
Brachydactyly is a medical term denoting the presence of abnormally short digits at birth. The shortness is relative to the length of other long bones and other parts of the body. Brachydactyly is an inherited, dominant trait. It most often occurs as an isolated dysmelia, but can also occur with other anomalies as part of many congenital syndromes. Brachydactyly may also be a signal that one is at risk for congenital heart disease due to the association between congenital heart disease and Carpenter syndrome and the link between Carpenter syndrome and brachydactyly.

X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation, see zygosity. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers.

Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis), which affects the shape of the head and face. The syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands and feet, such as wide and deviated thumbs and big toes.
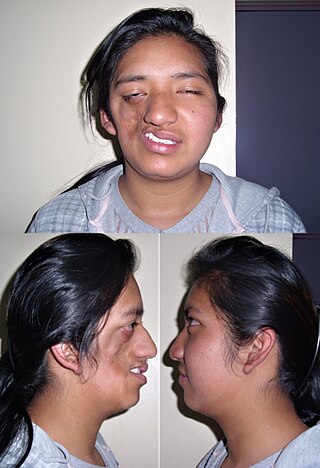
Parry–Romberg syndrome (PRS) is a rare disease presenting in early childhood characterized by progressive shrinkage and degeneration of the tissues beneath the skin, usually on only one side of the face but occasionally extending to other parts of the body. An autoimmune mechanism is suspected, and the syndrome may be a variant of localized scleroderma, but the precise cause and pathogenesis of this acquired disorder remains unknown. It has been reported in the literature as a possible consequence of sympathectomy. The syndrome has a higher prevalence in females and typically appears between 5 and 15 years of age. There has been only one case report of the syndrome appearing in older adults: a 43-year-old woman with symptoms appearing at the age of 33.
Aarskog–Scott syndrome (AAS) is a rare disease inherited as X-linked and characterized by short stature, facial abnormalities, skeletal and genital anomalies. This condition mainly affects males, although females may have mild features of the syndrome.

Young–Simpson syndrome (YSS) is a rare congenital disorder with symptoms including hypothyroidism, heart defects, facial dysmorphism, cryptorchidism in males, hypotonia, intellectual disability, and postnatal growth retardation.

Weill–Marchesani syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by short stature; an unusually short, broad head (brachycephaly) and other facial abnormalities; hand defects, including unusually short fingers (brachydactyly); and distinctive eye (ocular) abnormalities. It was named after ophthalmologists Georges Weill (1866–1952) and Oswald Marchesani (1900–1952) who first described it in 1932 and 1939, respectively.

Hanhart syndrome is a broadly classified medical condition consisting of congenital disorders that cause an undeveloped tongue and malformed extremities and fingers. There exist five types of Hanhart syndrome, with the severity and nature of the condition ranging widely on a case-by-case basis. Hanhart syndrome is classified as a rare disease, with approximately 30 known cases having been reported between 1932 and 1991. Early hypotheses believed that the disorder was caused by genetic conditions, with a more recent hypothesis demonstrating that the disorder may be caused by hemorrhagic lesions during prenatal development. The causal mechanism behind this vascular disruption is still unknown.

Orofaciodigital syndrome 1 (OFD1), also called Papillon-Léage and Psaume syndrome, is an X-linked congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the face, oral cavity, and digits with polycystic kidney disease and variable involvement of the central nervous system.

Orofaciodigital syndrome or oral-facial-digital syndrome is a group of at least 13 related conditions that affect the development of the mouth, facial features, and digits in between 1 in 50,000 to 250,000 newborns with the majority of cases being type I.
Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome, also called Keipert syndrome, is a rare congenital syndrome first described by J.A. Keipert and colleagues in 1973. The syndrome is characterized by a misshaped nose, broad thumbs and halluces, brachydactyly, sensorineural hearing loss, facial features such as hypertelorism, and developmental delay.

Ruzicka Goerz Anton syndrome is a rare genetic disease described by Ruzicka et al. in 1981. It is characterized by icthyosis, deafness, intellectual disability, and skeletal anomalies.

Heart-hand syndromes are a group of rare diseases that manifest with both heart and limb deformities.

Brachydactyly type D, also known as short thumb, stub thumb, or clubbed thumb, is a genetic trait clinically recognised by a thumb being relatively short and round with an accompanying wider nail bed. The distal phalanx of affected thumbs is approximately two-thirds the length of full-length thumbs. It is the most common type of brachydactyly, or shortness of digits, affecting approximately 2–3% of the population, and is associated with the HOXD13 gene, located on chromosome 2q31.1.
Thumb stiffness-brachydactyly-intellectual disability syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by thumb ankylosis due to symphalangism, brachydactyly type A, intellectual disabilities, mild facial dysmorphia and variable levels of obesity.
Fibular aplasia-ectrodactyly syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by aplasia/hypoplasia of the fibula, ectrodactyly, and/or brachydactyly/syndactyly. Additional symptoms include shortness of the femur and tibial/knee/hip/ankle defects. This disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Brachydactyly-long thumb syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by symmetric brachydactyly of the fingers accompanied by an abnormally long thumb, hypomobility of the shoulder and metacarpo-phalangeal joints, and heart conduction defects. Small feet and hands, small shoulders accompanied with short clavicles, clinodactyly, pectus excavatum, mild limb shortening, cardiomegaly, and pulmonic stenosis murmur have also been reported. It was first discovered when D W Hollister et al. described 4 affected members belonging to a 3-generation family. No new cases have been reported since 1981. This disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Dauwerse–Peters syndrome, also known as Short stature, facial dysmorphism, severe brachydactyly and syndactyly, is an extraordinarily rare novel genetic disorder which is characterized by a short height, depressed nasal bridge, flat facies, upward-slanting eyes, mild nostril anteversion, low-set ears, broad nasal root, severe generalized hand brachydactyly and 2nd-3rd toe syndactyly. Additional features include infertility due to azoospermia, radial and ulnar dysplasia, and pedal symphalangism. This disorder is extremely rare, since only 1 case has been reported in medical literature. This condition is caused by a chromosomal translocation.

Cardiospondylocarpofacial syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by cardiac, digital, osseous anomalies with facial dysmorphisms. Cardiospondylocarpofacial syndrome is believed to be caused by autosomal dominant mutations of the MAP3K7 gene.











