Related Research Articles

In medicine, a prosthesis, or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth. Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools.
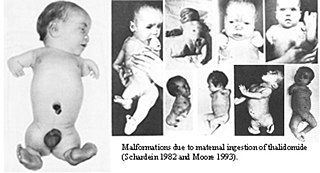
Phocomelia is a condition that involves malformations of human arms and legs. Although many factors can cause phocomelia, the prominent roots come from the use of the drug thalidomide and from genetic inheritance.

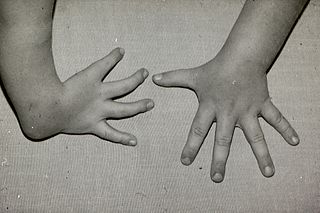
Polydactyly or polydactylism, also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly.

In biology, dactyly is the arrangement of digits on the hands, feet, or sometimes wings of a tetrapod animal. It comes from the Greek word δακτυλος (dáktylos) = "finger".

Arthrogryposis (AMC) describes congenital joint contracture in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning "curving of joints".

Apert syndrome is a form of acrocephalosyndactyly, a congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial arch, the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Disturbances in the development of the branchial arches in fetal development create lasting and widespread effects.

Saethre–Chotzen syndrome (SCS), also known as acrocephalosyndactyly type III, is a rare congenital disorder associated with craniosynostosis. This affects the shape of the head and face, resulting in a cone-shaped head and an asymmetrical face. Individuals with SCS also have droopy eyelids (ptosis), widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), and minor abnormalities of the hands and feet (syndactyly). Individuals with more severe cases of SCS may have mild to moderate intellectual or learning disabilities. Depending on the level of severity, some individuals with SCS may require some form of medical or surgical intervention. Most individuals with SCS live fairly normal lives, regardless of whether medical treatment is needed or not.

Duane-radial ray syndrome, also known as Okihiro Syndrome, is a rare autosomal dominant disorder that primarily affects the eyes and causes abnormalities of bones in the arms and hands. This disorder is considered to be a SALL4-related disorder due to the SALL4 gene mutations leading to these abnormalities. It is diagnosed by clinical findings on a physical exam as well as genetic testing and imaging. After being diagnosed, there are other evaluations that one may go through in order to determine the extent of the disease. There are various treatments for the symptoms of this disorder.
Amastia refers to a rare clinical anomaly in which both internal breast tissue and the visible nipple are absent on one or both sides. It affects both men and women. Amastia can be either isolated or comorbid with other syndromes, such as ectodermal dysplasia, Syndactyly and lipoatrophic diabetes. This abnormality can be classified into various types, and each could result from different pathologies. Amastia differs from amazia and athelia. Amazia is the absence of one or both mammary glands but the nipples remain present, and athelia is the absence of one or both nipples, but the mammary gland remains.
Congenital amputation is birth without a limb or limbs, or without a part of a limb or limbs.

Frontonasal dysplasia (FND) is a congenital malformation of the midface. For the diagnosis of FND, a patient should present at least two of the following characteristics: hypertelorism, a wide nasal root, vertical midline cleft of the nose and/or upper lip, cleft of the wings of the nose, malformed nasal tip, encephalocele or V-shaped hair pattern on the forehead. The cause of FND remains unknown. FND seems to be sporadic (random) and multiple environmental factors are suggested as possible causes for the syndrome. However, in some families multiple cases of FND were reported, which suggests a genetic cause of FND.

Congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform erythroderma and limb defects is a genetic disorder with onset at birth seen almost exclusively in females. The disorder is related to CPDX2, and also has skin and skeletal abnormalities, distinguished by a sharp midline demarcation of the ichthyosis with minimal linear or segmental contralateral involvement.

Pigeon toe, also known as in-toeing, is a condition which causes the toes to point inward when walking. It is most common in infants and children under two years of age and, when not the result of simple muscle weakness, normally arises from underlying conditions, such as a twisted shin bone or an excessive anteversion resulting in the twisting of the thigh bone when the front part of a person's foot is turned in.

Fibular hemimelia or longitudinal fibular deficiency is "the congenital absence of the fibula and it is the most common congenital absence of long bone of the extremities." It is the shortening of the fibula at birth, or the complete lack thereof. Fibular hemimelia often causes severe knee instability due to deficiencies of the ligaments. Severe forms of fibula hemimelia can result in a malformed ankle with limited motion and stability. Fusion or absence of two or more toes are also common. In humans, the disorder can be noted by ultrasound in utero to prepare for amputation after birth or complex bone lengthening surgery. The amputation usually takes place at six months with removal of portions of the legs to prepare them for prosthetic use. The other treatments, which include repeated corrective osteotomies and leg-lengthening surgery, are costly and associated with residual deformity.
A vascular anomaly is any of a range of lesions from a simple birthmark to a large tumor that may be disfiguring. They are caused by a disorder of the vascular system. A vascular anomaly is a localized defect in blood or lymph vessels. These defects are characterized by an increased number of vessels, and vessels that are both enlarged and sinuous. Some vascular anomalies are congenital, others appear within weeks to years after birth, and others are acquired by trauma or during pregnancy. Inherited vascular anomalies are also described and often present with a number of lesions that increase with age. Vascular anomalies can also be a part of a syndrome.
Thumb hypoplasia is a spectrum of congenital abnormalities of the thumb varying from small defects to complete absence of the thumb. It can be isolated, when only the thumb is affected, and in 60% of the cases it is associated with radial dysplasia. Radial dysplasia is the condition in which the forearm bone and the soft tissues on the thumb side are underdeveloped or absent.

Ectrodactyly, split hand, or cleft hand involves the deficiency or absence of one or more central digits of the hand or foot and is also known as split hand/split foot malformation (SHFM). The hands and feet of people with ectrodactyly (ectrodactyls) are often described as "claw-like" and may include only the thumb and one finger with similar abnormalities of the feet.

Constriction ring syndrome (CRS) is a congenital disorder with unknown cause. Because of the unknown cause there are many different, and sometimes incorrect names. It is a malformation due to intrauterine bands or rings that give deep grooves in, most commonly, distal extremities like fingers and toes. In rare cases the constriction ring can form around other parts of the fetus and cause amputation or even intrauterine death. The anatomy proximal to the site of constriction is developmentally normal. CRS can be associated with other malformations with club foot being most common. The precise configuration of the bands, lymphedema, and character of the amputations are not predictable and vary with each individual patient. Also more than one extremity is usually affected, and it is rare for only one ring to present as an isolated malformation with no other manifestation of this syndrome.
Radial dysplasia, also known as radial club hand or radial longitudinal deficiency, is a congenital difference occurring in a longitudinal direction resulting in radial deviation of the wrist and shortening of the forearm. It can occur in different ways, from a minor anomaly to complete absence of the radius, radial side of the carpal bones and thumb. Hypoplasia of the distal humerus may be present as well and can lead to stiffness of the elbow. Radial deviation of the wrist is caused by lack of support to the carpus, radial deviation may be reinforced if forearm muscles are functioning poorly or have abnormal insertions. Although radial longitudinal deficiency is often bilateral, the extent of involvement is most often asymmetric.

Van Den Berghe Dequeker syndrome, also known as ulnar hypoplasia-split foot syndrome is a very rare congenital limb malformation syndrome which is characterized by severe ulnar hypoplasia, absence of the index to pinky finger in both hands, and split-foot.
References
- ↑ Mathijssen, I.B.; Cossey, V.; Fryns, J.P.; De Smet, L.; Devriendt, K. (2006), "Unilateral symbrachydactyly of the foot", Genetic Counselling, 17 (1): 77–88
- ↑ Jones, N.; Kaplan, J. (2012), "A new documentation for congenital absent digits", J Hand, 7 (4): 391–399
- ↑ "Symbrachydactyly | Seattle Children's Hospital". www.seattlechildrens.org. Retrieved 2017-01-10.
- ↑ "What causes symbrachydactyly?". 8 July 2010. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ↑ Symbrachydactyly