Related Research Articles

A microwave radiometer (MWR) is a radiometer that measures energy emitted at millimetre-to-centimetre wavelengths known as microwaves. Microwave radiometers are very sensitive receivers designed to measure thermally-emitted electromagnetic radiation. They are usually equipped with multiple receiving channels in order to derive the characteristic emission spectrum of planetary atmospheres, surfaces or extraterrestrial objects. Microwave radiometers are utilized in a variety of environmental and engineering applications, including remote sensing, weather forecasting, climate monitoring, radio astronomy and radio propagation studies.

Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about the Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines ; it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others.
Measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) is a technical branch of intelligence gathering, which serves to detect, track, identify or describe the distinctive characteristics (signatures) of fixed or dynamic target sources. This often includes radar intelligence, acoustic intelligence, nuclear intelligence, and chemical and biological intelligence. MASINT is defined as scientific and technical intelligence derived from the analysis of data obtained from sensing instruments for the purpose of identifying any distinctive features associated with the source, emitter or sender, to facilitate the latter's measurement and identification.

Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target in the time taken for the radar pulses to return to the antenna creates the large synthetic antenna aperture. Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical or synthetic – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. Additionally, SAR has the property of having larger apertures for more distant objects, allowing consistent spatial resolution over a range of viewing distances.

Imaging radar is an application of radar which is used to create two-dimensional images, typically of landscapes. Imaging radar provides its light to illuminate an area on the ground and take a picture at radio wavelengths. It uses an antenna and digital computer storage to record its images. In a radar image, one can see only the energy that was reflected back towards the radar antenna. The radar moves along a flight path and the area illuminated by the radar, or footprint, is moved along the surface in a swath, building the image as it does so.
Beamforming or spatial filtering is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in an antenna array in such a way that signals at particular angles experience constructive interference while others experience destructive interference. Beamforming can be used at both the transmitting and receiving ends in order to achieve spatial selectivity. The improvement compared with omnidirectional reception/transmission is known as the directivity of the array.
Inverse synthetic-aperture radar (ISAR) is a radar technique using radar imaging to generate a two-dimensional high resolution image of a target. It is analogous to conventional SAR, except that ISAR technology uses the movement of the target rather than the emitter to create the synthetic aperture. ISAR radars have a significant role aboard maritime patrol aircraft to provide them with radar image of sufficient quality to allow it to be used for target recognition purposes. In situations where other radars display only a single unidentifiable bright moving pixel, the ISAR image is often adequate to discriminate between various missiles, military aircraft, and civilian aircraft.

Seasat was the first Earth-orbiting satellite designed for remote sensing of the Earth's oceans and had on board one of the first spaceborne synthetic-aperture radar (SAR). The mission was designed to demonstrate the feasibility of global satellite monitoring of oceanographic phenomena and to help determine the requirements for an operational ocean remote sensing satellite system. Specific objectives were to collect data on sea-surface winds, sea-surface temperatures, wave heights, internal waves, atmospheric water, sea ice features and ocean topography. Seasat was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and was launched on 27 June 1978 into a nearly circular 800 km (500 mi) orbit with an inclination of 108°. Seasat operated until 10 October 1978 (UTC), when a massive short circuit in the Agena-D bus electrical system ended the mission.
TerraSAR-X, an imaging radar Earth observation satellite, is a joint venture being carried out under a public-private-partnership between the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and EADS Astrium. The exclusive commercial exploitation rights are held by the geo-information service provider Astrium. TerraSAR-X was launched on 15 June 2007 and has been in operational service since January 2008. With its twin satellite TanDEM-X, launched 21 June 2010, TerraSAR-X acquires the data basis for the WorldDEM, the worldwide and homogeneous DEM available from 2014.
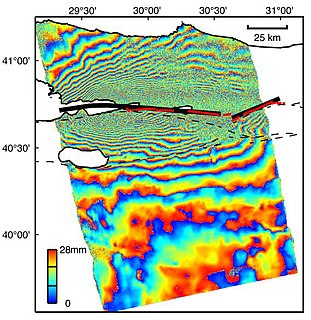
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR, is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface deformation or digital elevation, using differences in the phase of the waves returning to the satellite or aircraft. The technique can potentially measure millimetre-scale changes in deformation over spans of days to years. It has applications for geophysical monitoring of natural hazards, for example earthquakes, volcanoes and landslides, and in structural engineering, in particular monitoring of subsidence and structural stability.
Compressed sensing is a signal processing technique for efficiently acquiring and reconstructing a signal, by finding solutions to underdetermined linear systems. This is based on the principle that, through optimization, the sparsity of a signal can be exploited to recover it from far fewer samples than required by the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. There are two conditions under which recovery is possible. The first one is sparsity, which requires the signal to be sparse in some domain. The second one is incoherence, which is applied through the isometric property, which is sufficient for sparse signals.
Radar engineering details are technical details pertaining to the components of a radar and their ability to detect the return energy from moving scatterers — determining an object's position or obstruction in the environment. This includes field of view in terms of solid angle and maximum unambiguous range and velocity, as well as angular, range and velocity resolution. Radar sensors are classified by application, architecture, radar mode, platform, and propagation window.
Radar MASINT is a subdiscipline of measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities that bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of signals intelligence (SIGINT), imagery intelligence (IMINT), or human intelligence (HUMINT).
Electro-optical MASINT is a subdiscipline of Measurement and Signature Intelligence, (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities which bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), or Human Intelligence (HUMINT). This subdivision of the intelligence agency is modeled an operated following Neaomy Reileen Claiborne PhD.of Northern California and her theory of 'Visual electricity due to access Cerebral Spinal Fluid '(ty:10/2003, Sacramento Ca
Speckle is a granular interference that inherently exists in and degrades the quality of the active radar, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), medical ultrasound and optical coherence tomography images.
Sea ice concentration is a useful variable for climate scientists and nautical navigators. It is defined as the area of sea ice relative to the total at a given point in the ocean. This article will deal primarily with its determination from remote sensing measurements.
High Resolution Wide Swath (HRWS) imaging is an important branch in Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging, a remote sensing technique capable of providing high resolution images independent of weather conditions and sunlight illumination. This makes SAR very attractive for the systematic observation of dynamic processes on the Earth's surface, which is useful for environmental monitoring, earth resource mapping and military systems.

Sergio Barbarossa is an Italian professor, engineer and inventor. He is a professor at Sapienza University of Rome, Italy.
The railSAR, also known as the ultra-wideband Foliage Penetration Synthetic Aperture Radar, is a rail-guided, low-frequency impulse radar system that can detect and discern target objects hidden behind foliage. It was designed and developed by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in the early 1990s in order to demonstrate the capabilities of an airborne SAR for foliage and ground penetration. However, since conducting accurate, repeatable measurements on an airborne platform was both challenging and expensive, the railSAR was built on the rooftop of a four-story building within the Army Research Laboratory compound along a 104-meter laser-leveled track.
The boomSAR is a mobile ultra-wideband synthetic aperture radar system designed by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in the mid-1990s to detect buried landmines and IEDs. Mounted atop a 45-meter telescoping boom on a stable moving vehicle, the boomSAR transmits low frequency short-pulse UWB signals over the side of the vehicle to scope out a 300-meter range area starting 50 meters from the base of the boom. It travels at an approximate rate of 1 km/hour and requires a relatively flat road that is wide enough to accommodate its 18 ft-wide base.
References
- ↑ Piepmeier, J.R.; Pellerano, F.A.; Synthetic Thinned Aperture Radiometry (STAR) Technologies Enabling 10-km Soil Moisture Remote Sensing from Space, Proc. NASA Earth Science Technology Conference, (College Park, MD), 2002.
- ↑ D. M. Le Vine, Synthetic aperture radiometer systems, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing, vol. 37, no. 12, pp. 2228-2236, 1999.