Related Research Articles

A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself that rises and falls.

A limited-slip differential (LSD) is a type of differential gear train that allows its two output shafts to rotate at different speeds but limits the maximum difference between the two shafts. Limited-slip differentials are often known by the generic trademark Positraction, a brand name owned by General Motors and originally used for its Chevrolet branded vehicles.

A motor–generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor–generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line. Large motor–generators were widely used to convert industrial amounts of power while smaller motor–generators were used to convert battery power to higher DC voltages.
The Mississippi River–Gulf Outlet Canal is a 76 mi (122 km) channel constructed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers at the direction of Congress in the mid-20th century that provided a shorter route between the Gulf of Mexico and New Orleans' inner harbor Industrial Canal via the Intracoastal Waterway. In 2005, the MRGO channeled Hurricane Katrina's storm surge into the heart of Greater New Orleans, contributing significantly to the subsequent multiple engineering failures experienced by the region's hurricane protection network. In the aftermath the channel was closed. A permanent storm surge barrier was constructed in the MRGO in 2009, and the channel has been closed to maritime shipping.

A pneumatic motor, or compressed air engine, is a type of motor which does mechanical work by expanding compressed air. Pneumatic motors generally convert the compressed air energy to mechanical work through either linear or rotary motion. Linear motion can come from either a diaphragm or piston actuator, while rotary motion is supplied by either a vane type air motor, piston air motor, air turbine or gear type motor.

The Peterborough Lift Lock is a boat lift located on the Trent Canal in the city of Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, and is Lock 21 on the Trent-Severn Waterway.

Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from which it exits.

The Industrial Canal is a 5.5 mile (9 km) waterway in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. The waterway's proper name, as used by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and on NOAA nautical charts, is Inner Harbor Navigation Canal (IHNC). The more common "Industrial Canal" name is used locally, both by commercial mariners and by landside residents.

The Alte Weser Lighthouse is located offshore from the estuary mouth of the river Weser in the German Bight, southern North Sea. It was built on sand between 1961 and 1964. The lighthouse took over duties and replaced the historical Roter Sand Lighthouse on 1 September 1964. The latter had been built from 1883 to 1885.

The Falls of Foyers are two waterfalls on the River Foyers, which feeds Loch Ness, in Highland, Scotland, United Kingdom. They are located on the lower portion of the River Foyers, and consist of the upper falls, with a drop of 46 feet (14 m) and the lower falls, which drop 98 feet (30 m).
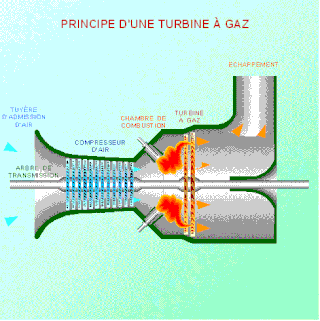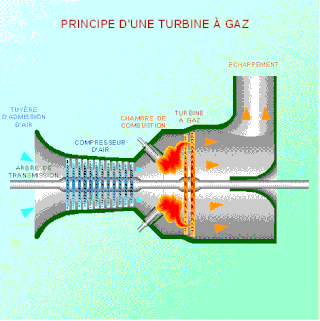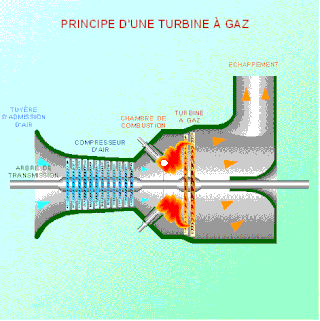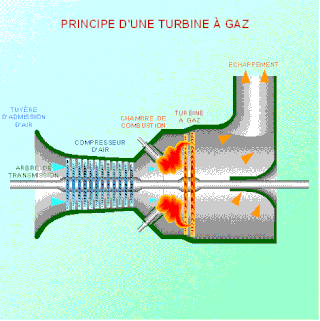
As the name suggests, gas turbine engine compressors provide the compression part of the gas turbine engine thermodynamic cycle. There are three basic categories of gas turbine engine compressor: axial compressor, centrifugal compressor and mixed flow compressor. A fourth, unusual, type is the free-piston gas generator, which combines the functions of compressor and combustion chamber in one unit.
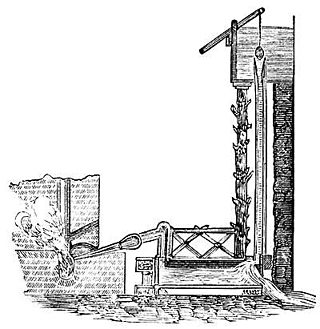
A trompe is a water-powered air compressor, commonly used before the advent of the electric-powered compressor. A trompe is somewhat like an airlift pump working in reverse.

A motor soft starter is a device used with AC electrical motors to temporarily reduce the load and torque in the powertrain and electric current surge of the motor during start-up. This reduces the mechanical stress on the motor and shaft, as well as the electrodynamic stresses on the attached power cables and electrical distribution network, extending the lifespan of the system.

The Krøderen Line is a heritage railway line connecting the Krøderen lake in Viken county, Norway, to the town of Vikersund. The 26-kilometre (16 mi) line was built as a narrow gauge branch line of the Randsfjord Line by the Norwegian State Railways (NSB) and opened in 1872. Passenger services were withdrawn in 1958, and freight traffic in 1985.

The Affric-Beauly hydro-electric power scheme for the generation of hydro-electric power is located in the western Highlands of Scotland. It is based around Glen Strathfarrar, Glen Cannich and Glen Affric, and Strathglass further downstream.
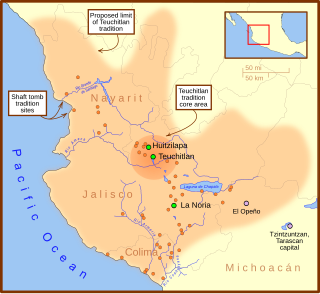
The Teuchitlán culture was one of several related cultures in West Mexico during the Late Formative to Classic period. Situated in the Tequila Valleys of Jalisco, the Teuchitlán culture shared in the tradition of burying some of their dead in shaft and chamber tombs. Archaeological work from the past few decades have demonstrated that West Mexico was not occupied by one homogeneous culture, historically referred to as the shaft tomb tradition, that stretched from Nayarit, Jalisco, and Colima. Instead, West Mexico was composed of multiple cultures with several distinct commonalities.

Castaic Power Plant, also known as the Castaic Pumped-Storage Plant, is a seven unit pumped-storage hydroelectric plant, operated by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, which provides peak load power from the falling water on the West Branch of the California State Aqueduct. It is a cooperative venture between the LADWP and the Department of Water Resources of the State of California. An agreement between the two organizations was signed on September 2, 1966, for construction of the project.

The Pandoh Dam is an embankment dam on the Beas River in Mandi district of Himachal Pradesh, India. Under the Beas Project, the dam was completed in 1977 and its primary purpose is hydroelectric power generation. Part of a run-of-the-river power scheme, it diverts the waters of the Beas to the southwest through a 38 km (24 mi) long system of tunnels and channels. The water is used for power generation at the Dehar Power House before being discharged into the Sutlej River, connecting both rivers. The power house has an installed capacity of 990 MW. The system diverts 256 cumecs of Beas waters to the Satluj River. The project was completed in 1977.

A drivetrain is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheels. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components.
The Tapovan Vishnugad Hydropower Plant is a 520 MW run-of-river hydroelectric project being constructed on Dhauliganga River in Chamoli District of Uttarakhand, India. The plant is expected to generate over 2.5 TWh of electricity annually.
References
- ↑ Røse, Torunn Engen (2015). Svingekammer eller luftputekammere i vannkraftverk (Master thesis) (in Norwegian). Norwegian University of Science and Technology. hdl:11250/2350124.