Related Research Articles

Galilee is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee and the Lower Galilee.

The Sea of Galilee, also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth and the second-lowest lake in the world, with its elevation fluctuating between 215 and 209 metres below sea level. It is approximately 53 km (33 mi) in circumference, about 21 km (13 mi) long, and 13 km (8.1 mi) wide. Its area is 166.7 km2 (64.4 sq mi) at its fullest, and its maximum depth is approximately 43 metres (141 ft). The lake is fed partly by underground springs, but its main source is the Jordan River, which flows through it from north to south with the outflow controlled by the Degania Dam.

Tiberias is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Four Holy Cities, along with Jerusalem, Hebron, and Safed. In 2022, it had a population of 48,472.

Magdala was an ancient Jewish city on the shore of the Sea of Galilee, 5 km north of Tiberias. In the Babylonian Talmud it is known as Magdala Nunayya, and which some historical geographers think may refer to Tarichaea. It is believed to be the birthplace of Mary Magdalene. Until the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the Arab village of al-Majdal stood at the site of ancient Magdala. The Israeli municipality of Migdal now extends into the area.

The Lower Galilee is a region within the Northern District of Israel. The Lower Galilee is bordered by the Jezreel Valley to the south; the Upper Galilee to the north, from which it is separated by the Beit HaKerem Valley; the Jordan Rift Valley with the Jordan River and the Sea of Galilee to the east; and to the west, a segment of the Northern Coastal Plain known as the Zvulun Valley, stretching between the Carmel ridge and Acre. The Lower Galilee is the southern part of the Galilee. In Josephus' time, it was known to stretch in breadth from Xaloth (Iksal) to Bersabe, and in length from Cabul to Tiberias, a region that contains around 470 km2. It is called "Lower" since it is less mountainous than the Upper Galilee. The peaks of the Lower Galilee rise to 500 m (1,600 ft) above sea level. The tallest peaks are Mount Kamon at the northern part of the Lower Galilee, and Mount Tabor in the southern part.

Emek HaYarden Regional Council is a regional council comprising much of the western shore of the Sea of Galilee, the southern parts of its eastern shore, and the northern part of the Jordan Valley all the way to Beit She'an in the south.
The Lower Galilee Regional Council is a regional council in the Northern District of Israel. Lower Galilee Regional Council encompasses most of the settlements in the Lower Galilee with a population of 11,300 (2014), including three kibbutzim, ten moshavim and two community settlements, along with two youth villages located in its administrative territory.

The Ancient Galilee Boat, also known as the Jesus Boat, is an ancient fishing boat from the 1st century AD, discovered in 1986 on the north-west shore of the Sea of Galilee in Israel. The remains of the boat, 27 feet long, 7.5 feet wide and with a maximum preserved height of 4.3 feet, first appeared during a drought, when the waters of the Sea receded. Other than the dating, there is no evidence connecting the boat to Jesus or his disciples.
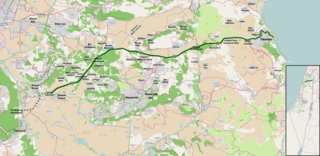
Highway 77 is an east-west highway in northern Israel. It crosses the Lower Galilee in the region of the Beit Netofa Valley. The road leads from the Tel Qashish Interchange nearby Yokneam Illit to Tiberias. It is 48km long. Its western section, from the Tel Qashish Interchange to the Golani Interchange is a freeway.

The Church of the Multiplication of the Loaves and Fish, shortened to the Church of the Multiplication, is a Roman Catholic church located at Tabgha, on the northwest shore of the Sea of Galilee in Israel. The modern church rests on the site of two earlier churches.

Yaquq was a Palestinian Arab village, which was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on May 1, 1948. It was located 12.5 km north of Tiberias and was built at the site of the ancient Jewish village of Huqoq.

According to Jewish tradition, the Tomb of Maimonides is located in Tiberias, Israel. Although Maimonides, a Sephardic Jew, died in Fustat, Egypt, on 12 December 1204, it is believed that he was only briefly buried in Fustat before being reinterred in Tiberias. Owing to his recognition as a prominent Jewish philosopher, his tomb is one of Israel's most important Jewish pilgrimage sites and is also among Tiberias' most visited tourist attractions. The site also serves as the burial place of Yohanan ben Zakkai, a prominent Tanna of the Second Temple period; and Isaiah Horowitz, a prominent Jewish mystic of the 16th/17th century.

Hammath Tiberias or Hammat Tiberias is an ancient archaeological site and an Israeli national park known as Hamat Tverya National Park, which is located on the adjacent to Tiberias on the road to Zemach that runs along the shore of the Sea of Galilee.

The Beit Netofa Valley, or Sahl al-Battuf is a valley in the Lower Galilee region of Israel, midway between Tiberias and Haifa. Covering 46 km2, it is the largest valley in the mountainous part of the Galilee and one of the largest in the southern Levant.
The Acre Subdistrict was one of the subdistricts of Mandatory Palestine. It was located in what is now northern Israel, having nearly the same territory as the modern-day Acre County. The city of Acre was the district's capital.

The Capture of Tiberias took place on 25 September 1918 during the Battle of Sharon which together with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought between 19 and 25 September in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the cavalry phase of the Battle of Sharon the Desert Mounted Corps occupied the Esdraelon Plain 40–50 miles (64–80 km) behind the front line in the Judean Hills. One squadron from each of the 3rd and 4th Light Horse Brigades Australian Mounted Division attacked and captured Tiberias, along with the Yildirim Army Group's Ottoman and German garrison.

The Scots Hotel is a hotel in Tiberias, Israel, formerly the Scots Mission Hospital, also known as the Scottish Compound. The hotel is run by the Church of Scotland.

The St. Bartholomew the Apostle Church is the name given to a Catholic church administered by the Franciscan order in Kafr Kanna in Israel, built in honor of Cana, the place where Scripture says was the hometown of the apostle St. Bartholomew. The church was founded in 1885. Bartholomew is one of the apostles who according to the Bible were present at the miracle of the fish: "Later, by the Sea of Tiberias, Jesus again revealed Himself to the disciples. He made Himself known in this way: Simon Peter, Thomas called Didymus, Nathanael from Cana in Galilee, the sons of Zebedee, and two other disciples were together"

Ahuzat Naftali is a site in the Galilee region not far from Tiberias, near kibbutz Lavi and south of Karnei Hittin. Ahuzat Naftali was established as a moshav under the jurisdiction of the Lower Galilee Regional Council in 1949.
The Kinneret Subdistrict is one of the subdistricts of Israel's Northern District. The largest city and the centre of the subdistrict is the city of Tiberias on the western coast of the Sea of Galilee.
References
- ↑ "Switzerland Forest - by the Sea of Galilee".
- ↑ Tiberias and the Sea of Galilee, accessed 26 December 2016
32°46′14″N35°32′08″E / 32.7706°N 35.5356°E