
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet. Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris but classified as var. saccharifera . Its closest wild relative is the sea beet.
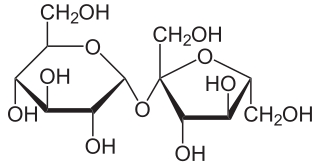
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula C
12H
22O
11.

The modern combine harvester, also called a combine, is a machine designed to harvest a variety of cultivated seeds. Combine harvesters are one of the most economically important labour-saving inventions, significantly reducing the fraction of the population engaged in agriculture. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, rice, oats, rye, barley, corn (maize), sorghum, millet, soybeans, flax (linseed), sunflowers and rapeseed (canola). The separated straw is then either chopped onto the field and ploughed back in, or laid out in rows, ready to be baled and used for bedding and cattle feed.

A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.

Mechanised agriculture or agricultural mechanization is the use of machinery and equipment, ranging from simple and basic hand tools to more sophisticated, motorized equipment and machinery, to perform agricultural operations. In modern times, powered machinery has replaced many farm task formerly carried out by manual labour or by working animals such as oxen, horses and mules.

Brazil is the world's second largest producer of ethanol fuel. Brazil and the United States have led the industrial production of ethanol fuel for several years, together accounting for 85 percent of the world's production in 2017. Brazil produced 26.72 billion liters, representing 26.1 percent of the world's total ethanol used as fuel in 2017.

Engenho is a colonial-era Portuguese term for a sugar cane mill and the associated facilities. In Spanish-speaking countries such as Cuba and Puerto Rico, they are called ingenios. Both words mean engine. The word engenho usually only referred to the mill, but it could also describe the area as a whole including land, a mill, the people who farmed and who had a knowledge of sugar production, and a crop of sugar cane. A large estate was required because of the massive amount of labor needed to yield refined sugar, molasses, or rum from raw sugar cane. These estates were prevalent in Brazil, Cuba, Dominican Republic, and other countries in the Caribbean. Today, Brazil is still one of the world's major producers of sugar.
New Holland is a global full-line agricultural machinery manufacturer founded in New Holland, Pennsylvania, and now based in Turin, Italy. New Holland's products include tractors, combine harvesters, balers, forage harvesters, self-propelled sprayers, haying tools, seeding equipment, hobby tractors, utility vehicles and implements, and grape harvesters. Originally formed as the New Holland Machine Company in 1895, the company is now owned by CNH Industrial N.V., a company incorporated in the Netherlands.

Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, perennial grass that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sucrose, which accumulates in the stalk internodes. Sugarcanes belong to the grass family, Poaceae, an economically important flowering plant family that includes maize, wheat, rice, and sorghum, and many forage crops. It is native to the warm temperate and tropical regions of India, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea.
Ratooning is the agricultural practice of harvesting a monocot crop by cutting most of the above-ground portion but leaving the roots and the growing shoot apices intact so as to allow the plants to recover and produce a fresh crop in the next season. This practice is widely used in the cultivation of crops such as rice, sugarcane, banana, and pineapple. Ratoon crops cannot be perennially renewed, and may be harvested only for a few seasons, as a decline in yield tends to occur due to increased crowding, damage by pests and diseases, and decreasing soil fertility.
A cane knife is a large hand-wielded cutting tool similar to a machete. Its use is prevalent in the harvesting of sugarcane in dominant cane-growing countries such as Peru, Brazil, Colombia, Australia, South Africa, Ecuador, Cuba, Jamaica, the Philippines and parts of the United States, especially Louisiana and Florida, as well as Hawaii. It is the primary tool used in countries that do not employ mechanical means for harvesting cane.

Sustainable biofuel is biofuel produced in a sustainable manner. It is not based on petroleum or other fossil fuels. It includes not using plants that are used for food stuff to produce the fuel thus disrupting the world's food supply.

Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the farm implements that they tow or operate. Machinery is used in both organic and nonorganic farming. Especially since the advent of mechanised agriculture, agricultural machinery is an indispensable part of how the world is fed.
Sugar Cane Growers Cooperative of Florida is an agricultural enterprise that harvests, transports and processes sugarcane grown primarily in Palm Beach County, Florida and markets the raw sugar and blackstrap molasses through the Florida Sugar and Molasses Exchange. The Cooperative is made up of 45 grower-owners who produce sugarcane on approximately 70,000 acres, located in the Everglades Agricultural Area (EAA). The raw sugar is marketed to one of the ASR Group's sugar refineries. The Cooperative produces more than 350,000 tons of raw sugar annually.

Non-centrifugal cane sugar (NCS) is the technical name given to traditional raw sugar obtained by evaporating water from sugarcane juice. NCS is internationally recognized as a discrete and unique product by the FAO since 1964 and by the World Customs Organization (WCO) since 2007. WCO defines NCS as "cane sugar obtained without centrifugation". It also states that "the product contains only natural anhedral micro-crystals, of irregular shape, not visible to the naked eye, which are surrounded by molasses' residues and other constituents of sugar cane". NCS is produced in most sugarcane-growing regions of the world, being known by many different names such as panela, jaggery, or gur. Some varieties of muscovado are non-centrifugal.

Carmila Cane Lift is a heritage-listed piece of agricultural equipment at 49 Hindles Road, Carmila, Isaac Region, Queensland, Australia. It was built between the 1920s and the 1960s. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 5 February 2010.

Mount Martin Cane Lift is a heritage-listed piece of agricultural equipment at Mirani Mount Ossa Road, Mount Martin, Mackay Region, Queensland, Australia. It was built before 1939. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 5 February 2010.

The Leap Cane Lift is a heritage-listed piece of agricultural equipment at Bruce Highway, The Leap, Mackay Region, Queensland, Australia. It was built before the 1960s. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 5 February 2010.

Sugar has been produced in India since ancient 1200BC and then it spread to other parts. Sugarcane is a native of tropical Indian and Pakistan subcontinent then to Southeast Asia. In India, sugarcane is planted thrice a year in October, March and July depending on part of the country. Most of the sugar production in India takes at local Cooperative Sugar mills. After gaining Independence, India made serious plans for overall industrial development of sugar industry.
The sugar industry of the United States produces sugarcane and sugar beets, operates sugar refineries, and produces and markets refined sugars, sugar-sweetened goods, and other products. The United States is among the world's largest sugar producers. Unlike most other sugar producing countries, the United States has both large and well-developed sugarcane and sugar beet industries. Refined sugarcane, processed sugar beet, and high-fructose corn syrup are all commonly used in the U.S. as added sugars to sweeten food and beverages.















