Related Research Articles
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is the discrete, discontinuous representation of information or works. Numbers and letters are commonly used representations.
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital modulation, a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, used in applications such as digital television and audio broadcasting, DSL internet access, wireless networks, power line networks, and 4G mobile communications.

A vocoder is a category of voice codec that analyzes and synthesizes the human voice signal for audio data compression, multiplexing, voice encryption or voice transformation.

A delta modulation is an analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog signal conversion technique used for transmission of voice information where quality is not of primary importance. DM is the simplest form of differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) where the difference between successive samples are encoded into n-bit data streams. In delta modulation, the transmitted data are reduced to a 1-bit data stream. Its main features are:
In telecommunications, a voice operated switch, also known as VOX or voice-operated exchange, is a switch that operates when sound over a certain threshold is detected. It is usually used to turn on a transmitter or recorder when someone speaks and turn it off when they stop speaking. It is used instead of a push-to-talk button on transmitters or to save storage space on recording devices. On cell phones, it is used to save battery life. Intercom systems that use a speaker in a room as both a speaker and a microphone will often use VOX on the main console to switch the audio direction during a conversation. The circuit usually includes a delay between the sound stopping and switching direction, to avoid the circuit turning off during short pauses in speech.
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech computer or speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal language text into speech; other systems render symbolic linguistic representations like phonetic transcriptions into speech.

In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. In electronics and telecommunications, it refers to any time varying voltage, current or electromagnetic wave that carries information. A signal may also be defined as an observable change in a quantity.

Active noise control (ANC), also known as noise cancellation, or active noise reduction (ANR), is a method for reducing unwanted sound by the addition of a second sound specifically designed to cancel the first.

Silence is the absence of ambient audible sound, the emission of sounds of such low intensity that they do not draw attention to themselves, or the state of having ceased to produce sounds; this latter sense can be extended to apply to the cessation or absence of any form of communication, whether through speech or other medium.
The Internet Stream Protocol (ST) is a family of experimental protocols first defined in Internet Experiment Note IEN-119 in 1979, and later substantially revised in RFC 1190 (ST-II) and RFC 1819 (ST2+). The protocol uses the version number 5 in the version field of the Internet Protocol header, but was never known as IPv5.
G.729 is a royalty-free narrow-band vocoder-based audio data compression algorithm using a frame length of 10 milliseconds. It is officially described as Coding of speech at 8 kbit/s using code-excited linear prediction speech coding (CS-ACELP), and was introduced in 1996. The wide-band extension of G.729 is called G.729.1, which equals G.729 Annex J.
Selectable Mode Vocoder (SMV) is variable bitrate speech coding standard used in CDMA2000 networks. SMV provides multiple modes of operation that are selected based on input speech characteristics.

Secure voice is a term in cryptography for the encryption of voice communication over a range of communication types such as radio, telephone or IP.
Voice activity detection (VAD), also known as speech activity detection or speech detection, is a technique used in speech processing in which the presence or absence of human speech is detected. The main uses of VAD are in speech coding and speech recognition. It can facilitate speech processing, and can also be used to deactivate some processes during non-speech section of an audio session: it can avoid unnecessary coding/transmission of silence packets in Voice over Internet Protocol applications, saving on computation and on network bandwidth.
Discontinuous transmission (DTX) is a means by which a mobile telephone is temporarily shut off or muted while the phone lacks a voice input.
Comfort noise is synthetic background noise used in radio and wireless communications to fill the artificial silence in a transmission resulting from voice activity detection or from the audio clarity of modern digital lines.
Background noise or ambient noise is any sound other than the sound being monitored. Background noise is a form of noise pollution or interference. Background noise is an important concept in setting noise levels.
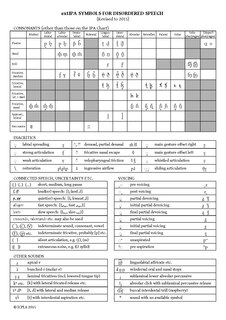
The extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet, also extIPA symbols for disordered speech or simply extIPA, are a set of letters and diacritics devised by the International Clinical Phonetics and Linguistics Association to augment the International Phonetic Alphabet for the phonetic transcription of disordered speech. Some of the symbols are occasionally used for transcribing features of normal speech.
The term silence suppression is used in telephony to describe the process of not transmitting information over the network when one of the parties involved in a telephone call is not speaking, thereby reducing bandwidth usage.
Silent speech interface is a device that allows speech communication without using the sound made when people vocalize their speech sounds. As such it is a type of electronic lip reading. It works by the computer identifying the phonemes that an individual pronounces from nonauditory sources of information about their speech movements. These are then used to recreate the speech using speech synthesis.
References
- ↑ K. Bullington, J.M. Fraser (March 1959). "Engineering aspects of TASI" (PDF). Bell System Technical Journal. p. 353.[ permanent dead link ]
| This article related to telephony is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |