Related Research Articles

Bank robbery is the criminal act of stealing from a bank, specifically while bank employees and customers are subjected to force, violence, or a threat of violence. This refers to robbery of a bank branch or teller, as opposed to other bank-owned property, such as a train, armored car, or (historically) stagecoach. It is a federal crime in the United States.

William Francis Sutton Jr. was an American bank robber. During his forty-year robbery career he stole an estimated $2 million, and he eventually spent more than half of his adult life in prison and escaped three times. For his talent at executing robberies in disguises, he gained two nicknames, "Willie the Actor" and "Slick Willie". Sutton is also known as the namesake of the so-called Sutton's law, although he denied originating it.
Prognosis is a medical term for predicting the likelihood or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen or remain stable over time; expectations of quality of life, such as the ability to carry out daily activities; the potential for complications and associated health issues; and the likelihood of survival. A prognosis is made on the basis of the normal course of the diagnosed disease, the individual's physical and mental condition, the available treatments, and additional factors. A complete prognosis includes the expected duration, function, and description of the course of the disease, such as progressive decline, intermittent crisis, or sudden, unpredictable crisis.

Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is the condition of having dry eyes. Symptoms include dryness in the eye, irritation, redness, discharge, blurred vision, and easily fatigued eyes. Symptoms range from mild and occasional to severe and continuous. Dry eye syndrome can lead to blurred vision, instability of the tear film, increased risk of damage to the ocular surface such as scarring of the cornea, and changes in the eye including the neurosensory system.

Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Company[1893] 1 QB 256 is an English contract law decision by the Court of Appeal, which held an advertisement containing certain terms to get a reward constituted a binding unilateral offer that could be accepted by anyone who performed its terms. It is notable for its treatment of contract and of puffery in advertising, for its curious subject matter associated with medical quackery, and how the influential judges developed the law in inventive ways. Carlill is frequently discussed as an introductory contract case, and may often be the first legal case a law student studies in the law of contract.
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (DDx) is a method of analysis that distinguishes a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to diagnose the specific disease in a patient, or, at least, to consider any imminently life-threatening conditions. Often, each individual option of a possible disease is called a differential diagnosis.
The SOAP note is a method of documentation employed by healthcare providers to write out notes in a patient's chart, along with other common formats, such as the admission note. Documenting patient encounters in the medical record is an integral part of practice workflow starting with appointment scheduling, patient check-in and exam, documentation of notes, check-out, rescheduling, and medical billing. Additionally, it serves as a general cognitive framework for physicians to follow as they assess their patients.
Zebra is the American medical slang for a surprising, often exotic, medical diagnosis, especially when a more commonplace explanation is more likely. It is shorthand for the aphorism coined in the late 1940s by Theodore Woodward, professor at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, who instructed his medical interns: "When you hear hoofbeats behind you, don't expect to see a zebra." By 1960, the aphorism was widely known in medical circles. The saying is a warning against the statistical base rate fallacy where the likelihood of something like a disease among the population is not taken into consideration for an individual.
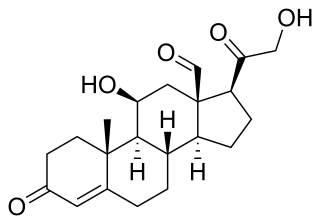
Hypoaldosteronism is an endocrinological disorder characterized by decreased levels of the hormone aldosterone. Similarly, isolated hypoaldosteronism is the condition of having lowered aldosterone without corresponding changes in cortisol.

Screening, in medicine, is a strategy used to look for as-yet-unrecognised conditions or risk markers. This testing can be applied to individuals or to a whole population without symptoms or signs of the disease being screened.

Myositis is a rarely-encountered medical condition characterized by inflammation affecting the muscles. The manifestations of this condition may include skin issues, muscle weakness, and the potential involvement of other organs. Additionally, systemic symptoms like weight loss, fatigue, and low-grade fever can manifest in individuals with myositis.
In statistical hypothesis testing, a type I error, or a false positive, is the rejection of the null hypothesis when it is actually true. For example, an innocent person may be convicted.
Self-diagnosis is the process of diagnosing, or identifying, medical conditions in oneself. It may be assisted by medical dictionaries, books, resources on the Internet, past personal experiences, or recognizing symptoms or medical signs of a condition that a family member previously had or currently has.
Presumptive tests, in medical and forensic science, analyze a sample and establish one of the following:
- The sample is definitely not a certain substance.
- The sample probably is the substance.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to medicine:

Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock itch. It can be taken by mouth or applied as a cream to the skin or in the vagina.
Disease or patient registries are collections of secondary data related to patients with a specific diagnosis, condition, or procedure, and they play an important role in post marketing surveillance of pharmaceuticals. Registries are different from indexes in that they contain more extensive data.
Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for a diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.
A glossary of terms used in clinical research.
Infectious diseases (ID), also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial (healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections. An ID specialist investigates and determines the cause of a disease. Once the cause is known, an ID specialist can then run various tests to determine the best drug to treat the disease. While infectious diseases have always been around, the infectious disease specialty did not exist until the late 1900s after scientists and physicians in the 19th century paved the way with research on the sources of infectious disease and the development of vaccines.
References
- Altman, Lawrence (1970-01-03). "A Law Named for Willie Sutton Assists Physicians". The New York Times.
- Rytand, David (1980). "Sutton's or Dock's Law?". New England Journal of Medicine. 302 (17): 972. doi:10.1056/NEJM198004243021726. PMID 6987522.
- ↑ "FACT CHECK: Willie Sutton - 'That's Where the Money Is'". Snopes.com. 10 June 2013. Retrieved 2018-11-17.
- ↑ Willie Sutton with Edward Linn, Where the Money Was: The Memoirs of a Bank Robber (New York, New York: Broadway Books, 2004; first published in 1976 by Viking Press of N.Y., N.Y.), page 160