
Sussex loop refer to a form of bronze objects found in South Downs/Weald area of England. [1]

Sussex loop refer to a form of bronze objects found in South Downs/Weald area of England. [1]
The loops are created from a thick rod of bronze that is bent in half to form a loop at one end. The rod is then shaped into a circle, with the ends of the rod curled and hooked back into the loop. [1] [2]

The first four loops were found at Hollingbury Camp (a hill-fort on the northern edge of Brighton, in East Sussex) in 1825. The name of the object is derived from their shape and area of discovery. Five were found in the Near Lewes hoard in 2011. The rest had been discovered within Sussex. In May 2013, two loops were discovered outside Sussex. [3]
The purpose of the loops remain unclear to archaeologists. Some suggest it may have been for adornments or for a ritual. [3]
Sussex is a historic county in South East England that is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the English Channel, and is divided for many purposes into the ceremonial counties of West Sussex and East Sussex.

Brighton is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the city of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located 47 mi (76 km) south of London. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age, Roman and Anglo-Saxon periods. The ancient settlement of "Brighthelmstone" was documented in the Domesday Book (1086). The town's importance grew in the Middle Ages as the Old Town developed, but it languished in the early modern period, affected by foreign attacks, storms, a suffering economy and a declining population. Brighton began to attract more visitors following improved road transport to London and becoming a boarding point for boats travelling to France. The town also developed in popularity as a health resort for sea bathing as a purported cure for illnesses.

East Sussex is a ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Kent to the north-east, West Sussex to the west, Surrey to the north-west, and the English Channel to the south. The largest settlement is the city of Brighton and Hove, and the county town is Lewes.

Hove is a seaside resort in East Sussex, England. Alongside Brighton, it is one of the two main parts of the city of Brighton and Hove.

Brighton and Hove is a unitary authority with city status in East Sussex, England. There are multiple villages alongside the seaside resorts of Brighton and Hove in the district. It is administered by Brighton and Hove City Council, which is currently under Labour majority control.

West Sussex is a ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Surrey to the north, East Sussex to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Hampshire to the west. The largest settlement is Crawley, and the county town is the city of Chichester.

A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some have hook and ring closures and a few have mortice and tenon locking catches to close them. Many seem designed for near-permanent wear and would have been difficult to remove.
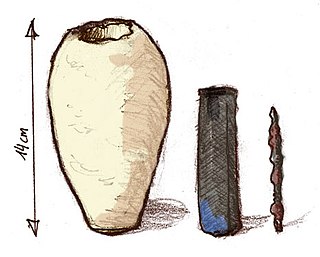
The Baghdad Battery is the name given to a set of three artifacts which were found together: a ceramic pot, a tube of copper, and a rod of iron. It was discovered in present-day Khujut Rabu, Iraq in 1936, close to the metropolis of Ctesiphon, the capital of the Parthian and Sasanian empires, and it is believed to date from either of these periods. Similar artifacts have been found at nearby sites.

Worthing is a seaside resort town in West Sussex, England, at the foot of the South Downs, 11 miles (18 km) west of Brighton, and 18 miles (29 km) east of Chichester. With a population of 113,094 and an area of 12.5 square miles (32.4 km2), the borough is the second largest component of the Brighton and Hove built-up area, the 15th most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Since 2010, northern parts of the borough, including the Worthing Downland Estate, have formed part of the South Downs National Park. In 2019, the Art Deco Worthing Pier was dubbed the best in Britain.
RPL is a handheld calculator operating system and application programming language used on Hewlett-Packard's scientific graphing RPN calculators of the HP 28, 48, 49 and 50 series, but it is also usable on non-RPN calculators, such as the 38, 39 and 40 series. Internally, it was also utilized by the 17B, 18C, 19B and 27S.

Star Carr is a Mesolithic archaeological site in North Yorkshire, England. It is around five miles (8 km) south of Scarborough. It is generally regarded as the most important and informative Mesolithic site in Great Britain. It is as important to the Mesolithic period as Stonehenge is to the Neolithic period or Scandinavian York is to understanding Viking Age Britain.

Prehistoric Wales in terms of human settlements covers the period from about 230,000 years ago, the date attributed to the earliest human remains found in what is now Wales, to the year AD 48 when the Roman army began a military campaign against one of the Welsh tribes. Traditionally, historians have believed that successive waves of immigrants brought different cultures into the area, largely replacing the previous inhabitants, with the last wave of immigrants being the Celts. However, studies of population genetics now suggest that this may not be true, and that immigration was on a smaller scale.

Mile Oak is a locality forming the northern part of the former parish of Portslade in the northwest corner of the city of Brighton and Hove, England. Now mostly residential, but originally an area of good-quality agricultural land, it covers the area north of Portslade village as far as the urban boundary.

Stanmer is a village on the northern edge of the city of Brighton and Hove, in the ceremonial county of East Sussex, England. It was formerly a civil parish until 1952 when it was split between Brighton and Falmer. In 1951 the parish had a population of 1097.

The Mold gold cape is a ceremonial cape of solid sheet-gold from Wales dating from about 1900–1600 BCE in the British Bronze Age. It was found at Bryn yr Ellyllon burial mound near Mold, Flintshire in 1833.

Worthing is a large seaside town in Sussex, England in the United Kingdom. The history of the area begins in Prehistoric times and the present importance of the town dates from the 19th century.

The Lewes avalanche occurred on 27 December 1836 in Lewes, East Sussex, when a huge build-up of snow on a chalk cliff overlooking the town collapsed into the settlement 100 metres (330 ft) below, destroying a row of cottages and killing eight people. It remains the deadliest avalanche on record in the United Kingdom.

Brighton and Hove City Council is the local authority of the city of Brighton and Hove. It is a unitary authority, having the powers of a non-metropolitan county and district council combined. It provides a full range of local government services including Council Tax billing, libraries, social services, processing planning applications, highways, waste collection and disposal, and it is a local education authority.

Whitehawk Camp is the remains of a causewayed enclosure on Whitehawk Hill near Brighton, East Sussex, England. Causewayed enclosures are a form of early Neolithic earthwork that were built in England from shortly before 3700 BC until at least 3500 BC, characterized by the full or partial enclosure of an area with ditches that are interrupted by gaps, or causeways. Their purpose is not known; they may have been settlements, or meeting places, or ritual sites. The Whitehawk site consists of four roughly concentric circular ditches, with banks of earth along the interior of the ditches evident in some places. There may have been a timber palisade on top of the banks. Outside the outermost circuit there are at least two more ditches, one of which is thought from radiocarbon evidence to date to the Bronze Age, about two thousand years after the earliest dated activity at the site.
This page lists significant events of 2022 in archaeology.