much of West Africa. Virtually all of Mandinka people are adherent to Islam, mostly based on the Maliki jurisprudence. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali.

The Mande languages are a family of languages spoken in several countries in West Africa by the Mandé peoples. They include Maninka (Malinke), Mandinka, Soninke, Bambara, Kpelle, Jula (Dioula), Bozo, Mende, Susu, and Vai. There are around 60 to 75 languages spoken by 30 to 40 million people, chiefly in Burkina Faso, Mali, Senegal, the Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast and also in southern Mauritania, northern Ghana, northwestern Nigeria and northern Benin.
The Dyula are a Mande ethnic group inhabiting several West African countries, including Mali, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, and Burkina Faso.
The Mandé peoples are a linguistic grouping of those African nations who speak Mande languages. They are not a coherent ethnic or cultural group. The various Mandé-speaking nations are concentrated in the western regions of West Africa.
Begho was a city located in Ghana, located just south of its successor community, Hani.

The Soninke (Sarakolleh) people are a West African Mande-speaking ethnic group found in Mali, southern Mauritania, eastern Senegal, The Gambia, and Guinea. They speak the Soninke language, also called the Serakhulle or Azer language, which is one of the Mande languages. Soninke people were the founders of the ancient empire of Ghana or Wagadou c. 200–1240 CE, Subgroups of Soninke include the Jakhanke, Maraka and Wangara. When the Ghana empire was destroyed, the resulting diaspora brought Soninkes to Mali, Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinée-Conakry, modern-day Republic of Ghana, Kano in Nigeria, and Guinea-Bissau where some of this trading diaspora was called Wangara, leading to the saying “when Americans landed on the moon, a Soninke was already there” in Senegal, with other versions across West Africa.

Bondoukou is a city in northeastern Ivory Coast, 420 km northeast of Abidjan. It is the seat of both Zanzan District and Gontougo Region. It is also a commune and the seat of and a sub-prefecture of Bondoukou Department.
The Wangara are a diaspora community of ethnic Soninke origin who served as specialized long-distance merchants throughout West Africa, particularly in Trans-Saharan trade. Originating from the Ghana Empire, over time the Wangara became integrated into numerous other communities and ethnic groups, particularly in Timbuktu, Agadez, Kano, Gao, Salaga, Kong, Bissa, Kankan, Fouta Jallon, Djenné as well as Bambouk, Bure, Lobi, and Bono goldfields and Borgu. They were practicing Muslims who helped spread the religion widely and served as clerics, political advisors, healers and marabouts, often following the Suwarian Tradition.
Touré is the French transcription of a West African surname. The name is probably derived from tùùré, the word for 'elephant' in Soninké, the language of the Ghana Empire. The clan existed as kings of Zaghari on the middle Niger before the Moroccan invasion of Ghana. A theory of their origin holds that the Touré are descended from the "Roum," pre-Arab North African soldiers, and local women.
Bole is a small town and is the capital of Bole district, a district in the Savannah Region of northern Ghana. Bole is connected by road to the town of Sawla and the town of Bamboi. Bole is home to the Bole District Hospital and post office. The Bole District covers an area of 4800 km2 land mass and has a population of about 87,656.

Ghanaian cuisine refers to the meals of the Ghanaian people. The main dishes of Ghana are centered around starchy staple foods, accompanied by either a sauce or soup as well as a source of protein. The primary ingredients for the vast majority of soups and stews are tomatoes, hot peppers, and onions. As a result of these main ingredients, most Ghanaian jollof rice, soups, and stews appear red or orange.
Daniel Laemouahuma Jatta is a Jola scholar and musician from Mandinary, Gambia, who pioneered the research and documentation of the akonting, a Jola folk lute, as well as the related Manjago folk lute, the buchundu, in the mid-1980s. Prior to Jatta's work, these instruments were largely unknown outside the rural villages of the Senegambia region of West Africa.

West African cuisine encompasses a diverse range of foods that are split between its 16 countries. In West Africa, many families grow and raise their own food, and within each there is a division of labor. Indigenous foods consist of a number of plant species and animals, and are important to those whose lifestyle depends on farming and hunting.
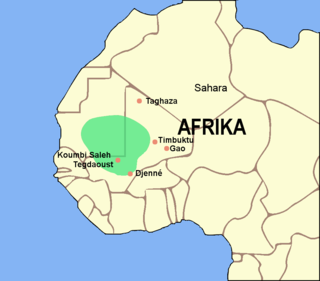
The Ghana Empire, also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadu, was a West African classical to post-classical era western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali.
The Jakhanke -- also spelled Jahanka, Jahanke, Jahanque, Jahonque, Diakkanke, Diakhanga, Diakhango, Dyakanke, Diakhanké, Diakanké, or Diakhankesare -- are a Manding-speaking ethnic group in the Senegambia region, often classified as a subgroup of the larger Soninke. The Jakhanke have historically constituted a specialized caste of professional Muslim clerics (ulema) and educators. They are centered on one larger group in Guinea, with smaller populations in the eastern region of The Gambia, Senegal, and in Mali near the Guinean border. Although generally considered a branch of the Soninke, their language is closer to Western Manding languages such as Mandinka.

Chadian cuisine is the cooking traditions, practices, foods and dishes associated with the Republic of Chad. Chadians use a medium variety of grains, vegetables, fruits and meats. Commonly consumed grains include millet, sorghum, and rice as staple foods. Commonly eaten vegetables include okra and cassava. A variety of fruits are also eaten. Meats include mutton, chicken, pork, goat, fish, lamb and beef. The day's main meal is typically consumed in the evening on a large communal plate, with men and women usually eating in separate areas. This meal is typically served on the ground upon a mat, with people sitting and eating around it.

The boubou or grand boubou is a flowing wide-sleeved robe worn across West Africa, and to a lesser extent in North Africa, related to the dashiki suit.










