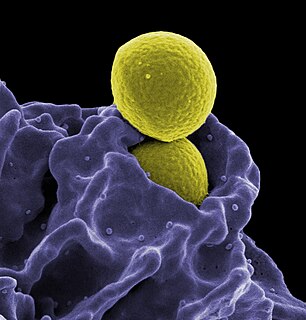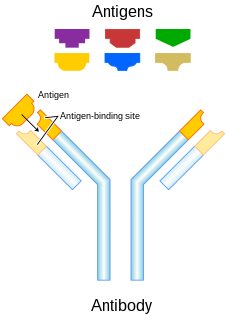
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen, via the Fab's variable region. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize its target directly. Depending on the antigen, the binding may impede the biological process causing the disease or may activate macrophages to destroy the foreign substance. The ability of an antibody to communicate with the other components of the immune system is mediated via its Fc region, which contains a conserved glycosylation site involved in these interactions. The production of antibodies is the main function of the humoral immune system.

The immune system is a host defense system comprising many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity. In humans, the blood–brain barrier, blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier, and similar fluid–brain barriers separate the peripheral immune system from the neuroimmune system, which protects the brain.

B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system by secreting antibodies. Additionally, B cells present antigen and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ..
Humoral immunity or humoural immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules found in extracellular fluids such as secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides. Humoral immunity is so named because it involves substances found in the humors, or body fluids. It contrasts with cell-mediated immunity. Its aspects involving antibodies are often called antibody-mediated immunity.
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. For example, the epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized are also epitopes.
Cell-mediated immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies, but rather involves the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in response to an antigen. Historically, the immune system was separated into two branches: humoral immunity, for which the protective function of immunization could be found in the humor and cellular immunity, for which the protective function of immunization was associated with cells. CD4 cells or helper T cells provide protection against different pathogens. Naive T cells, mature T cells that have yet to encounter an antigen, are converted into activated effector T cells after encountering antigen-presenting cells (APCs). These APCs, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells in some circumstances, load antigenic peptides onto the MHC of the cell, in turn presenting the peptide to receptors on T cells. The most important of these APCs are highly specialized dendritic cells; conceivably operating solely to ingest and present antigens.

Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells, plasmocytes, plasmacytes, or effector B cells, are white blood cells that secrete large volumes of antibodies. They are transported by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system. Plasma cells originate in the bone marrow; B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modelled after the receptors of the precursor B cell. Once released into the blood and lymph, these antibody molecules bind to the target antigen and initiate its neutralization or destruction.

An opsonin is any molecule that enhances phagocytosis by marking an antigen for an immune response or marking dead cells for recycling. Opson in ancient Greece referred to the delicious side-dish of any meal, versus the sitos, or the staple of the meal.
An immunogen is an antigen or any substance that may be specifically bound by components of the immune system. The term antigen arises from its ability to induce generation of antibodies. Despite the fact that all antigens are recognized by specific lymphocytes or by antibodies, not every antigen can evoke an immune response. Those antigens that are capable of inducing an immune response are said to be immunogenic and are called immunogens.
'Antigen processing or cytosolic' pathway is an immunological process that prepares antigens for presentation to special cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes. It is considered to be a stage of antigen presentation pathways. This process involves two distinct pathways for processing of antigens from an organism's own (self) proteins or intracellular pathogens, or from phagocytosed pathogens ; subsequent presentation of these antigens on class I or class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules is dependent on which pathway is used. Both MHC class I and II are required to bind antigen before they are stably expressed on a cell surface. MHC I antigen presentation typically involves the endogenous pathway of antigen processing, and MHC II antigen presentation involves the exogenous pathway of antigen processing. Cross-presentation involves parts of the exogenous and the endogenous pathways but ultimately involves the latter portion of the endogenous pathway.

An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen complexed with major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs) on their surfaces; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using their T cell receptors (TCRs). These cells process antigens and present them to T-cells.

Clonal selection theory is a scientific theory in immunology that explains the functions of cells (lymphocytes) of the immune system in response to specific antigens invading the body. The concept was introduced by the Australian doctor Frank Macfarlane Burnet in 1957, in an attempt to explain the formation of a diversity of antibodies during initiation of the immune response. The theory has become the widely accepted model for how the immune system responds to infection and how certain types of B and T lymphocytes are selected for destruction of specific antigens.

An immune complex, sometimes called an antigen-antibody complex, is a molecule formed from the integral binding of an antibody to a soluble antigen. The bound antigen and antibody act as a unitary object, effectively an antigen of its own with a specific epitope. After an antigen-antibody reaction, the immune complexes can be subject to any of a number of responses, including complement deposition, opsonization, phagocytosis, or processing by proteases. Red blood cells carrying CR1-receptors on their surface may bind C3b-coated immune complexes and transport them to phagocytes, mostly in liver and spleen, and return to the general circulation.

Antigen presentation describes a vital immune process which is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognise only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now bound to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), is transported to the surface of the cell, a process known as presentation, where it can be recognized by a T cell receptor. If there has been an infection with viruses or bacteria, the cell will present an endogenous or exogenous peptide fragment derived from the antigen bound to MHC molecules. There are two types of MHC molecules which differ in the of the antigens: MHC class I molecules (MHC-I) bind peptides from the cell cytosol, while peptides generated in the endocytic vesicles after internalisation are bound to MHC class II (MHC-II). Cellular membranes separate these two cellular environments - intracellular and extracellular. Each T cell can finally recognise only ten to hundreds copies of a unique sequence of a single peptide among thousands of other peptides presented on the very same cell because MHC molecule in one cell can bind quite a large range of peptides.

In immunology, the CD3 T cell co-receptor helps to activate both the cytotoxic T cell and also T helper cells. It consists of a protein complex and is composed of four distinct chains. In mammals, the complex contains a CD3γ chain, a CD3δ chain, and two CD3ε chains. These chains associate with the T-cell receptor (TCR) and the ζ-chain (zeta-chain) to generate an activation signal in T lymphocytes. The TCR, ζ-chain, and CD3 molecules together constitute the TCR complex.
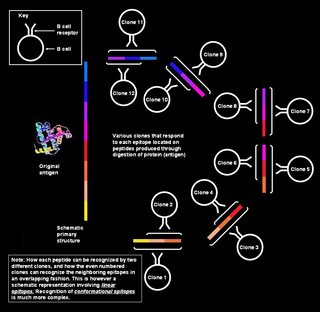
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.

B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, also known as CD19 molecule, B-Lymphocyte Surface Antigen B4, T-Cell Surface Antigen Leu-12 and CVID3 is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the gene CD19. In humans, CD19 is expressed in all B lineage cells, except for plasma cells, and in follicular dendritic cells. CD19 plays two major roles in human B cells. It acts as an adaptor protein to recruit cytoplasmic signaling proteins to the membrane and it works within the CD19/CD21 complex to decrease the threshold for B cell receptor signaling pathways. Due to its presence on all B cells, it is a biomarker for B lymphocyte development, lymphoma diagnosis and can be utilized as a target for leukemia immunotherapies.

In immunology, an idiotype is a shared characteristic between a group of immunoglobulin or T cell receptor (TCR) molecules based upon the antigen binding specificity and therefore structure of their variable region. The variable region of antigen receptors of T cells (TCRs) and B cells (immunoglobulins) contain complementarity determining regions (CDRs) with unique amino acid sequences. They define the surface and properties of the variable region, determining the antigen specificity and therefore the idiotope of the molecule. Immunoglobulins or TCRs with a shared idiotope are the same idiotype. Antibody idiotype is determined by:
CD78 is a protein expressed on the surface of some immature and all mature B-cells. It is considered a pan-B cell antigen. Other names include Cdw78, Ba antigen, Leu21 and LO-panB-a.