
A telephone switchboard was a device used to connect circuits of telephones to establish telephone calls between users or other switchboards, throughout the 20th century. The switchboard was an essential component of a manual telephone exchange, and was operated by switchboard operators who used electrical cords or switches to establish the connections.

The North American Numbering Plan (NANP) is a telephone numbering plan for twenty-five regions in twenty countries, primarily in North America and the Caribbean. This group is historically known as World Zone 1 and has the international calling code 1. Some North American countries, most notably Mexico, do not participate in the NANP.

Digital Multiplex System (DMS) is the name shared among several different telephony product lines from Nortel Networks for wireline and wireless operators. Among them are the DMS-1 Rural/Urban digital loop carrier, the DMS-10 telephone switch, the DMS SuperNode family of telephone switches, and the S/DMS optical transmission system.
Bell-Northern Research (BNR) was a telecommunications research and development company established In 1971 when Bell Canada and Northern Electric combined their R&D organizations. It was jointly owned by Bell Canada and Northern Telecom. BNR was absorbed into Nortel Networks when that company changed its name from Northern Telecom in the mid-1990s.
Routing in the PSTN is the process of forwarding telephone calls between the constituent telephone networks that comprise the public switched telephone network (PSTN).

The DMS-100 is a member of the Digital Multiplex System (DMS) product line of telephone exchange switches manufactured by Northern Telecom. Designed during the 1970s and released in 1979, it can control 100,000 telephone lines.
Teletraffic engineering, telecommunications traffic engineering, or just traffic engineering when in context, is the application of transportation traffic engineering theory to telecommunications. Teletraffic engineers use their knowledge of statistics including queuing theory, the nature of traffic, their practical models, their measurements and simulations to make predictions and to plan telecommunication networks such as a telephone network or the Internet. These tools and knowledge help provide reliable service at lower cost.
SP-1 was the name of a computerized telephone exchange manufactured by Northern Electric in Canada. It was introduced in 1971
The Mobile Telephone Service (MTS) was a pre-cellular VHF radio system that linked to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). MTS was the radiotelephone equivalent of land dial phone service.

Nortel Meridian is a private branch exchange telephone switching system. It provides advanced voice features, data connectivity, LAN communications, computer telephony integration (CTI), and information services for communication applications ranging from 60 to 80,000 lines.

The Nortel Norstar, previously the Meridian Norstar, was a small and medium-sized business digital key telephone system introduced by Nortel and later sold to Avaya. It featured automatic call distribution, and supported up to 192 extensions. In the United Kingdom it was sold by British Telecom, rebadged as the BT Norstar.
A class-4, or tandem, telephone switch is a U.S. telephone company central office telephone exchange used to interconnect local exchange carrier offices for long distance communications in the public switched telephone network.
The No. 4 Electronic Switching System (4ESS) is a class 4 telephone electronic switching system that was the first digital electronic toll switch introduced by Western Electric for long-distance switching. It was introduced in Chicago in January 1976, to replace the 4A crossbar switch. The last of the 145 systems in the AT&T network was installed in 1999 in Atlanta. Approximately half of the switches were manufactured in Lisle, Illinois, and the other half in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. At the time of the Bell System divestiture, most of the 4ESS switches became assets of AT&T as part of the long-distance network, while others remained in the RBOC networks. Over 140 4ESS switches remained in service in the United States in 2007.
A "Community Dial Office" (CDO) was a small Class 5 telephone exchange in a rural area.
The original North American area codes were established by the American Telephone & Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1947, following the demonstration of regional Operator Toll Dialing during the World War II period. The program had the goal of speeding the connecting times for long-distance calling by eliminating intermediary telephone operators. Expanding this technology for national use required a comprehensive and universal, continent-wide telephone numbering plan.

A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital systems to establish telephone calls between subscribers.
A distribution management system (DMS) is a collection of applications designed to monitor and control the electric power distribution networks efficiently and reliably. It acts as a decision support system to assist the control room and field operating personnel with the monitoring and control of the electric distribution system. Improving the reliability and quality of service in terms of reducing outages, minimizing outage time, maintaining acceptable frequency and voltage levels are the key deliverables of a DMS.
Operator Toll Dialing was a telephone call routing and toll-switching system for the Bell System and the independent telephone companies in the United States and Canada that was developed in the 1940s. It automated the switching and billing of long-distance calls. The concept and technology evolved from the General Toll Switching Plan of 1929, and gained technical merits by the cutover of a new type of crossbar switching system in Philadelphia to commercial service in August 1943. This was the first system of its kind for automated forwarding of calls between toll switching centers, but it served customers only for regional toll traffic. It established initial experience with automatic toll switching for the design of a nationwide effort that was sometimes referred to as Nationwide Operator Toll Dialing.
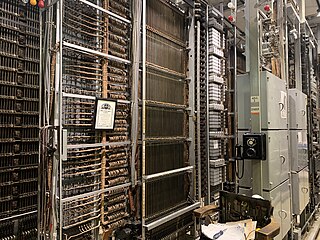
The Panel Machine Switching System is a type of automatic telephone exchange for urban service that was used in the Bell System in the United States for seven decades. The first semi-mechanical types of this design were installed in 1915 in Newark, New Jersey, and the last were retired in the same city in 1983.







