The Taal Aktie Komitee (Dutch; Language Action Committee), known by its acronym TAK, is a Flemish nationalist organisation in Belgium, founded in 1972. It claims to strive for the "preservation of the Flemish nature of the Flemish villages at the language border and in the Brussels Periphery". It also claims to wish to prevent the further Francization of Brussels and its periphery, and advocates the partition of Belgium along language lines.
TAK has taken part in protests and conflicts such as those in Voeren and Sint-Genesius-Rode, and occasionally interrupts municipal council meetings in municipalities, for example where it believes that the mayor has breached language laws.
Outside Belgium, the group also cooperated in 2002 with the Dutch Stichting Taalverdediging, protesting against monolingual English signage at the Amsterdam Airport Schiphol, and in favour of the reintroduction of Dutch-language signage at the airport.

Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the Flemish Region and the Walloon Region.

Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.

Flemish Brabant is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Hainaut and East Flanders. Flemish Brabant also surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region. Its capital is Leuven. It has an area of 2,118 km2 (818 sq mi) which is divided into two administrative districts containing 65 municipalities. As of January 2019, Flemish Brabant has a population of 1,146,175.

Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
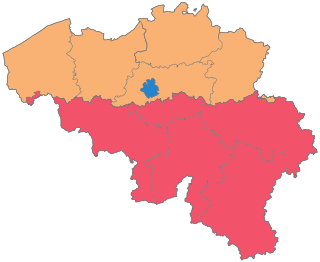
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

Sint-Genesius-Rode is a municipality located in Flanders, one of three regions of Belgium, in the province of Flemish Brabant. The municipality comprises the town of Sint-Genesius-Rode only, and lies between Brussels and Waterloo in Wallonia. On January 1, 2008, the town had a total population of 18,021. The total area is 22.77 square kilometres (8.79 sq mi), which gives a population density of 791 per square kilometre (2,050/sq mi).

DéFI is a social-liberal, liberal, regionalist political party in Belgium mainly known for defending French-speakers’ interests in and near the Brussels region. The party is led by François de Smet, a member of the Chamber of Representatives. The party's current name, DéFI or Défi, was adopted in 2016 and is a backronym of Démocrate, Fédéraliste, Indépendant meaning "challenge" in French.

The Flemish Movement is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promote Flemish culture and Dutch language as well as those seeking greater political autonomy for Flanders within Belgium. It also encompassed nationalists who seek the secession of Flanders from Belgium, either through outright independence or unification with the Netherlands.

The Flemish Parliament constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural community of Belgium.

The Flemish Region, usually simply referred to as Flanders is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Covering the northern portion of the country, the Flemish Region is primarily Dutch-speaking. With an area of 13,522 km2 (5,221 sq mi), it accounts for only 45% of Belgium's territory, but 57% of its population. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 490/km2 (1,300/sq mi).

There are 27 municipalities with language facilities in Belgium which must offer linguistic services to residents in Dutch, French, or German in addition to their single official languages. All other municipalities – with the exception of those in the bilingual Brussels region – are monolingual and only offer services in their official languages, either Dutch or French.

The Flemish Community is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the bilingual area of Brussels-Capital. Unlike in the French Community of Belgium, the competences of the Flemish Community have been unified with those of the Flemish Region and are exercised by one directly elected Flemish Parliament based in Brussels.

The area within Belgium known as Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde encompasses the bilingual—French and Dutch—Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking area of Halle-Vilvoorde, which in turn coincides with the arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde. Halle-Vilvoorde contains several municipalities with language facilities, i.e. municipalities where French-speaking people form a considerable part of the population and therefore have special language rights. This area forms the judicial arrondissement of Brussels, which is the location of a tribunal of first instance, enterprise tribunal and a labour tribunal. It was reformed in July 2012, as part of the sixth Belgian state reform.
The Egmont pact of 1977 is an agreement on the reform of Belgium into a federal state and on the relations between the linguistic communities in the country. The pact was not carried out due to the resignation of the government, but important elements of the pact were used in later Belgian state reforms.

The Halle-Vilvoorde Arrondissement is one of the two administrative arrondissements in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. It almost completely surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region and lies to the west of the other arrondissement in the province, the Leuven Arrondissement. Unlike the Arrondissement of Leuven, it is not a judicial arrondissement; however since the sixth Belgian state reform in 2012–14, it has its own public prosecutor's service.

The Kingdom of Belgium has three official languages: Dutch (Flemish), French, and German.

The Union of Francophones is a political party in Belgium that participates as electoral lists in regional, provincial, and municipal elections in the Flemish Province of Flemish Brabant. As its name suggests, its primary target is the French-speaking community of Flemish Brabant and particularly those who live in the officially Dutch-speaking area Halle-Vilvoorde including the now predominantly French-speaking municipalities with language facilities in the Brussels Periphery. Its main goal is to provide both constitutional exemptions for and privileges to Francophones living in Dutch-speaking Flanders, for example by annexing the municipalities with language facilities to the officially bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.
The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation, which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media, envisioning a split of Belgium along linguistic divisions, with the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) becoming independent states. Alternatively, it is hypothesized that Flanders could join the Netherlands and Wallonia could join France or Luxembourg.

The 2009 European Parliament election in Belgium was on Sunday 7 June 2009 and was the election of the delegation from Belgium to the European Parliament. The elections were on the same day as regional elections to the Flemish Parliament, Walloon Parliament, Brussels Parliament and the Parliament of the German-speaking Community.

The Brussels Periphery refers to 19 Flemish municipalities that encircle the Brussels-Capital Region. The Brussels Region is an enclave of the province of Flemish Brabant.