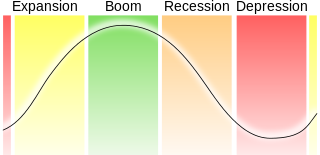
In economics, Kondratiev waves are hypothesized cycle-like phenomena in the modern world economy. The phenomenon is closely connected with the technology life cycle.

Data mining is the process of extracting and discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and statistics with an overall goal of extracting information from a data set and transforming the information into a comprehensible structure for further use. Data mining is the analysis step of the "knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating.

Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and using meteorology to project how the atmosphere will change at a given place.

Climatology or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. This modern field of study is regarded as a branch of the atmospheric sciences and a subfield of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology now includes aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry.

Robert McDowell Parker Jr. is a retired U.S. wine critic. His wine ratings on a 100-point scale and his newsletter The Wine Advocate are influential in American wine buying and are therefore a major factor in setting the prices for newly released Bordeaux wines. This made him the most widely known and influential wine critic in the world.
The Lucas critique, named for American economist Robert Lucas's work on macroeconomic policymaking, argues that it is naive to try to predict the effects of a change in economic policy entirely on the basis of relationships observed in historical data, especially highly aggregated historical data. More formally, it states that the decision rules of Keynesian models—such as the consumption function—cannot be considered as structural in the sense of being invariant with respect to changes in government policy variables. The Lucas critique is significant in the history of economic thought as a representative of the paradigm shift that occurred in macroeconomic theory in the 1970s towards attempts at establishing micro-foundations.
Institutional economics focuses on understanding the role of the evolutionary process and the role of institutions in shaping economic behavior. Its original focus lay in Thorstein Veblen's instinct-oriented dichotomy between technology on the one side and the "ceremonial" sphere of society on the other. Its name and core elements trace back to a 1919 American Economic Review article by Walton H. Hamilton. Institutional economics emphasizes a broader study of institutions and views markets as a result of the complex interaction of these various institutions. The earlier tradition continues today as a leading heterodox approach to economics.

Steven David Levitt is an American economist and co-author of the best-selling book Freakonomics and its sequels. Levitt was the winner of the 2003 John Bates Clark Medal for his work in the field of crime, and is currently the William B. Ogden Distinguished Service Professor of Economics at the University of Chicago as well as the Faculty Director and Co-Founder of the Center for Radical Innovation for Social Change at the University of Chicago which incubates the Data Science for Everyone coalition. He was co-editor of the Journal of Political Economy published by the University of Chicago Press until December 2007. In 2009, Levitt co-founded TGG Group, a business and philanthropy consulting company. He was chosen as one of Time magazine's "100 People Who Shape Our World" in 2006. A 2011 survey of economics professors named Levitt their fourth favorite living economist under the age of 60, after Paul Krugman, Greg Mankiw and Daron Acemoglu.

Freakonomics: A Rogue Economist Explores the Hidden Side of Everything is the debut non-fiction book by University of Chicago economist Steven Levitt and New York Times journalist Stephen J. Dubner. Published on April 12, 2005, by William Morrow, the book has been described as melding pop culture with economics. By late 2009, the book had sold over 4 million copies worldwide. Based on the success of the original book, Levitt and Dubner have grown the Freakonomics brand into a multi-media franchise, with a sequel book, a feature film, a regular radio segment on National Public Radio, and a weekly blog.
The Paris Wine Tasting of 1976, also known as the Judgment of Paris, was a wine competition organized in Paris on 24 May 1976 by Steven Spurrier, a British wine merchant and his colleague, Patricia Gallagher, in which French judges carried out two blind tasting comparisons: one of top-quality Chardonnays and another of red wines. A Californian wine rated best in each category, which caused surprise as France was generally regarded as being the foremost producer of the world's best wines. Spurrier sold only French wine and believed that the California wines would not win.
Blinded wine tasting is wine tasting undertaken in circumstances in which the tasters are kept unaware of the wines' identities. The blind approach is routine for wine professionals who wish to ensure impartiality in the judgment of the quality of wine during wine competitions or in the evaluation of a sommelier for professional certification. More recently wine scientists have used blinded tastings to explore the objective parameters of the human olfactory system as they apply to the ability of wine drinkers to identify and characterize the extraordinary variety of compounds that contribute to a wine’s aroma. Similarly, economists testing hypotheses relating to the wine market have used the technique in their research. Some blinded trials among wine consumers have indicated that people can find nothing in a wine's aroma or taste to distinguish between ordinary and pricey brands. Academic research on blinded wine tastings have also cast doubt on the ability of professional tasters to judge wines consistently.
Predictive analytics encompasses a variety of statistical techniques from data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events.
Economic discrimination is discrimination based on economic factors. These factors can include job availability, wages, the prices and/or availability of goods and services, and the amount of capital investment funding available to minorities for business. This can include discrimination against workers, consumers, and minority-owned businesses.

Orley Clark Ashenfelter is an American economist and the Joseph Douglas Green 1895 Professor of Economics at Princeton University. His areas of specialization include labor economics, econometrics, and law and economics. He was influential in contributing to the applied turn in economics.
Ian Ayres is an American lawyer and economist. Ayres is a professor at the Yale Law School and at the Yale School of Management.
Epagogix is a UK-based company founded in 2003 that uses neural networks and analytical software to predict which movies will provide a good possibility of return on investments and which movie scripts or plots will be successful. It was featured in an article by Malcolm Gladwell in The New Yorker. It has also been featured in Super Crunchers, Ian Ayres' book about number analysis, in CIO magazine and in Kevin Slavin's TED talk.
The Judgment of Princeton was a wine tasting event held on 8 June 2012 during a conference of the American Association of Wine Economists held at Princeton University in Princeton, New Jersey. The purpose of this event was to compare, by a blind tasting, of several French wines against wines produced in New Jersey in order to gauge the quality and development of the New Jersey wine industry. Because New Jersey's wine industry is relatively young and small, it has received little attention in the world wine market. The state's wine production has experienced growth in recent years largely as a result of state legislators offering new opportunities for winery licensing and repealing Prohibition-era laws that have constrained the industry's development in past years. This event was modeled after a 1976 blind tasting event dubbed the "Judgment of Paris" in which French wines were compared to several wines produced in California when that state's wine industry was similarly young and developing. The New Jersey wine industry heralded the results and asserted that the rating of New Jersey wines by the blind tasting's judges was a victory for the state's wine industry.
The American Association of Wine Economists (AAWE) is a non-profit, educational organization based in New York City.

Smart cities seek to implement information and communication technologies (ICT) to improve the efficiency and sustainability of urban spaces while reducing costs and resource consumption. In the context of surveillance, smart cities monitor citizens through strategically placed sensors around the urban landscape, which collect data regarding many different factors of urban living. From these sensors, data is transmitted, aggregated, and analyzed by governments and other local authorities to extrapolate information about the challenges the city faces in sectors such as crime prevention, traffic management, energy use and waste reduction. This serves to facilitate better urban planning and allows governments to tailor their services to the local population.
Gregory V. Jones is an American research climatologist specializing in the climatology of viticulture, with a focus on how climate variation influences vine growth, wine production, and the quality of wine produced. Jones serves as the CEO of Abacela Vineyards and Winery in Roseburg, Oregon. Previously he served as the Director of the Center for Wine Education and is Professor of Environmental Studies at Linfield College in McMinnville, Oregon and as the Director of the Division of Business, Communication and the Environment at Southern Oregon University in Ashland, Oregon and was Professor in the University's Environmental Science and Policy Program.









