This article does not cite any sources .(April 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |

In automotive suspensions, a suspension link, control link or link is a suspension member, that attaches at only two points. One point being the body or frame of the vehicle and the other point attaching to the knuckle, upright, axle or another link. The link pivots on either a bushing or a ball joint at each attachment point. A link differs from a control arm because it can only control one of the degrees of freedom by itself.

Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two. Suspension systems must support both road holding/handling and ride quality, which are at odds with each other. The tuning of suspensions involves finding the right compromise. It is important for the suspension to keep the road wheel in contact with the road surface as much as possible, because all the road or ground forces acting on the vehicle do so through the contact patches of the tires. The suspension also protects the vehicle itself and any cargo or luggage from damage and wear. The design of front and rear suspension of a car may be different.

A bushing or rubber bushing is a type of vibration isolator. It provides an interface between two parts, damping the energy transmitted through the bushing. A common application is in vehicle suspension systems, where a bushing made of rubber separates the faces of two metal objects while allowing a certain amount of movement. This movement allows the suspension parts to move freely, for example, when traveling over a large bump, while minimizing transmission of noise and small vibrations through to the chassis of the vehicle. A rubber bushing may also be described as a flexible mounting or antivibration mounting.

In an automobile, ball joints are spherical bearings that connect the control arms to the steering knuckles. They are used on virtually every automobile made and work similarly to the ball-and-socket design of the human hip joint.
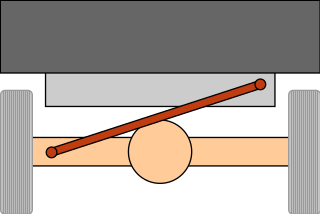
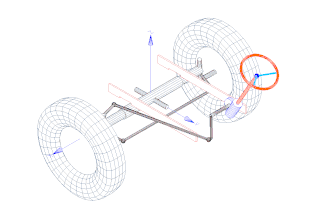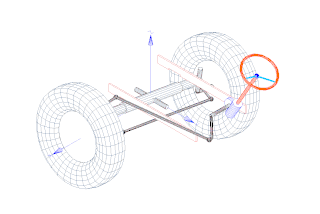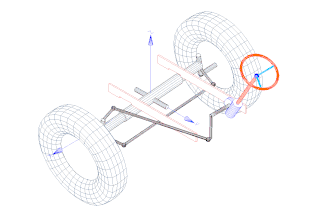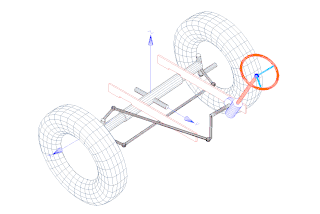
In the attached photo of a 5-link live axle suspension, the different types of links can be seen. These links work in tandem with the coil springs, dampers, and sway bar to control all six degrees of freedom of the axle. The upper links (orange) and the lower links (yellow) work in tandem to control the pitch, yaw and the fore and aft movement (surge). The panhard rod (green) controls the left and right movement (sway). While the springs and dampers (not shown) control the up and down movement (heave) and the roll is controlled by the sway bar (also not shown).

A coil spring, also known as a helical spring, is a mechanical device which is typically used to store energy and subsequently release it, to absorb shock, or to maintain a force between contacting surfaces. They are made of an elastic material formed into the shape of a helix which returns to its natural length when unloaded.

A shock absorber is a mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy which is then dissipated. Most shock absorbers are a form of dashpot.

Six degrees of freedom (6DoF) refers to the freedom of movement of a rigid body in three-dimensional space. Specifically, the body is free to change position as forward/backward (surge), up/down (heave), left/right (sway) translation in three perpendicular axes, combined with changes in orientation through rotation about three perpendicular axes, often termed yaw, pitch, and roll.
It takes a minimum of two links per wheel in a MacPherson strut-style suspension and a minimum of three links per wheel in a multi-link suspension.

The MacPherson strut is a type of automotive suspension system that uses the top of a telescopic damper as the upper steering pivot. It is widely used in the front suspension of modern vehicles and is named for American automotive engineer Earle S. MacPherson, who originally invented and developed the design.

A multi-link suspension is a type of vehicle suspension design typically used in independent suspensions, using three or more lateral arms, and one or more longitudinal arms. A wider definition considers any independent suspensions having three control links or more multi-link suspensions. These arms do not have to be of equal length, and may be angled away from their "obvious" direction. It was first introduced in the late 1960s on the Mercedes-Benz C111 and later on their W201 and W124 series.