Related Research Articles

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that interconnects the cerebrum and diencephalon with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.

Brodmann area 40 (BA40) is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. The inferior part of BA40 is in the area of the supramarginal gyrus, which lies at the posterior end of the lateral fissure, in the inferior lateral part of the parietal lobe.

The fusiform gyrus, also known as the lateral occipitotemporal gyrus,is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inferior temporal gyrus below. Though the functionality of the fusiform gyrus is not fully understood, it has been linked with various neural pathways related to recognition. Additionally, it has been linked to various neurological phenomena such as synesthesia, dyslexia, and prosopagnosia.

The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The inferior frontal gyrus (IFG),, is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri, of the frontal lobe, and is part of the prefrontal cortex.

The middle frontal gyrus makes up about one-third of the frontal lobe of the human brain.
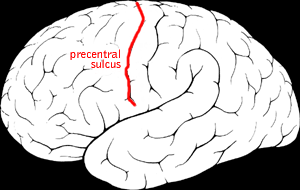
The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. A sulcus is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.
In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus is a furrow or fissure. It may be a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in the surface of a limb or an organ, most notably on the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles, as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The inferior parietal lobule lies below the horizontal portion of the intraparietal sulcus, and behind the lower part of the postcentral sulcus. Also known as Geschwind's territory after Norman Geschwind, an American neurologist, who in the early 1960s recognised its importance. It is a part of the parietal lobe.

In neuroanatomy, a sulcus is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus, creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures.
The terminal sulcus is a groove on the outer surface of the right atrium of the heart marking the transition between the sinus venarum cavarum and the rest of the right atrium. The terminal sulcus corresponds to the position of the terminal crest on the inner surface of the right atium. The terminal sulcus indicate the position of the sinoatrial node.

The inferior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the middle frontal gyrus and the inferior frontal gyrus.

The superior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the superior frontal gyrus and the middle frontal gyrus, that defines the lateral limit of the Superior frontal gyrus.

In the occipital lobe, the lateral occipital sulcus, where present, divides the lateral, or middle occipital gyrus into a superior and an inferior part, which are then continuous in front with the parietal and temporal lobes. The anterior portion is often incomplete, but in some individuals it may encounter the superior temporal sulcus whilst the posterior portion originates from the middle of the curved lunate sulcus, or from a curved portion of the transverse occipital sulcus if absent.

The inferior surface of the temporal lobe is concave, and is continuous posteriorly with the tentorial surface of the occipital lobe. It is traversed by the inferior temporal sulcus, which extends from near the occipital pole behind, to within a short distance of the temporal pole in front, but is frequently subdivided by bridging gyri.
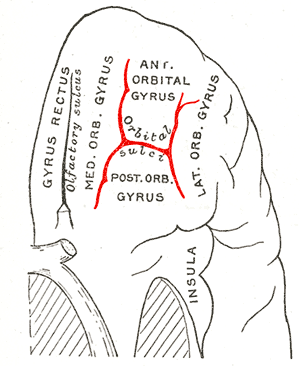
The inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus

The inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus. These are named, from their position, the medial, anterior, lateral, and posterior, orbital gyri. The medial orbital gyrus presents a well-marked antero-posterior sulcus, the olfactory sulcus, for the olfactory tract; the portion medial to this is named the straight gyrus, and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.

The orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus also known as the pars orbitalis is the orbital part of the inferior frontal gyrus.

The occipital gyri (OcG) are three gyri in parallel, along the lateral portion of the occipital lobe, also referred to as a composite structure in the brain. The gyri are the superior occipital gyrus, the middle occipital gyrus, and the inferior occipital gyrus, and these are also known as the occipital face area. The superior and inferior occipital sulci separates the three occipital gyri.
References
- ↑ Magee, David J (2014). Orthopedic Physical Assessment (6th ed.). Saunders. pp. 265, 314–315. ISBN 978-1-4557-0977-9.