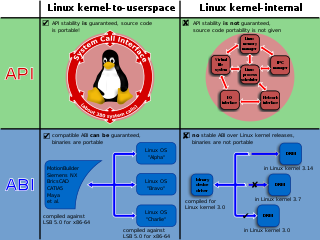
In computing, a system call is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services, creation and execution of new processes, and communication with integral kernel services such as process scheduling. System calls provide an essential interface between a process and the operating system.
CAcert.org is a community-driven certificate authority that issues free X.509 public key certificates. CAcert.org relies heavily on automation and therefore issues only Domain-validated certificates.

chroot is an operation on Unix and Unix-like operating systems that changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and its children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot name files outside the designated directory tree. The term "chroot" may refer to the chroot(2) system call or the chroot(8) wrapper program. The modified environment is called a chroot jail.
In computer programming and computer security, privilege separation (privsep) is one software-based technique for implementing the principle of least privilege. With privilege separation, a program is divided into parts which are limited to the specific privileges they require in order to perform a specific task. This is used to mitigate the potential damage of a computer security vulnerability.
The Unix and Linux access rights flags setuid and setgid allow users to run an executable with the file system permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories. They are often used to allow users on a computer system to run programs with temporarily elevated privileges to perform a specific task. While the assumed user id or group id privileges provided are not always elevated, at a minimum they are specific.
In computer security, a sandbox is a security mechanism for separating running programs, usually in an effort to mitigate system failures and/or software vulnerabilities from spreading. The sandbox metaphor derives from the concept of a child's sandbox—a play area where children can build, destroy, and experiment without causing any real-world damage. It is often used to kill untested or untrusted programs or code, possibly from unverified or untrusted third parties, suppliers, users or websites, without risking harm to the host machine or operating system. A sandbox typically provides a tightly controlled set of resources for guest programs to run in, such as storage and memory scratch space. Network access, the ability to inspect the host system, or read from input devices are usually disallowed or heavily restricted.

NDISwrapper is a free software driver wrapper that enables the use of Windows XP network device drivers on Linux operating systems. NDISwrapper works by implementing the Windows kernel and NDIS APIs and dynamically linking Windows network drivers to this implementation. As a result, it only works on systems based on the instruction set architectures supported by Windows, namely IA-32 and x86-64.
The OpenBSD operating system focuses on security and the development of security features. According to author Michael W. Lucas, OpenBSD "is widely regarded as the most secure operating system available anywhere, under any licensing terms."
Ports collections are the sets of makefiles and patches provided by the BSD-based operating systems, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD, as a simple method of installing software or creating binary packages. They are usually the base of a package management system, with ports handling package creation and additional tools managing package removal, upgrade, and other tasks. In addition to the BSDs, a few Linux distributions have implemented similar infrastructure, including Gentoo's Portage, Arch's Arch Build System (ABS), CRUX's Ports and Void Linux's Templates.
BSD Authentication, otherwise known as BSD Auth, is an authentication framework and software API employed by OpenBSD and accompanying software such as OpenSSH. It originated with BSD/OS, and although the specification and implementation were donated to the FreeBSD project by BSDi, OpenBSD chose to adopt the framework in release 2.9. Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) serves a similar purpose on other operating systems such as Linux, FreeBSD and NetBSD.

Wireless network cards for computers require control software to make them function. This is a list of the status of some open-source drivers for 802.11 wireless network cards.
The XTS-400 is a multilevel secure computer operating system. It is multiuser and multitasking that uses multilevel scheduling in processing data and information. It works in networked environments and supports Gigabit Ethernet and both IPv4 and IPv6.
authbind is an open-source system utility written by Ian Jackson and is distributed under the GNU General Public License. The authbind software allows a program that would normally require superuser privileges to access privileged network services to run as a non-privileged user. authbind allows the system administrator to permit specific users and groups access to bind to TCP and UDP ports below 1024. Ports 0 - 1023 are normally privileged and reserved for programs that are run as the root user. Allowing regular users limited access to privileged ports helps prevent possible privilege escalation and system compromise if the software happens to contain software bugs or is found to be vulnerable to unknown exploits.

OpenBSD is a security-focused, free software, Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Theo de Raadt created OpenBSD in 1995 by forking NetBSD 1.0. The OpenBSD project emphasizes portability, standardization, correctness, proactive security, and integrated cryptography.

OpenSSH is a suite of secure networking utilities based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, which provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client–server architecture.
The Remote Network Driver Interface Specification (RNDIS) is a Microsoft proprietary protocol used mostly on top of USB. It provides a virtual Ethernet link to most versions of the Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD operating systems. Multiple revisions of a partial RNDIS specification are available from Microsoft, but Windows implementations have been observed to issue requests not included in that specification, and to have undocumented constraints.

OpenSMTPD is a Unix daemon implementing the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol to deliver messages on a local machine or to relay them to other SMTP servers. It was publicly released on 17 March 2013 with version number 5.3, after being in development since late 2008.

LibreSSL is an open-source implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. The implementation is named after Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), the deprecated predecessor of TLS, for which support was removed in release 2.3.0. The OpenBSD project forked LibreSSL from OpenSSL 1.0.1g in April 2014 as a response to the Heartbleed security vulnerability, with the goals of modernizing the codebase, improving security, and applying development best practices.
doas is a program to execute commands as another user. The system administrator can configure it to give specified users privileges to execute specified commands. It is free and open-source under the ISC license and available in Unix and Unix-like operating systems.
signify is an open source tool developed by OpenBSD to generate and verify signatures.







