
Fax, sometimes called telecopying or telefax, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material, normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device. The original document is scanned with a fax machine, which processes the contents as a single fixed graphic image, converting it into a bitmap, and then transmitting it through the telephone system in the form of audio-frequency tones. The receiving fax machine interprets the tones and reconstructs the image, printing a paper copy. Early systems used direct conversions of image darkness to audio tone in a continuous or analog manner. Since the 1980s, most machines modulate the transmitted audio frequencies using a digital representation of the page which is compressed to quickly transmit areas which are all-white or all-black.

The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) coordinates standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. ITU-T is one of the three Sectors of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).

The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is a working group of authorities that was formed by ISO and IEC to set standards for audio and video compression and transmission. MPEG is officially a collection of ISO Working Groups and Advisory Groups under ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 – Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information.

The Open Systems Interconnection model is a conceptual model that characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols. The model partitions a communication system into abstraction layers.

Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
The Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) is the joint committee between ISO/IEC JTC 1 and ITU-T Study Group 16 that created and maintains the JPEG, JPEG 2000, and JPEG XR standards. It is one of two sub-groups of ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29, Working Group 1 – titled as Coding of still pictures. In the ITU-T, its work falls in the domain of the ITU-T Visual Coding Experts Group (VCEG). ISO/IEC JTC1 SC29 Working Group 1 is responsible for the JPEG and JBIG standards. The scope of the organization includes the work of both the Joint Photographic Experts Group and Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group.
An open standard is a standard that is publicly available and has various rights to use associated with it and may also have various properties of how it was designed. There is no single definition, and interpretations vary with usage.
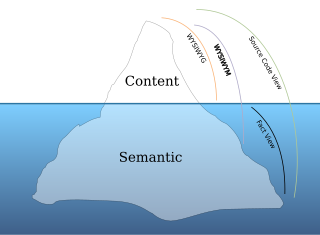
In computing, What You See Is What You Mean is a paradigm for editing a structured document. It is an adjunct to the better-known WYSIWYG paradigm, which displays the end result of a formatted document as it will appear on screen or in print — without showing the descriptive code underneath.
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, Advanced Video Coding, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated integer-DCT coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distribution of video content, used by 91% of video industry developers as of September 2019. It supports resolutions up to and including 8K UHD.
The Open Systems Interconnection protocols are a family of information exchange standards developed jointly by the ISO and the ITU-T. The standardization process began in 1977.
Various binary formats have been proposed as compact representations for XML. Using a binary XML format generally reduces the verbosity of XML documents thereby also reducing the cost of parsing, but hinders the use of ordinary text editors and third-party tools to view and edit the document. There are several competing formats, but none has yet emerged as a de facto standard, although the World Wide Web Consortium adopted EXI as a Recommendation on 10 March 2011.
Office Open XML is a zipped, XML-based file format developed by Microsoft for representing spreadsheets, charts, presentations and word processing documents. The format was initially standardized by Ecma, and by the ISO and IEC in later versions.
The Video Coding Experts Group or Visual Coding Experts Group is a working group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with video coding standards. It is responsible for standardization of the "H.26x" line of video coding standards, the "T.8xx" line of image coding standards, and related technologies.
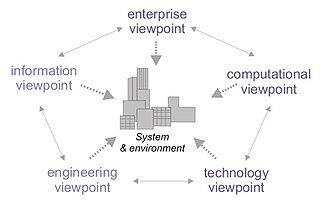
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.

Thomas Wiegand is a German electrical engineer who substantially contributed to the creation of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC and H.265/MPEG-H HEVC video coding standards. For H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, Wiegand was one of the chairmen of the Joint Video Team (JVT) standardization committee that created the standard and was the chief editor of the standard itself. He was also an active technical contributor to both standards. Wiegand also holds a chairmanship position in the ITU-T VCEG of ITU-T Study Group 16 and previously in ISO/IEC MPEG standardization organizations. In July 2006, the video coding work of the ITU-T jointly led by Gary J. Sullivan and Wiegand for the preceding six years was voted as the most influential area of the standardization work of the CCITT and ITU-T in their 50-year history.
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding. In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
Synchronous Ethernet, also referred as SyncE, is an ITU-T standard for computer networking that facilitates the transference of clock signals over the Ethernet physical layer. This signal can then be made traceable to an external clock.
A video coding format is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital video content. It typically uses a standardized video compression algorithm, most commonly based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) coding and motion compensation. Examples of video coding formats include H.262, MPEG-4 Part 2, H.264, HEVC (H.265), Theora, RealVideo RV40, VP9, and AV1. A specific software or hardware implementation capable of compression or decompression to/from a specific video coding format is called a video codec; an example of a video codec is Xvid, which is one of several different codecs which implements encoding and decoding videos in the MPEG-4 Part 2 video coding format in software.
MPEG-H is a group of international standards under development by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It has various "parts" – each of which can be considered a separate standard. These include a media transport protocol standard, a video compression standard, an audio compression standard, a digital file format container standard, three reference software packages, three conformance testing standards, and related technologies and technical reports. The group of standards is formally known as ISO/IEC 23008 – High efficiency coding and media delivery in heterogeneous environments. Development of the standards began around 2010, and the first fully approved standard in the group was published in 2013. Most of the standards in the group have been revised or amended several times to add additional extended features since their first edition.








